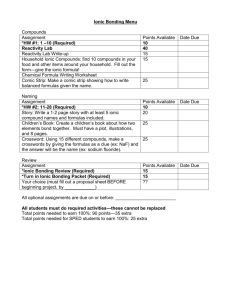
Problem Set 5
advertisement

Problem Set 4a CP Chemistry / Chemistry Due Monday, May 2nd Chapter 8 Ionic Bonding Read Chapter 8 as we work through this material. Forming Ionic Compounds Conceptual questions 1) Describe and diagram the process by which a neutral sodium atom becomes positively charged. 2) Describe and diagram the process by which a neutral chlorine atom becomes negatively charged. 3) What do atoms of a metal do to become a positively charged ion? What are these positively charged ions called? 4) What do atoms of a non-metal do to become a negatively charged ion? What are these negatively charged ions called? 5) Describe the concept of electroneutrality and how it applies to ionic crystals. 6) What is lattice energy and how is it involved in an ionic bond? Practice Questions 7) Use the periodic table to predict the noble gas that is isoelectric with each of the following ions. a. Br-1 b. Sr2+ c. Rb+ d. Al3+ e. If. S28) Give the charge that each of these metals forms when losing electrons to become cations: a. Sodium b. Magnesium c. Aluminum d. Potassium 9) Give the charge that each of these non-metals forms when gaining electrons to become anions: a. Fluorine b. Oxygen c. Phosphorous d. Chlorine Extension Question 10) Using the concepts of ionic radii and lattice energy account for the trend in melting points shown in the following table: Ionic Compound Melting Point Lattice Energy Ionic Radii KF 858 oC -808 kJ/mol K+1 = 138 pm, F-1 = 133 pm o KCl 770 C -740 kJ/mol K+1 = 138 pm, Cl-1 = 181 pm KBr 734 oC -671 kJ/mol K+1 = 138 pm, Br-1 = 195 pm o KI 681 C -632 kJ/mol K+1 = 138 pm, I-1 = 220 pm Conceptual Questions Ionic Formulas and Names 11) What do the subscripts in a chemical formula tell you about the make up of the ionic compound? 12) Why are roman numerals used to name some ionic compounds, like copper (II) chloride, but not used to name others, like sodium chloride? 13) What subscripts would be used if an ionic compound was formed… a. Between an alkali metal and a halogen b. Between an alkaline earth metal and a halogen c. Between an alkali metal and the oxide anion d. Between an alkaline earth metal and an oxide anion e. Between a group 3A element and a halogen. 14) Name this binary ionic compound: K2S 15) Name this binary ionic compound –the cation can take multiple charges: NbN 16) Give the formula for the binary ionic compound: calcium fluoride 17) Give the formula for the binary ionic compound: gold (II) chloride 18) Name this ternary ionic compound: Cd2SiO4 19) Name this ternary ionic compound – the cation can take multiple charges: Ni(NO3)3 Practice Questions Ionic Formulas and Names 20) Name these binary ionic compounds. (None of these metals take multiple charges) a. NaI b. CaBr2 c. Mg3P2 d. Al2O3 21) Name these binary ionic compounds. (All of these metals take multiple charges) a. CuI b. CrBr3 c. Au3P d. PtO2 22) Name these binary ionic compounds. (Some of these metals take multiple charges) a. Sr3N2 b. CuBr2 c. RbCl d. CoO 23) Name these copper compounds. a. CuO d. b. Cu2O e. c. CuOH f. Cu(OH)2 CuC2O4 Cu2C2O4 g. h. i. CuCO3 Cu2CO3 CuC2H3O2 24) Give the formula for the following binary ionic compounds. a. sodium sulfide e. lithium bromide b. magnesium oxide f. aluminum fluoride c. manganese (III) iodide g. iron (II) chloride d. vanadium (II) nitride h. copper (I) phosphide 25) Name the following ternary ionic compounds. (None contain roman metals) a. NaIO3 b. NH4Br c. K2CO3 d. Ba(CN)2 26) Name the following ternary ionic compounds. (All contain roman metals) a. CuIO3 b. Cr(BrO3)3 c. AuOH d. PtSO4 27) Name the following ternary ionic compounds. (Some contain roman metals) a. Sr(NO3)2 b. Cu(C2H3O2)2 c. RbClO4 d. CrPO4 28) Give the formula for each of the following ternary ionic compounds: a. aluminum sulfate e. cobalt (II) phosphate b. sodium cyanide f. lithium hydroxide c. iron (II) chlorate g. calcium acetate d. copper (I) iodate h. titanium (IV) carbonate 29) Give the formula for the following compounds. a. chromium (II) oxide b. chromium (III) oxide c. chromium (VI) oxide d. chromium (II) hydroxide e. chromium (III) hydroxide f. chromium (VI) hydroxide Extension Questions Ionic Formulas and Names 30) Why is it important to be able to name compounds correctly? 31) Why is being able to write the formulas for compounds important? 32) Compare AND contrast binary ionic compounds to ternary ionic compounds. 33) Why are parenthesis used in writing a formula of an ionic compound with a polyatomic ion? (example: Ca(OH)2 = calcium hydroxide) Conceptual Questions Metallic Bonds 34) Define a metallic bond. How does it differ from an ionic bond? 35) Why does an applied force (like hitting a piece of metal with a hammer) cause metal ions to move? What unique properties of metals are due to this mobility? 36) In a previous lab we used a hammer to tap samples of elements. How did you determine if a substance was a metal or a non metal with this test? What is it about metallic bonding that allows for this unique property? Practice Question Answers 7) Predict the noble gas that is isoelectric with each of the following ions a. Br-1 Kr b. Sr2+ Kr c. Rb+ Kr d. Al3+ Ne e. I- Xe f. S2- Ar 8) Give the charge that these metals form when they become cations: a. Sodium (+1) b. Magnesium(+2) c. Aluminum(+3) d. Potassium(+1) 9) Give the charge that these non-metals form when they become anions: a. Fluorine (-1) b. Oxygen(-2) c. Phosphorous(-3) d. Chlorine (-1) 20) Name the following binary ionic compounds. . a. NaI sodium iodide c. Mg3P2 magnesium phosphide b. CaBr2 calcium bromide d. Al2O3 aluminum oxide 21) Name the following binary ionic compounds. a. CuI copper (I) iodide c. Au3P gold (I) phosphide b. CrBr3 chromium (III) bromide d. PtO2 platinum (IV) oxide 22) Name the following binary ionic compounds. a. Sr3N2 strontium nitride c. RbCl rubidium chloride b. CuBr2 copper (II) bromide d. CoO cobalt (II) oxide a. b. c. d. 23) Give the formula for the following binary ionic compounds. sodium sulfide Na2S e. lithium bromide LiBr magnesium oxide MgO f. aluminum fluoride AlF3 manganese (III) iodide MnI2 g. iron (II) chloride FeCl2 vanadium (II) nitride V3N2 h. copper (I) phosphide Cu3P 24) Name the following ternary ionic compounds a. NaIO3 sodium iodate c. K2CO3 potassium carbonate b. NH4Br ammonium bromide d. Ba(CN)2 barium cyanide 25) Name the following ternary ionic compounds. a. CuIO3 copper (I) iodate c. AuOH gold (I) hydroxide d. PtSO4 platinum (II) sulfate b. Cr(BrO3)3 chromium (III) bromate 26) Name the following ternary ionic compounds. a. Sr(NO3)2 strontium nitrate c. RbClO4 rubidium perchlorate b. Cu(C2H3O2)2 copper (II) acetate d. CrPO4 chromium phosphate a. b. c. d. 27) Give the formula for each of these ternary ionic compounds: sodium sulfate Na2SO4 e. barium phosphate Ba3(PO4)2 sodium sulfite Na2SO3 f. calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2 copper (II) chlorate Cu(ClO3)2 g. calcium acetate Ca(C2H3O2)2 copper (I) chlorite CuClO2 h. calcium carbonate CaCO3 a. b. c. d. 28) Give the formula for each of the following ternary ionic compounds: aluminum sulfate AlSO4 e. cobalt (II) phosphate Co3(PO4)2 sodium cyanide NaCN f. lithium hydroxide LiOH iron (II) chlorate Fe(ClO3)2 g. calcium acetate Ca(C2H3O2)2 copper (I) iodite CuIO3 h. titanium (IV) carbonate Ti(CO3)2 29) Give the formula for the following compounds. a. chromium (II) oxide CrO d. chromium (II) hydroxide Cr(OH)2 b. chromium (III) oxide Cr2O3 e. chromium (III) hydroxide Cr(OH)3 c. chromium (VI) oxide CrO3 f. chromium (VI) hydroxide Cr(OH)6