microbiology
advertisement
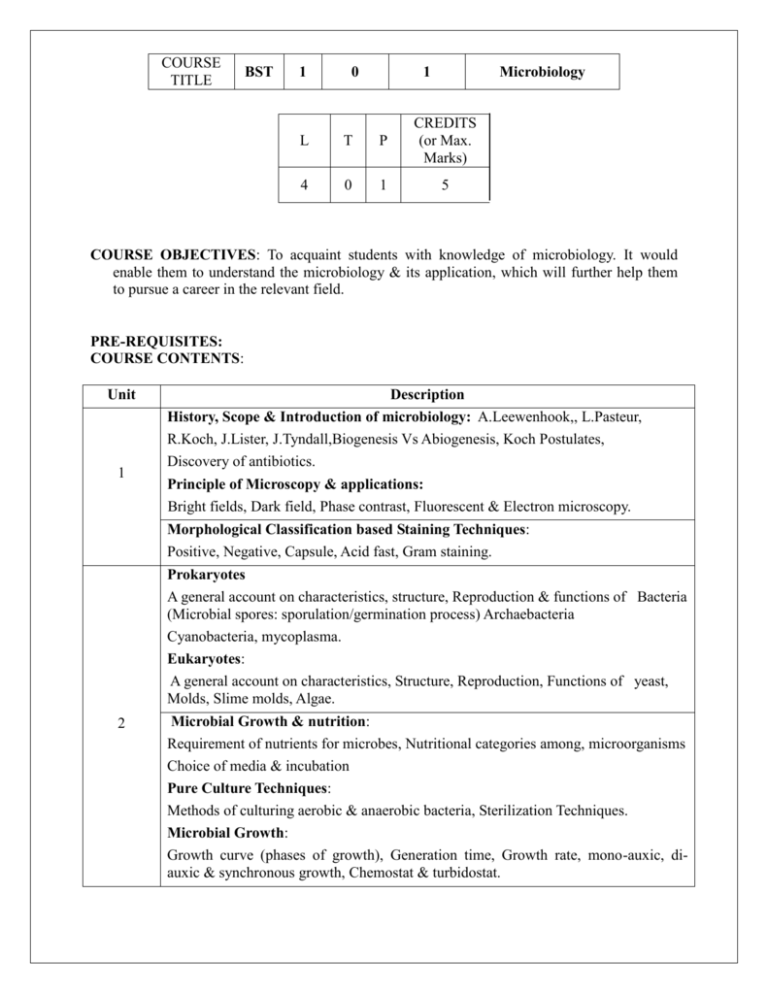
COURSE TITLE BST 1 0 1 Microbiology L T P CREDITS (or Max. Marks) 4 0 1 5 COURSE OBJECTIVES: To acquaint students with knowledge of microbiology. It would enable them to understand the microbiology & its application, which will further help them to pursue a career in the relevant field. PRE-REQUISITES: COURSE CONTENTS: Unit 1 Description History, Scope & Introduction of microbiology: A.Leewenhook,, L.Pasteur, R.Koch, J.Lister, J.Tyndall,Biogenesis Vs Abiogenesis, Koch Postulates, Discovery of antibiotics. Principle of Microscopy & applications: Bright fields, Dark field, Phase contrast, Fluorescent & Electron microscopy. Morphological Classification based Staining Techniques: Positive, Negative, Capsule, Acid fast, Gram staining. Prokaryotes A general account on characteristics, structure, Reproduction & functions of Bacteria (Microbial spores: sporulation/germination process) Archaebacteria Cyanobacteria, mycoplasma. Eukaryotes: A general account on characteristics, Structure, Reproduction, Functions of yeast, Molds, Slime molds, Algae. 2 Microbial Growth & nutrition: Requirement of nutrients for microbes, Nutritional categories among, microorganisms Choice of media & incubation Pure Culture Techniques: Methods of culturing aerobic & anaerobic bacteria, Sterilization Techniques. Microbial Growth: Growth curve (phases of growth), Generation time, Growth rate, mono-auxic, diauxic & synchronous growth, Chemostat & turbidostat. Normal Micro-flora in humans/animals: Types of microbial pathogens & diseases caused by them, Microbial Interactions like symbiosis & antibiosis etc. 3 Microbial Genetics: Introduction to microbial genetics, Modes of bacterial conjugation, transduction transformation. Economic Importance: Importance of Prokaryotes & eukaryotes, animal (1H1N1, Hepatitis, HIV, HSV1 and HSV-2, Dengue) & Plant viruses (Wheat Yellow Mosaic, Barley Yellow Dwarf of Wheat, Oats, and Barley, Tobacco Mosaic Virus, Cucumber Mosaic Virus) Structure & reproduction of above mentioned viruses, causative agent, disease caused by these viruses Suggested Readings: 1. Tortora, G.J., Funke, B.R. and Case, C.L. (2009) Microbiology: An introduction (Benjamin/ Cummings publishing company, Inc). 2. R. Y. Stanier, M. Doudoroff, E. A. Adelberg (1999). General microbiology (MacMillian Press London). 3. M.J. Pelczar, E.C. Sun Chan, N.R. Krieg (1986). Microbiology (Tata McGraw Hill Publication, New Delhi). 4. H.G. Schlegel, C.Zaborosch, M. Kogut (1993). General microbiology (Cambridge University Press). 5. S.C. Prescott, C.G. Dunn (1959). Industrial microbiology (McGraw- Hill). 6. Purohit, S.S. (2003). Microbiology: Fundamentals and applications(Agrobios, India) 7. Postgate, J.R. (2000). Microbes and man (Cambridge Uni) Instructions for paper setter. The syllabus has been divided into three equal units. The paper setter is required to set Ten questions in all, three questions from each unit and a compulsory question consisting of five sub parts and based on the whole syllabus. The candidate will be required to attempt six questions including the compulsory question number no 1 and not more than two questions from each unit.