Energy Change & Thermochemistry Practice Test #2
advertisement

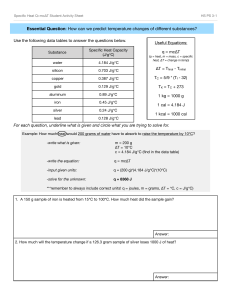
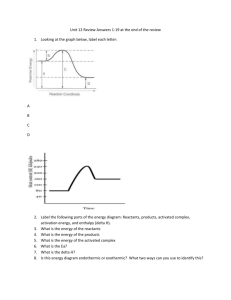
Energy Change & Thermochemistry Practice Test #2 1. Increase, decrease or constant? Motion of Kinetic particles Energy Temperature rising Temperature falling Melting Potential Energy Temperature States of Matter Change xxxxxxxxx Distance Between Particles Randomness of Particles xxxxxxxxx Solid → liquid Freezing Vaporization Condensation Sublimation Deposition 2. What are the two basic forms of energy? 3. Label the heating curve below with the phase change name or state of matter. 1) _____________________________ 2) _____________________________ 3) _____________________________ 4) _____________________________ 5) _____________________________ 4. Endothermic or exothermic? a) Feels cool to the touch. B) Energy is absorbed. Use the Chemistry Reference Tables for specific heat values for metals, water, ice and steam and for the heat of fusion/vaporization values for water for #4-9. Show all work. Use Q = mcΔT, Q = mHv or Q = mHf. 5. How much heat in joules is required to melt 31.0 grams of ice (solid water) at 0°C? 6. How much heat in joules does it take to raise 13 g of water from 22°C to 38°C? 7. What is the change in temperature if 80.0 g of magnesium absorbs 1890 J of heat? 8. How many grams of water would change its temperature from 37°C to 49°C if it absorbed 3280 J? 9. How much heat is needed to change the temperature of a 25-gram sample of copper from 23.0°C to 57.0°C? 10. If 1.65 J of heat are added to a 1.90 g sample of a metal and the temperature of the metal increases by 0.828oC, what is the specific heat of the metal? 11. Label the cooling curve below with the phase change name or state of matter. A) _____________________________ A B B) _____________________________ C) _____________________________ C D) _____________________________ D E E) _____________________________ 12. For which lines in the cooling curve above would you find solid matter? ________________ 13. Which 3 phase changes are endothermic processes? 14. True or False. The melting point and freezing point occur at the same temperature. Use the Chemistry Reference Tables for specific heat values for metals, water, ice and steam for #14-15. Show all work. The problems use mcΔT = − mcΔT. 15. Calorimetry - A 52.5 gram sample of a metal at a temperature of 415°C is placed in 1.02 liters (1020 g) of water which had an initial temperature of 18°C. What is the specific heat capacity of the metal if the final temperature of the metal and water at equilibrium is 23°C? 16. Calorimetry - A sample of water has an initial temperature of 5.0°C. What is the mass of the water if 23.0 grams of 123°C zinc can be placed in the water so that the equilibrium temperature is 12.0°C? 17. Use the graph to the right to answer the following questions. a. What does letter F represent? •C •E •F b. What is the name of the phase change as the temperature increases from A to B? c. At what point does freezing occur? •G •D 5.11 atm •A d. At what temperature does the triple point occur? e. What two states of matter exist at point G? 1 atm -78°C 10°C •B