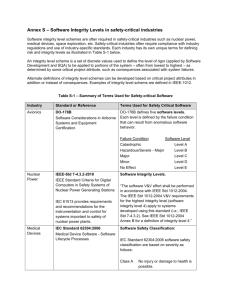
Table 2: Characteristics of the NIST
advertisement

Sara Biyabani, P2030 IT Task Force, 08/20/09 INTRODUCTION This document has two objectives: 1) Identification of the Demarcation points where communication and information exchange occurs between the seven different domains of the SmartGrid. 2) Identification of the Standards which are pertinent at each Demarcation points, and their characteristics. SUMMARY - - - Investigated the applicability of the 16 NIST-recommended standards [1] to the Demarcation Points, or interfaces between the 7 domains. Many of the 16 standards are limited to intra-domain, rather than inter-domain, communication/information exchange: - Transmission Domain: (6) IEC 61850, (8) IEC 62351, (9) IEEE C37.118 - Distribution Domain: (7) IEC 61968, (9) IEEE C37.118 There are many big gaps for inter-domain information exchange, especially between Operations and Bulk Generation & Distribution, and also between Service Provider and Markets & Customer. Several of the 16 NIST-recommended Standards deal only with general Security aspects and not Grid Operations (and hence are not self-sufficient for information exchange between the 7 Domains): - (8) IEC 62351, (11) IEEE 1686-2007, (12) NERC CIP 002-009, (13) NIST SP 800-53 & 800-82 (5) IEC 60870-6/TASE.2 & (1) IEEE 1547 seem to have the widest scope (i.e. touching multiple Domains) - Identified following Message Protocols (used by some of the above 16 Standard) as potential candidates for us to consider for information exchange: 1) SCL - Substation Configuration Language 2) MMS - Manufacturing Message Specification 3) ICCP Inter-Control Center Communications Protocol (ICCP or IEC 60870-6/TASE.2) 4) GOOSE: Generic Object Oriented Substation Events - Additional Standards: Would like to add following additional standards for P2030 IT Task Force consideration: - (1) DMTF (Distributed Management Task Force, Inc.) for Manageability Standards (e.g., augment CIM Schema v 2.22.0 to introduce our TF2 recommendations for SmartGrid-specific objects/entities) - (2) SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) J2847-1 (Communication/information exchange between Plug-in Vehicles and the Utility Grid). [1] Standards Identified for Inclusion in the Smart Grid Interoperability Standards Framework, Release 1.0 http://www.nist.gov/smartgrid/standards.html NEXT STEPS 1) Actively Seek to fill the gaps between the Bulk Generation, Transmission, Distribution, Operations Domain & Service Provider either by identifying other standards not on the NIST list of 16, and/or proposing and formulating new ones. Table 1: Standards pertinent to Demarcation points amongst the Seven Identified Domains Domain: Bulk Generation Transmission Distribution Opera-tions Service Provider M Customer a r k e t s Bulk Generation Transmission (10) IEEE 1547 (12) NERC CIP 002-009 (10) IEEE 1547 Distribution Operations Service Provider Markets ? (5) IEC 608706/TASE.2 (6) IEC 61850 substationsubstation (8) IEC 62351 Security (9) IEEE C37.118 (5) IEC 608706/TASE.2 (7) IEC 61968 (work in progress?) (9) IEEE C37.118 ? (5) IEC 608706/TASE.2 ( 1 4 ) O p e n A D R Customer - (1) ANSI C12.19 (2) AMR (3) ISO 16484-5 ANSI ASHRA E 1352008 (*)Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles: SAE J2847 (comm) SAE J1772(conne ctor) (15) OpenHAN (16) ZigBee/Ho mePlug Smart Energy Profile (10) IEEE 1547 Table 2: Characteristics of the NIST-Identified Standards [1] Protocol/Standard (1) AMI-end-to-end security (2) ANSI C12.19/MC1219 (3) ISO 16484-5 (4) DNP3<> IEC 60870-5 (5) IEC 60870-6/TASE.2 (ICCP) (6) IEC 61850 (7) IEC 61968 IEC 61970 (8) IEC 62351<> IEC 61850 (9) IEEE C37.118 (10) IEEE 1547 (11) IEEE 1686-2007 (12) NERC CIP 002-009 (13) NIST SP 800-53 & 800-82 (14) Open ADR (15) Open HAN (16) ZigBee/HomePlug Smart Energy Profile Built in Security Privacy Manageability None None None Some Perf./RT Req. (? thru IEC 62351) None (@ lower levels) IEC 62351 (GOOSE: 4 ms) Some (CIM) CIM Part 11 Yes None ?? Yes Yes Yes ?? Some None None None None None Some None Yes None None None None Some [1] Standards Identified for Inclusion in the Smart Grid Interoperability Standards Framework, Release 1.0 http://www.nist.gov/smartgrid/standards.html GLOSSARY CIM: Common Information Model GOOSE: Generic Object Oriented Substation Events MMS: Manufacturing Message Specification SAE: Society of Automotive Engineers SCADA: Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition SCL: Substation Configuration Language ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- APPENDIX Message Protocols: 1) SCL - Substation Configuration Language Src: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SCL_-_Substation_Configuration_Language Substation Configuration Description Language (SCL) is the language and representation format specified by IEC 61850 for the configuration of electrical substation devices. This includes representation of modeled data and communication services specified by IEC 61850 – 7 –X standard documents. The complete SCL representation and its details are specified in IEC 61850-6 standard document. It includes data representation for substation device entities; it’s associated functions represented as logical nodes, communication systems and capabilities. The complete representation of data as SCL enhances the different devices of a substation to exchange the SCL files and to have a complete interoperability. Parts of SCL files An SCL file contains the following parts: 1. Header – This part is used to identify version and other basic details of an SCL configuration file. 2. Substation – This is the part dealing with the different entities of a substation including various devices, interconnections and other functionalities. The elements include power transformers, Voltage Levels, bays, General Equipment, conducting equipment like breakers, logical nodes etc. 3. Communication – This section deals with different communication points (access points) for accessing the different IEDs of the complete system. This part contains different Sub Networks and access points. 4. IED – The IED section describes the complete pre-configuration of an Intelligent Electronic Device (IED). It contains different access points of the specific IED, the logical devices, and logical nodes, report control blocks etc coming under the IED. 5. DataTypeTemplates – It defines different logical devices, logical nodes, data and other details separated into different instances. The complete data modeling according to IEC 61850-7-3 & 7-4 are represented in this part of SCL. It is again subdivided into LnodeType, DOType, DAType and EnumType. 2) MMS - Manufacturing Message Specification Src: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Manufacturing_Message_Specification Manufacturing Message Specification (MMS) is an international standard (ISO 9506) dealing with messaging system for transferring real time process data and supervisory control information between networked devices and/or computer applications. The standard is developed and maintained by the ISO Technical Committee 184 (TC184). MMS defines the following A set of standard objects which must exist in every device, on which operations like read, write, event signaling etc can be executed. Virtual manufacturing device (VMD) is the main object and all other objects like variables, domains, journals, files etc comes under VMD. A set of standard messages exchanged between a client and a server stations for the purpose of monitoring and/or controlling these objects. A set of encoding rules for mapping these messages to bits and bytes when transmitted. MMS stack over TCP/IP As the original MMS stack was completely over heavy ISO layer, it was never got popularized. In 1999, Boeing decided to replace relevant 4 layers of ISO with TCP/IP. They introduced ISO Transport over TCP (RFC 1006) to have interaction between the top ISO layers of MMS to the bottom TCP/IP layers. This had revolutionized MMS into a globally accepted standard. MMS stack after this adoption is as shown below Application Association Control Service Element ( ACSE )- ISO 8649/8650 Presentation Connection Oriented Presentation - ISO 8822/8823 Abstract Syntax Notation (ASN)- ISO 8824/8825 Session Connection Oriented Session - ISO 8326/8327 Transport ISO transport over TCP - RFC 1006 Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) - RFC 793 Network Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) - RFC 792 Internet Protocol (IP)- RFC 791 Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)- RFC 826 Link IP datagrams over Ethernet - RFC 894 MAC - ISO 8802-3 [Ethernet] Physical Ethernet ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 3) ICCP Inter-Control Center Communications Protocol (ICCP or IEC 60870-6/TASE.2) Basic ICCP functionality is specified as “Conformance Blocks” listed below. The objects that are used to convey the data are defined in various parts of IEC 60870-6. Block Description Data Examples: Periodic System Data: Status points, analogue points, quality flags, time stamp, change of value counter, protection events. Association objects to control ICCP sessions. Extended Data Set Condition Monitoring: Provides report by exception capability for the data types that block 1 is able to transfer periodically. Block Data Transfer: Provides a means transferring Block 1 and Block 2 data types as block transfers instead of point by point. In some situations this may reduce bandwidth requirements. Information Messages: Simple text and binary files. Device Control: Device control requests: on/off, trip/close, raise/lower etc and digital setpoints. Includes mechanisms for interlocked controls and select-beforeoperate. Program Control: Allows an ICCP client to remote control programs executing on an ICCP server. Event Reporting: Extended reporting to a client of error conditions and device state changes at a server. Additional User Objects: Scheduling, accounting, outage and plant information. Time Series Data: Allows a client to request a report from a server of historical time series data between a start and end date. 4) GOOSE: Generic Object Oriented Substation Events Used for fast transmission of substation events, such as commands, alarms, indications, as messages http://seclab.uiuc.edu/docs/iec61850-intro.pdf