Notes
advertisement

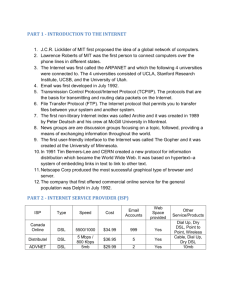
BROADBAND ACCESS TECHNOLOGIES DSL (DIGITAL SUBSCRIBER LOOP) TECHNOLOGY Introduction: DSL Technology provides a point-to-point connection between a customer location and the public Network over the existing local loop twisted pair copper wire. It provides a reliable and secure high-speed access to the Public network for high-speed data transfer, interactive video as well as regular telephone service simultaneously over the existing local loop. Consider fig 8.1 and 8.2 in your textbook. It uses either DMT (Discrete Multitone) or CAP (Carrier less Amplitude Modulation) technique to provide various DSL services such as ADSL, VDSL, SDSL, and RADSL etc. The term x.DSL stands for various versions of DSL technology with different data rates CAP: A proprietary digital Modulation Technique based on QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation). You will learn QAM in the PCS course. DMT: Discrete Multitone: The existing local loop can handle upto 1.1 MHZ BW The first 4KHz BW is used for regular telephone voice service Rest of the BW is divided into 256 channels each occupying a BW of 4.312 KHz as shown on P 261 of your text book Each subchannel can carry upto 60 Kbps data rate. (4KHz15bits/Signal Change)= 60 Kbps Current designs allow 1.5 Mbps to 9 Mbps data rate depending upon the S/N ratio of the line and distance between the customer location and the CO. Channel 0 is used for voice Channel 1 to 5 are not used to allow a gap between voice and Data Channels 6 to 30 ( 25 channels) are used for up stream transmission and control. One for Control and 24 for data. Thus upstream data rate is: 244KHz15bits/ Signal change= 1.44Mbps Channel 31 to 255 (225 Channels ) are used for downstream transmission, one for control and 224 for data. Thus the downstream data rate is : 2244K15 = 13.4 Mbps as shown below: Voice Ch 0 4K Hyder Khoja Upstream Ch 6 to 30 26 K Downstream Ch 31 to 255 1.1 M 13.4 M Page 1 3/6/2016 Notice that these are theoretical maximum BW. The actual practical data rate is reduced because of S/N Ratio of the link. The actual data rates are as follows Upstream : 64Kbps to 1.5 Mbps Downstream: 500Kbps to 9 Mbps The DSL modems, when turned ON, check the quality of line and automatically adjust the data rate Fig below shows a complete DSL system. FILTER Local Loop VOICE TO PSTN FILTER PC Adsl modem DSLAM TO ISP DSLAM stands for Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer. It performs dual function. a) Acts as an ADSL Modem b) Creates data packets for ISP and converts data packets from ISP into DSL format DSL uses 2B1Q line encoding over the Subscriber loop. We learnt this scheme in ISDN. In fact DSL is very similar to ISDN BRI service Study fig 8-9 p262 Text Book. ADSL frame format uses HDLC frame as shown in the fig below. Draw this picture in the space provided DSL Versions: ADSL: Asymmetric DSL: - - Hyder Khoja Used for Residential customers Operates on a single twisted wire pair Provides 64Kbps to 250 Kbps up stream and 1.5 to 2 Mbps downstream over 18000 ft for remote LANS and Internet Access as well as voice connection to PSTN Uses 2B1Q line encoding over the twisted pair wiring Page 2 3/6/2016 SDSL: SYMMETRIC DSL: - Operates FDX on a single pair with Echo Cancellers over a distance of 3KM (10,000 ft) Suitable for T1/E1 circuits Used for business and Web Server Applications Divides the BW half-half for upstream and downstream transmission with a data rate of 768 Kbps in both directions - HDSL: HIGH BIT RATE DSL: - Used for high speed digital transmission between corporate sites or between customer and Local Office Uses 2 twisted wire pairs ( 4 Wire Circuit) Provides a data rate of 1.544 Mbps or 2.048 Mbps (T1 or E1 rates) symmetrically in both directions Maximum distance is 3.7KM Uses 2B1Q encoding VDSL: VERY HIGH DATA RATE DSL: - - Asymmetric Provides 12.5 Mbps to 52.8 Mbps downstream and 1.5 to 2.3 Mbps upstream over a single pair Distance up to 1.35 Km ( 4500 ft) Requires fiber Optic feed and ATM support Cable operators are in the process of launching new service for aggregated HDTV, voice and data signals using VDSL technology in combination with GPON (Gigabit Ethernet Passive Optical Network). This configuration works in conjunction with FTTN and FTTC technologies. FTTN and FTTC provide intermediate concentration points. This configuration is shown in the fig below. Draw this picture in the space provided. RADSL: Read p265 to 267 text book and also study tables 8-1 and 8-2 Hyder Khoja Page 3 3/6/2016 - Data rate (Mbps 1.5 to 2 1.5 to 2 6.1 6.1 Table below shows claimed data rates and corresponding AWG and distances for different flavors of DSL AWG Distance (ft) 24 26 24 26 18000 15000 12000 9000 Wire Size (mm) 0.5 0.4 0.5 0.4 Distance (Km) 5.5 4.6 3.7 2.7 CABLE MODEM: - - Structure is already in place Less susceptible to EMI Allows simultaneous transmission of TV and Internet Signals up to a speed of 30 Mbps downstream ( typically only 10 Mbps) and 768 Kbps upstream Uses a shared architecture over a COAX cable as shown below. - Complete system is shown on p271 Text Traditional Cable Network : - Fig below shows traditional cable network. HFC: HYBRIDE FIBER COAX: - Hyder Khoja Fig below shows Hybrid Fiber Coax Architecture. Page 4 3/6/2016 - A combination of fiber and Coax Up to 40,000 customers can be serves Cable BW is shown below. Upstream Data 5 Video Band 6MHz/Channel 80 channels 42 54 Downstream Data 550 750 Upstream: - Uses QPSK to reduce Noise and Interference - Uses 2 bits/baud - Theoretical Data rate is 26 =12 Mbps Downstream Transmission: - Uses 64 or 256 QAM - With 64 QAM, it uses 6 bits/ Hz. One bit for error detection and 5 for data - With 5 bits, the theoretical Data rate is 56 = 30 Mbps - The actual data rate is about 10 Mbps - Both upstream and Downstream BW is shared by several subscribers - Uses TDM and FDM to share the channels Customer Premises Equipment for Cable Modem Implementation: - Fig below shows the Cable Modem implementation(Read p272-278Text Hyder Khoja Page 5 3/6/2016 ADSL/ CABLE MODEM APPLICATIONS: There are four major applications of ADSL and Cable Modem Technologies. 1. Data Access - Personal Shopping - Corporate LANS - Computer Telephony Integration - Library Research - Distance Learning - Remote LAN Access - WEB access 2. Home Video - Interactive games - Movies 3. Internet Access - Surfing - Research - E Commerce 4. Video on demand - ADSL-1 Provides one MPEG-1 channel on twisted pair wiring over 18000 ft - ADSL –3 provides 4, 1.5 Mbps MPEG –1 or one MPEG-2 HDTV on the subscriber loop over 9000 ft Note: Because of limited capacity, ADSL is an inexpensive interim solution for Video on Demand service until fiber proliferation. Hyder Khoja Page 6 3/6/2016