CONSTITUTION & RECONSTRUCTION UNIT
advertisement

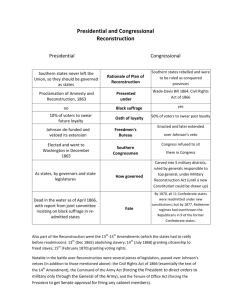
Name: U.S. History Honors CONSTITUTION & RECONSTRUCTION UNIT A PEOPLE & A NATION: NOTE TAKING SUGGESTIONS General Introduction to A People and A Nation (APAN) • chapters open with short vignettes offering a ‘story’ about the time period • a summary of the chapter follows – this is worth a close read to get a ‘handle’ on the chapter • next skim the subheaders to get an overview of how the chapter is organized and what is highlighted • review terms also (see other side) Note Taking Using APAN • strongly suggest you take notes in outline form (i.e., not complete sentences or running text, which takes longer and is harder to skim later; indent as applicable to show subtopics and how info is related/connected) • one format: use the subheaders in the chapter to organize your own notes (or “Goals” below) • focus on key ideas, important terms, people, events – with enough detail to recall and to explain – but do NOT rewrite the textbook; ALWAYS PUT IN YOUR OWN WORDS • note down page numbers in case you need to return to the textbook Goals for Understanding the Constitution 1. The Articles of Confederation: origins and weaknesses 2. The U.S. Constitution: Conflicts and Compromises Principles Branches of U.S. government Bill of Rights Goals for Understanding Reconstruction 1. The 3 main stages of Reconstruction: Presidential (Lincoln’s, Johnson’s plans) Radical Republicans in Congress “Redeemers” (white Southerners gain political control from Radicals) 2. Experiences of African Americans 3. Role of the Supreme Court 4. Why Reconstruction ended Textbook Sections and Key Terms: Constitution and Reconstruction I. From Crisis to Constitution 190 - 194 - Philadelphia Constitutional Convention - James Madison - principle of checks and balances - state representation compromises - slavery compromises - electoral college - 3 branches of government/separation of powers II. Opposition and Ratification 194 - 196 - Federalists - Anti-Federalists - Bill of Rights compromise III. Equal Rights: The Unresolved Issue 443-446 - Northern attitudes toward land redistribution IV. Johnson’s and Congressional Reconstruction Plans 446-453 - Lincoln's "10 percent" plan - Johnson's amnesty plan - black codes - "legal suicide" theory - Thaddeus Stevens and Radical Republicans - Freedman's Bureau and Civil Rights Act of 1866 - Memphis and New Orleans riots - 13th and 14th Amendments - Congressional elections of 1866 - Reconstruction Act of 1867 - Johnson's impeachment trial - 15th Amendment V. Reconstruction Politics in the South 453-460 - state constitutional conventions: Republicans v Democrats - industrialization policies - carpetbaggers and scalawags - Ku Klux Klan VI. Meaning of Freedom 460-465 - opportunities for education - role of family and church - sharecropping's appeal and abuse VII. Reconstruction's Decline and Fall 465-471 Revise - Greeley, greenbacks, Democrats in House - election of 1868 - Ulysses S Grant - failures of Anti-Klan laws - Liberal Republicans - Amnesty Act - Panic of 1873 - Slaughter-House Cases - U.S. v Cruikshank - U.S. v Reese - grandfather clauses (not in APAN: poll taxes, gerrymandering) - election of 1876 - Rutherford B. Hayes - Exodusters