Leaves
advertisement

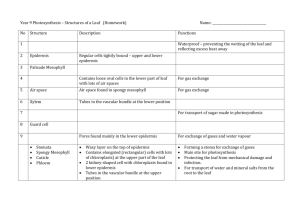
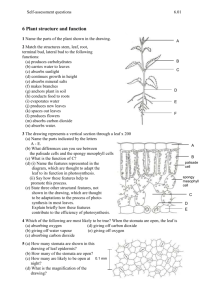
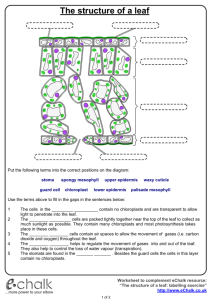
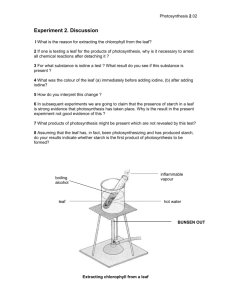
Name ______________________________ Class ___________________ Date __________________ CHAPTER 29 ACTIVE READING WORKSHEETS PLANT STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Section 29-4: Leaves Read the passage below, which covers topics from your textbook. Answer the questions that follow. Leaves come in a wide variety of shapes and sizes and are an important feature used for plant identification. Leaves can be round, straplike, needlelike, or heart-shaped. The broad, flat portion of a leaf, called the blade, is the site of most photosynthesis. The blade is usually attached to the stem by a stalklike petiole. The maple leaf is a simple leaf; it has a single blade. In compound leaves such as the white clover, the blade is divided into leaflets. In some species, the leaflets themselves are divided. The result is a doubly compound leaf, such as that of the honeylocust. Leaves consist of three tissue systems. The dermal tissue system is represented by the epidermis. In most leaves the epidermis is a single layer of cells coated with a nearly impermeable cuticle. Water, oxygen, and carbon dioxide enter and exit the leaf through stomata in the epidermis. Epidermal hairs are often present and usually function to protect the leaf from insects and intense light. In most plants, photosynthesis occurs in the leaf mesophyll, a ground tissue composed of chloroplast-rich parenchyma cells. In most plants, the mesophyll is organized into layers. The palisade mesophyll layer occurs directly beneath the upper epidermis and is the site of most photosynthesis. Palisade cells are columnar and appear to be packed tightly together in one or two layers. However, there are air spaces between the long side walls of palisade cells. Beneath the palisade layer is the spongy mesophyll. It consists of irregularly shaped cells surrounded by large air spaces, which allow oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water to diffuse into and out of the leaf. Read the question and write your answer in the space provided. SKILL: Vocabulary Development 1. What is the meaning of the term impermeable in the passage? _______________________________________________________________ Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Modern Biology 119 Leaves Name ______________________________ Class ___________________ Date __________________ Read each description related to leaves. On the line, write the term described. _____________________ 2. the leaf’s dermal tissue system _____________________ 3. structure that attaches the blade to the stem _____________________ 4. structure that consists of irregularly shaped cells surrounded by large air spaces _____________________ 5. the broad, flat leaf part where most photosynthesis occurs _____________________ 6. ground tissue made up of chloroplast-rich parenchyma cells _____________________ 7. leaf with a single blade _____________________ 8. the plant part whose columnar cells have air spaces between them _____________________ 9. leaf with a divided blade Write your answers in the spaces provided. SKILL: Interpreting Graphics 10. The figure below shows the internal structure of a leaf. Write the following labels on the figure: “Spongy mesophyll,” “Cuticle,” “Palisade mesophyll,” and “Upper epidermis.” Write your answers Circle the letter of the word or phrase that best completes the analogy. 11. Simple is to maple leaf as compound is to a. corn leaf. b. white clover. c. vein. d. Both (a) and (b) Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Modern Biology 120 Leaves