Módulo: Mecanizado (MEC)
advertisement

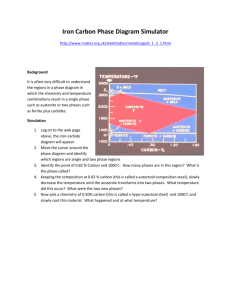
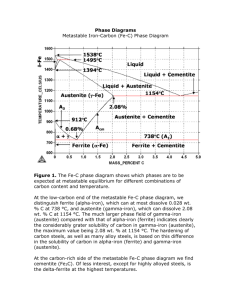
AF_FM01_ Fabricació Mecànica. Ferrous Materials Unit 2 The Iron-Carbon diagram Contents. 2.1 Constituents of ferrous alloys 2.2 The Iron-Carbon diagram 2.3 Questions 2.1 Constituents of ferrous alloys There are some words related to different constituents of ferrous alloys that you have to know: FERRITE /ˈfɛraɪt/: AUSTENITE: Ferrite is a solid solution of Carbon or more elements in alpha iron or delta iron. It's crystalline structure is BCC. Austenite is a solid solution of Carbon or more elements in gamma iron. It's crystalline structure is FCC. CEMENTITE: Cementite is triiron carbide produced by excess Carbon on the Iron solubility limit. It's formula is Fe3C representing a content in carbon of 6.7% related to the total mass. Cementite is a hard and brittle constituent. PEARLITE /ˈpɜːlaɪt/: Pearlite is a structure which results from an eutectoid transformation and consists of ferrite and cementite. LEDEBURITE: Ledeburite is a structure which results from an eutectic transformation and consists of austenite and cementite. 2.2 The Iron-Carbon diagram As we have seen in previous unit, pure iron has different transformation temperatures when cooling from liquid state to room temperature. These temperatures are called critical points because they are where a change in the structure of the material occurs. Critical points for pure Iron (wt 0% C): 1540 ºC the melting point (when heating) or solidification temperature (when cooling) 1390 ºC temperature where delta iron (BCC) transforms to gamma iron (FCC) when cooling 910 ºC temperature where gamma iron (FCC) transforms to alpha iron (BCC) when cooling If we analyse different samples of iron-carbon alloys, we observe that the value of the critical points is different depending on the content of carbon. If we plot these values in a Temperature / Composition diagram and we make lines between the same critical temperatures with different carbon content, we will obtain the Iron-Carbon diagram. With this diagram we will have a tool to know which will be the phase of an alloy by knowing the composition and the temperature. Interactive Iron-Carbon diagram (1) Iron-Carbon diagram (2) with explanations The Iron-carbon diagram shows the different phases that will be present depending on the temperature and composition (Carbon content in wt%). The lines in the diagram show the transformation temperatures where changes in phases occur. AF_FM01- Fabricació Mecànica. Ferrous materials / AF 1 Here you have an Iron-Carbon diagram with the different constituents present. a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o A B AF_FM01- Fabricació Mecànica. Ferrous materials / AF ferrite + pearlite pearlite + ledeburite + cementite ledeburite + cementite cementite ferrite ferrite + austenite austenite austenite + ledeburite + cementite ledeburite + cementite austenite + liquid liquid cementite + liquid delta iron + austenite delta iron delta iron + liquid Pearlite - Eutectoid 0,8%C Ledeburite - Eutectic 4,3%C 2 It's recommended for you to take a look at these activities to practice. Quizlet – IRON-CARBON diagram IRON-CARBON alloys Quizlet – Structure of Ferrous alloys Scribd – IRON-CARBON diagram TO KNOW MORE … about the steel microstructure, take a look at this video. Video Slow cooling of hypoeutectoid steels Here you will find a complete class about this subject. Video (56 min) Iron-carbon phase diagram With the aid of the definitions of this unit and using the diagrams (the links to the interactive diagrams on the previous page, and the diagram on this page) try to solve the following questions: 2.3 Questions 21. What is the name of the solid solution of carbon in alpha iron? a) Austenite b) Cementite c) Ferrite d) Ledeburite e) Pearlite 22. What is the name of the solid solution of carbon in gamma iron? a) Austenite b) Cementite c) Ferrite d) Ledeburite e) Pearlite 23. Which is the crystal structure of austenite? a) ABC b) BCC c) FCC d) SC 24. What is Fe3C? a) Austenite b) Cementite c) Ferrite d) Ledeburite e) Pearlite 25. What is the name of the eutectic? a) Austenite b) Cementite c) Ferrite d) Ledeburite e) Pearlite 26. What is the name of the eutectoid? a) Austenite b) Cementite c) Ferrite d) Ledeburite e) Pearlite 27. Ledeburite is a structure that consists of ... a) Austenite+Cementite b) Austenite+Ferrite c) Cementite+Ferrite 28. Pearlite is a structure that consists of ... a) Austenite+Cementite b) Austenite+Ferrite c) Cementite+Ferrite 29. Find the letter (in diagram) and the maximum amount of carbon for solid austenite. 30. Find the letter (in diagram) and the maximum amount of carbon for solid ferrite. 31. Find the letter (in diagram) and the carbon content for cementite. AF_FM01- Fabricació Mecànica. Ferrous materials / AF 3 32. Find the letter (in diagram) and the carbon content for ledeburite. 33. Find the letter (in diagram) and the carbon content for pearlite. 34. What is the minimum melting temperature of steel? What is the %C at this point? 35. What is the minimum melting temperature of cast iron? What is the %C at this point? 36. What is the maximum temperature for Ferrite? 37. What is the maximum temperature for Ledeburite? 38. What is the maximum temperature for Pearlite? 39. Which phases are present with 2%C at 1000 K? a) Austenite+Cementite b) Austenite+Ferrite 40. Which phase is present with 6.7%C at 1500 K? a) Austenite b) Cementite c) Ferrite AF_FM01- Fabricació Mecànica. Ferrous materials / AF c) Cementite+Ferrite d) Ledeburite e) Pearlite 4