Sounds to Symbols
advertisement
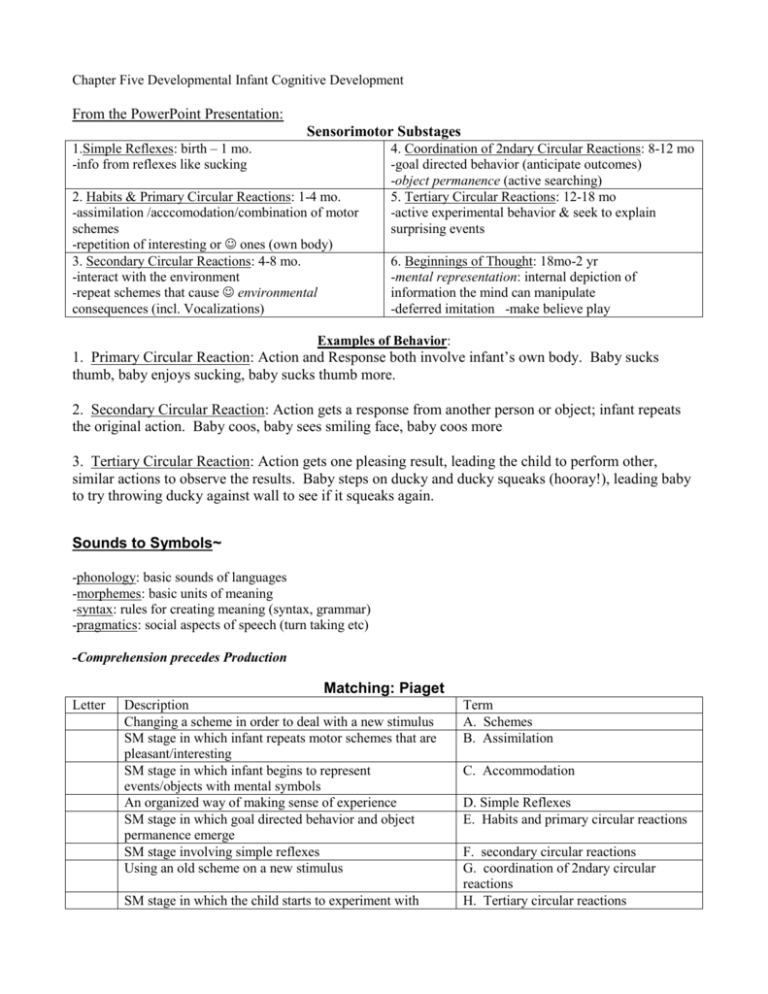
Chapter Five Developmental Infant Cognitive Development From the PowerPoint Presentation: Sensorimotor Substages 1.Simple Reflexes: birth – 1 mo. -info from reflexes like sucking 2. Habits & Primary Circular Reactions: 1-4 mo. -assimilation /acccomodation/combination of motor schemes -repetition of interesting or ones (own body) 3. Secondary Circular Reactions: 4-8 mo. -interact with the environment -repeat schemes that cause environmental consequences (incl. Vocalizations) 4. Coordination of 2ndary Circular Reactions: 8-12 mo -goal directed behavior (anticipate outcomes) -object permanence (active searching) 5. Tertiary Circular Reactions: 12-18 mo -active experimental behavior & seek to explain surprising events 6. Beginnings of Thought: 18mo-2 yr -mental representation: internal depiction of information the mind can manipulate -deferred imitation -make believe play Examples of Behavior: 1. Primary Circular Reaction: Action and Response both involve infant’s own body. Baby sucks thumb, baby enjoys sucking, baby sucks thumb more. 2. Secondary Circular Reaction: Action gets a response from another person or object; infant repeats the original action. Baby coos, baby sees smiling face, baby coos more 3. Tertiary Circular Reaction: Action gets one pleasing result, leading the child to perform other, similar actions to observe the results. Baby steps on ducky and ducky squeaks (hooray!), leading baby to try throwing ducky against wall to see if it squeaks again. Sounds to Symbols~ -phonology: basic sounds of languages -morphemes: basic units of meaning -syntax: rules for creating meaning (syntax, grammar) -pragmatics: social aspects of speech (turn taking etc) -Comprehension precedes Production Matching: Piaget Letter Description Changing a scheme in order to deal with a new stimulus SM stage in which infant repeats motor schemes that are pleasant/interesting SM stage in which infant begins to represent events/objects with mental symbols An organized way of making sense of experience SM stage in which goal directed behavior and object permanence emerge SM stage involving simple reflexes Using an old scheme on a new stimulus SM stage in which the child starts to experiment with Term A. Schemes B. Assimilation C. Accommodation D. Simple Reflexes E. Habits and primary circular reactions F. secondary circular reactions G. coordination of 2ndary circular reactions H. Tertiary circular reactions explaining surprising events SM stage in which infant repeats actions that cause + environmental consequences I. Beginnings of thought/mental representations Matching: Language Letter Description Basic units of meaning Examples of this are burps, smiles, gestures and imitation Speech like but meaningless sounds Rules for organizing language Two word combinations of words that children form Using a word to only apply to a few specific examples of that word Basic units of sound A child’s one word utterances A type of speech adults often use when talking to children Using a word to apply to a number of objects similar to that word Term A. phonology B. morphemes C. prelinguistic communication D. babbling E. holophrases F. telegraphic speech G. underextension H. overextension I. child-directed speech/motherese J. grammar Concept Review Letter Description Two year old Jessie's mother yells at her when she spills her milk. Later, Jessie yells at her doll with the same way her mother yelled at the doll. The baby is entertained by a rattle for several minutes but then gets bored and fussy. A child figures out why the light comes on when he opens the refrigerator and feels good about himself because he now understand more about his world A 2 month old baby makes open-mouthed vowel sounds Jordan is left alone in the kitchen with a pile of tupperware which gives him the opportunity to practice building a tower which he loved to do. . Zoe throws her hands up to get her grandfather to say, "How big is my baby girl?" Mother asks Peter, "Did you break the lamp." Peter answers, "No, Joey breaked it." Term A. affordances Three year old Jack believes that vegetables are green and do not taste good. His mother fixes a new vegetable for him, broccoli. Obviously, it is green and Jack thinks it tastes bad. He now adds broccoli to his vegetable schema. A young child has a concept of "pet" that includes dogs and cats. The child believes that pets have four legs and are furry. When his friend gets a frog as a pet, the child has to change his concept of "pet." H. assimilation B. cognitive equilibrium C. cooing D. over-regularization E. goal-directed behavior F. habituation G. accommodation I. deferred imitation