heat of combustion
advertisement

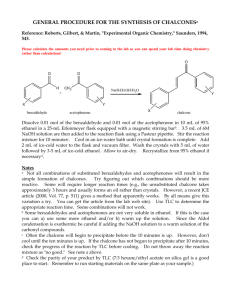
HEAT OF COMBUSTION The purpose of this experiment is to measure the amount of energy released when alcohol burns. As the alcohol burns, it releases energy as heat, which you will use to warm some water. You will calculate the amount of heat captured in the water using the equation q = mc∆T, where q is heat, m is the mass of water, c is a constant, and ∆T is the change in the temperature of the water. The unit of energy is joule (J). A joule is a very small amount of energy, so we usually express the energy of a chemical reaction in kilojoules (kJ). One kJ equals 1000 J. The energy produced by the burning alcohol is part of the chemical reaction, so we can include it in the chemical equation. Reactions that release energy are called exothermic processes; the energy is added to the right side of the balanced equation, as a product. Reactions that absorb energy are called endothermic processes; the energy is added to the left side of the balanced equation, as a reactant. Procedure 1. Weigh a 50 mL flask and add about 40 mL of water. Weigh the flask + water and subtract to determine the mass of water. Weigh a microburner filled with ethanol. 2. Clamp the flask above a microburner, so that the flask bottom is about one inch above the burner. . Record the temperature of the water, then light the microburner , and slide the burner under the flask. 3. Stir the water gently with a thermometer and allow the ethanol to burn until the temperature of the water has risen by about 10 to 12 °C. Keep stirring the water gently as you slide the burner out from under the beaker, and extinguish the microburner. Record the highest temperature the water reaches. 4. Weigh the microburner and subtract to determine the mass of ethanol burned. Data Mass of flask empty Mass of flask and water Mass of water Mass of burner before Mass of burner after Mass of ethanol burned Temperature of water before heating Temperature of water after heating Temperature change Analysis 1. Calculate q, the amount of energy gained by the water, using the equation q mwater c T mwater is the mass of the water (after subtracting the beaker), c is 4.184 J/g °C, and ∆Twater is the final temperature of the water minus the initial temperature of the water. Divide your answer by 1000 to convert the value of q from J to kJ. 2. The formula for ethanol is C2H5OH. Convert the grams of ethanol burned into moles, and calculate the energy released in kJ per mole ethanol –– that is, the amount of energy in kJ divided by the number of moles that burned. 3. Calculate the grams of CO2 produced when the ethanol burns. (This is a three step question.) Balance the equation first. C2H5OH + O2 CO2 + H2O Discussion 1. Write the balanced thermochemical equation for the combustion of ethanol and indicate whether the process is exothermic or endothermic. 2. The accepted value for the amount of energy released by this reaction is 1400 kJ/mol C2H5OH. Calculate the percent error in your result. 3. This lab assume that all the mass lost was from the burning of the ethanol, are there any other places where mass could have been lost and how would that have affected the results?