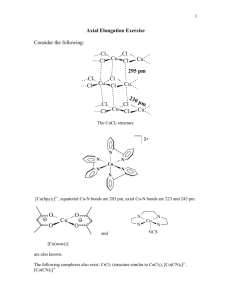
RS 10B
advertisement
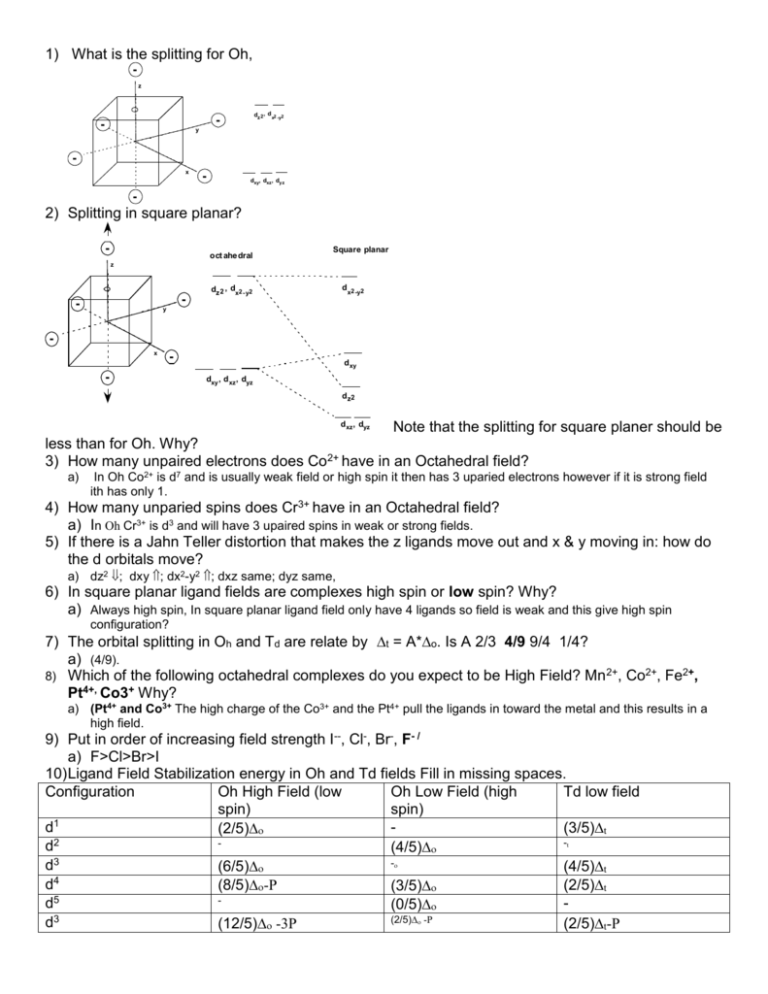
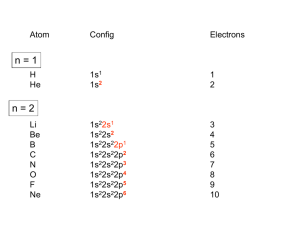
1) What is the splitting for Oh, z dz 2 , d x2 -y2 - - y x - dxy, dxz , dy z - 2) Splitting in square planar? - oct ahe dral Square planar z - - dz 2 , dx2 - y2 d x2 -y2 y x - - d xy dxy , d xz , dyz d z2 Note that the splitting for square planer should be less than for Oh. Why? 3) How many unpaired electrons does Co2+ have in an Octahedral field? d xz , dyz a) In Oh Co2+ is d7 and is usually weak field or high spin it then has 3 uparied electrons however if it is strong field ith has only 1. 4) How many unparied spins does Cr3+ have in an Octahedral field? a) In Oh Cr3+ is d3 and will have 3 upaired spins in weak or strong fields. 5) If there is a Jahn Teller distortion that makes the z ligands move out and x & y moving in: how do the d orbitals move? a) dz2 ; dxy ; dx2-y2 ; dxz same; dyz same, 6) In square planar ligand fields are complexes high spin or low spin? Why? a) Always high spin, In square planar ligand field only have 4 ligands so field is weak and this give high spin configuration? 7) The orbital splitting in Oh and Td are relate by t = A*o. Is A 2/3 4/9 9/4 1/4? a) (4/9). 8) Which of the following octahedral complexes do you expect to be High Field? Mn 2+, Co2+, Fe2+, Pt4+, Co3+ Why? a) (Pt4+ and Co3+ The high charge of the Co3+ and the Pt4+ pull the ligands in toward the metal and this results in a high field. 9) Put in order of increasing field strength I--, Cl-, Br-, F- / a) F>Cl>Br>I 10) Ligand Field Stabilization energy in Oh and Td fields Fill in missing spaces. Configuration Oh High Field (low Oh Low Field (high Td low field spin) spin) d1 (3/5)t (2/5) 2 -t d (4/5) - d3 (4/5)t (6/5) 4 d (8/5)-P (2/5)t (3/5) 5 d (0/5) (2/5) -P d3 (12/5) -3P (2/5)t-P d7 d8 d9 d10 (9/5) -3P (3/5) -4P 0-5P (4/5) -2P - - (6/5)t-3P - - 0-5P 0-5P (2/5)Do ( (6/5)Dt (6/5)Do t a. answers d1 d2 d3 d4 d5 d3 d7 d8 d9 d10 (4/5)Do (10/5)Do-2P (0/5)Dt (2/5)Do -P (4/5)Dt-2P (6/5)Do -3P (6/5)Do -3P (3/5)Do -4P (3/5)Do -4P 11) What is the LF stabilization energy for a d5 high field complex, a d10 high-field complex, and a d5 low field complex. a) d5 H.F.: (10/5 O), b) d10 H.F.: 0 c) d5 L.F.:, 0 12) (Unit cells) A corner atom is part of how many unit cells? i) 8 13) In the two-dimensional square packing shown, what is the coordination number of the central atom? (4) 14) A tetrahedron can be inscribed inside a cube, represented in the layer sequence formalism shown below. If sphere 1 is part of the tetrahedron, which other three spheres are as well? 5 6 2 1 8 4 7 3 (1,3,8,6) 15) An octahedron can be inscribed in a cube. If spheres 9 and 14 (below) are part of the octahedron, which are the other four spheres? What is their arrangement? 5 6 14 1 13 11 8 12 2 10 7 9 4 3 a) (10,11,12,13, they are the face center spheres. 16) The figure below is a ZnS (zinc blend) layer sequence. The atom indicated by an arrow sits in one of the tetrahedral holes of the structure. Which atoms form this hole? a) (1,6,7,3) 17) In the zinc blend layer sequence below, what fraction of the tetrahedral holes are filled? (1/2) 18) C60 (buckyball) is cubic closest packed (face-centered cubic) in its crystalline form. If you insert potassium atoms into all the tetrahedral and octahedral holes of the C60 structure, the formula would become KxC60 . What is the value of x? (3) 19) What is the coordination number in the diamond structure? (4) 20) What is the coordination geometry in the Oh hole? (6) 21) What is the coordination geometry in the BCC center? (8) 22) A layer sequence for an FCC = CCP metal is shown below. a) The plane 1,1,1 passes through which atoms (2,4,6,9,10,5) b) A body diagonal passes through the center of atom 4 and the center(s) of which other atom(s)? (11) c) A close-packed plane is comprised of six atoms. If atoms 2, 4, 5 are three of the six atoms, which other three atoms are need to define the plane? (2,4,6,9,10,5) d) If four identical spheres are placed in contact to form a tetrahedral hole, can an identical sphere fit into the hole? no 23) Show the splitting if the geometry of the ligands is linear, square planar or T d. Splitting of the d orbitals in various ligand fields linear square planar Oh Td 15 x2-y2 10 z2 5 z2 x2-y2 xy 0 -5 xy x2-y2 -10 xy xz yz xz yz xy xz yz x2-y2 z2 xz yz z2