Pyramids of the Nile
advertisement

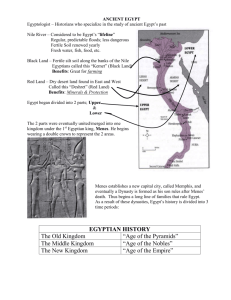
Pyramids of the Nile Chapter 2, Section 2 Setting the Stage: The Egyptian Civilization emerged around the Nile River Valley Different from other civilizations because it was at one point one single kingdom which allowed it to enjoy a high degree of unity, stability, and cultural continuity for 3,000 years The Geography of Egypt Nile river flows northward across Africa for 4,100 miles [longest river in the world] Settlements arose along the Nile on a narrow strip of fertile land by the river Figure 1 http://www.egyptweb.norfolk.gov.uk/images/egmap.jpg The Gift of the Nile: Yearly floods and rains brought the water and rich soil made the river spill over and left behind a rich deposit of fertile black mud called silt Water field through a network of irrigation ditches Egyptians worshiped the Nile as a god who gave life and seldom turned against them because it brought so much abundance to them Environmental Challenges Risks associated with the Nile: o When the floodwaters are a few feet lower than normal, the amount of fresh silt and water for crops is reduced- thousands starve o When the floodwaters are a few feet higher than normal, the unwanted water destroyed houses, granaries, and precious seeds for planting 1 o Deserts on both sides of the Nile acted as natural barriers between Egypt and other lands- forced them to live on a very small portion of land and reduced interaction with other people Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt Lived along the whole river and traveled by river up until where boulders turn the river into churning rapids called a cataract…called First Cataract Between the First Cataract and the Mediterranean, there are two regions: o Upper Egypt: river area in the south because elevation is higher o Lower Egypt: to the north near the sea and it includes the Nile delta region Broad, marshy, triangular area of land formed by deposits of silt at the mouth of the river Nile flows north so northbound boats floated with the current: helped unify Egypt’s villages and promote trade Egypt Unites into a Kingdom Lived in farming villages with unique rituals, gods, and chieftain 3200 B.C, villages under the rule of to separate kingdoms: Lower Egypt and Upper Egypt o Two kingdoms eventually united under a king called Narmer Crowns: o King of Lower Egypt wore a red crown o King of Upper Egypt wore a white crown shaped like a bowling pin o Narmer created the Narmer Palette which lets him wear both crowns at the same time, which celebrates the unification of Egypt around 3,000 B.C. Figure 2 Figure 3: http://www.toutankharton.com/IMG/gif/pschent.gif New capital was Memphis, which was at the spot where Upper and Lower Egypt met He created first Egyptian dynasty o Total of 31 dynasties over 2,600 years o Pattern for Egypt’s great civilization set from 3200 to 2700 B.C. o From 2660 to 2180 B.C. was known as the Old Kingdom Pharaohs Rule as Gods Differences in Kings o In Mesopotamia, kings were representatives of Gods o In Egypt, kings were Gods 2 These god-kings were called Pharaohs who were thought to be as powerful as the gods in heaven This type of government based on religious authority is called a theocracy Roles of a Pharaoh: o Head of religion o Head of government o Responsible for Kingdom’s well-being o Caused the sun to rise, Nile to flood, crops to grow o Duty to promote justice and truth Builders of the Pyramids Believed King rules even after his death Kings had an eternal life force, or ka, which continued to take part in governing Egypt Because they were to reign forever, tombs were more important than palaces o For Kings of the Old Kingdom, resting place after death was an immense structure called a Pyramid Granite and limestone Each stone block weighed at least 2.5 tons-15 tons Great Pyramid of Giza had over 2 million blocks, stacked to a height of 481 feet…. Covered 13 acres Pyramids show strength of Egyptian civilization, economic strength, technological means to support massive projects, leadership, and government organization Figure 4 http://aceflashman.files.wordpress.com/2009/12/pyramid-diagram.png?w=500&h=500 Egyptian Culture Religion is an important part of Egyptian culture Religion and Life: Like Mesopotamians, Polytheistic: believed in many gods…over 2,000 o Important gods were: 3 Re: the sun god Osiris: god of the dead o Built temples to honor the major deities Unlike Mesopotamians who had a bleak look at death, Egyptians believed in an afterlife- a life that continued after death o Will be judged for their deeds when they died o Anubis is the god and guide of the underworld He would weigh person’s heart: to win eternal life, heart has to weight no more than a feather… If the heart tips the scale, it means its heavy with sin and a beast called the Devourer of Souls would pounce on heart and eat it Everyone planned their burial so they would safely reach the Other World o Kings/queens built tombs in Pyramids o Royals and elites were preserved through mummification, which involved embalming and drying the corpse to prevent it from decaying Mummy placed in a coffin inside tomb… filled the tomb with items the dead person could use in the afterlife [clothing/food/cosmetics/jewelry/guards/animals] Organs divided into different containers http://library.thinkquest.org/C0116982/HTML%20page%20folder/hm ummification.htm [Show mummy picture and the organ containers] 1.Imsety the human - headed god looks after the liver. 2.Hapy the baboon - headed god looks after the lungs 3.Duamutef the jackal - headed god looks after the stomach 4.Qebehsenuef the falcon - headed god looks after the intestines o Book of the Dead is a collection of hymns, prayers, and magic spells that is supposed to guide the soul in the afterlife Life in Egyptian Society Egyptian society forms a pyramid of classes: o King/Queen/Family o Priests/Army commanders/wealthy landowners/government officials o Middle class: artisans/crafts workers/merchants o Lower class: Peasant farmers/laborers o Slaves 4 Figure 5 http://www.mrwanat.info/worldhistory/egypt/vizier/pictures/01.jpg Could gain higher classes by marriage or success in their jobs and had to know how to read/write Women had same rights as men: own and trade property, postpone marriage, seek divorce [then would get one-third of couple’s property] Egyptian Writing: Simple pictographs were earliest forms of writing Then developed hieroglyphics, a writing system where a picture stood for an idea or sounds First carved into stone then they invented a writing surface from papyrus reeds o Grew in marshes and pressed into sheets Figure 6 http://www.idstyle.com/safari/egypt/hieroglyphics-table.jpg 5 Egyptian Science and Technology : Achievements: o Calendar to keep track of time between floods and plan planting season…used start Sirius which appeared about the eastern horizon before floods came 365 days…divided into 12 months, 30 days each: 5 extra days for holidays Figure 7 http://www.fromcairo.com/images/natural-calendar.jpg o o o o o o o System of written numbers for counting, adding, and subtracting Early form of geometry to survey/reset property boundaries First to use stone columns Knew how to check pulse rate Set broken parts with splints Effective treatments for wounds/fevers Surgery for some conditions Invaders control Egypt Power of Pharaohs declined around 2180 B.C. and ended Old Kingdom o They regained power during the Middle Kingdom 2040-1640 B.C….improved trade, transportation, built huge dikes to trap Nile water, drained swamps for new farmland 1640 B.C., Hyksos from Palestine moved in to Egypt and ruled from 1630-1523 B.C. Regained control again in the New Kingdom 6