Circulatory system Major functions of circulatory system: A circulate
advertisement

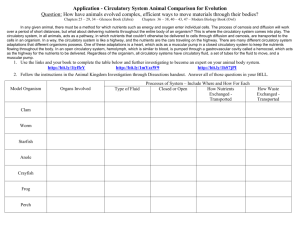
Circulatory system Major functions of circulatory system: 1. A circulate food to different part of the body 2. Distribution of oxygen to all parts of body 3. Remove the carbondioxide 4. Carries hormones and enzymes to all part of the body 5. Collect the waste from the body to all other parts of the body Transport ting materials inside the body are: A Circulatory fluid: lymph and blood A system of tubes through which the fluid circulates through body: blood vessels A pumping organ that pumps the fluid into the vessels: heart. In protozoan circulatory system is absent but circulation of food materials is carried out by the streaming movement of the cytoplasm. Food particles are diffuse into the body and distributed through cytoplasmic movement called streaming In porifera, canal system has substituted the circulatory system. Canal system helps to transport the water along with food material, food particle are absorbed in the body. Water enters through ostium to the spongocoel and exit from the mouth. Major functions are nutrition, respiration, excretion and reproduction In coelenterate, there is no true circulatory system but it has gastrovascular system that creates water current. Major functions of this system is to carry out nutrition, excretion and respiration Water flow canal mouth gullet gullet stomach gastric pouches oral groove. In Platyhelmithes: The circulatory system absent in this group. circular In nemahelminthes : are pseudocoelomate. It has cavity between the body wall and alimentary canal.This space is klnown as pseudocoelom. This cavity is filled with fluid called pseudocoelomic fluid. It contains amoebic cells called pseudocoelomocytes. In annelids: It has true circulatory system, has four haemocoelic canals that runs parallel to body from anterior to posterior. The blood is red, the pigment is haemoglobin dissolved in plasma. No heart but lateral canal serve as a heart as being contractile. In arthropods: It has open type of circulatory system. The circulatory system consists of heart, arteries, sinuses and veins. The blood is either colourless or blue due to presence of haemocyanin (cu containing pigment. It has seven chambered heart to pump the blood. In Mollusks: open type circulatory system. Circulatory system consists of blood, pericardium, heart, arteries, sinuses and vein. In echinoderms: Open type, formed by two systems: 1. Perihaemaln system 2. Haemal system Perihaemal system derived from coelom, lined by ciliated epithelium. It encloses the water vascular system and perihaemal system. It consists of aboral ring sinuses, genital sinuses, oral ring sinuses, Axial sinus, Marginal sinuses and peribranchial sinuses. Haemal system is derived from the blatocoel and filled with coelomic fluid. It is similar circulatory system of annelids, arthropods and mollusks. It consists of oral haemal ring, Aboral haemal ring. The open type of circulatory system has no capillaries. Blood vessels directly opens into space called sinuses where body organ bathe in the blood, thus there is direct exchange of materials between the blood and the organs. Such types of system are present in Arthropods and mollusks. The closed type of circulatory system blood flow through tube called arteries and veins. These two tubes are connected by thin tube called capillaries. The blood does not come direct contact with organ and tissues. The exchange of materials between the tissue and blood occur through the fluid and lymph. Such systems are found in annelid, echinoderm and vertebrate. Generalization The complexity of circulatory system increased with the higher order of Phylum. No circulatory system in protozoan and complex system in echinoderm. First four phyla do not have true circulatory system. Annelid is the earliest group to have true circulatory system. Arthropods have the true circulatory system with heart for pumping the blood. There are two type of circulatory system Open and closed circulatory system.