File
advertisement
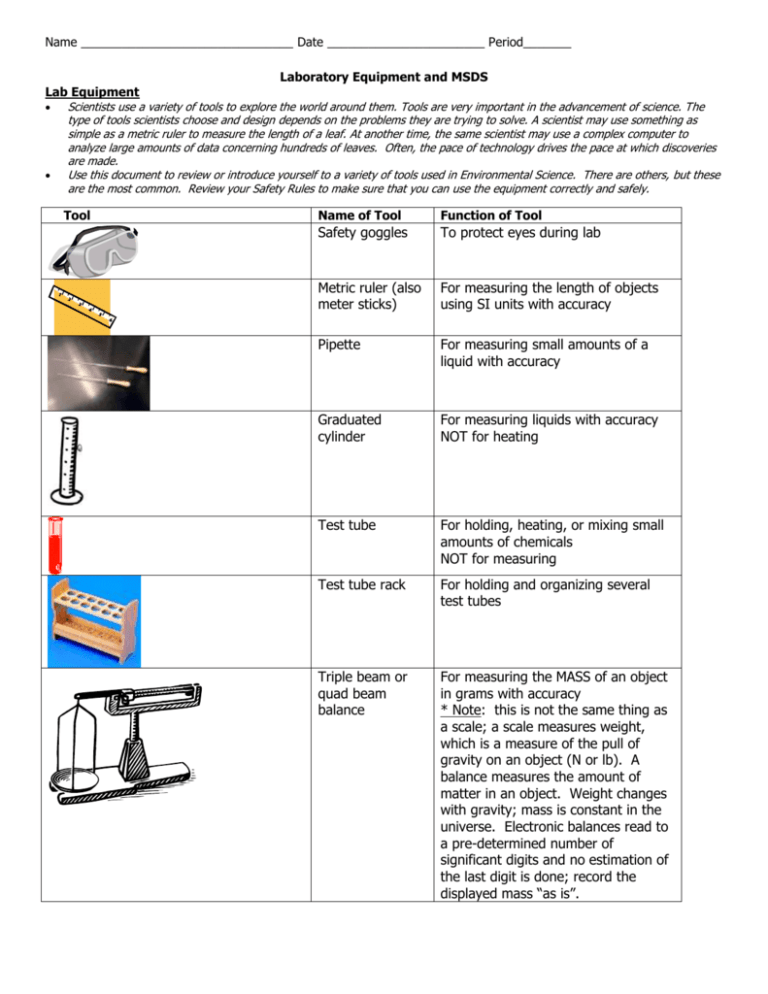
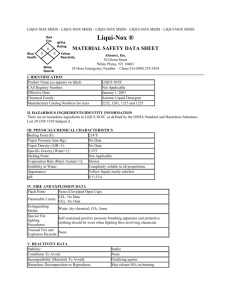
Name _______________________________ Date _______________________ Period_______ Laboratory Equipment and MSDS Lab Equipment Scientists use a variety of tools to explore the world around them. Tools are very important in the advancement of science. The type of tools scientists choose and design depends on the problems they are trying to solve. A scientist may use something as simple as a metric ruler to measure the length of a leaf. At another time, the same scientist may use a complex computer to analyze large amounts of data concerning hundreds of leaves. Often, the pace of technology drives the pace at which discoveries are made. Use this document to review or introduce yourself to a variety of tools used in Environmental Science. There are others, but these are the most common. Review your Safety Rules to make sure that you can use the equipment correctly and safely. Tool Name of Tool Function of Tool Safety goggles To protect eyes during lab Metric ruler (also meter sticks) For measuring the length of objects using SI units with accuracy Pipette For measuring small amounts of a liquid with accuracy Graduated cylinder For measuring liquids with accuracy NOT for heating Test tube For holding, heating, or mixing small amounts of chemicals NOT for measuring Test tube rack For holding and organizing several test tubes Triple beam or quad beam balance For measuring the MASS of an object in grams with accuracy * Note: this is not the same thing as a scale; a scale measures weight, which is a measure of the pull of gravity on an object (N or lb). A balance measures the amount of matter in an object. Weight changes with gravity; mass is constant in the universe. Electronic balances read to a pre-determined number of significant digits and no estimation of the last digit is done; record the displayed mass “as is”. Timing device Used to accurately and precisely time laboratory events; includes digital timers (shown), as well as clocks and watches Probeware Electronic devices with interchangeable “probes” used to collect data in a digital format, including dissolved oxygen content, CO2 content, turbidity, pH, and temperature; can interface with a computer or graphing calculator for digital analysis of the data Thermometer For measuring temperature (heat) with accuracy (always in Celsius on a laboratory thermometer) Hand lens (magnifying glass); to enlarge small objects or view details on a large object; can be used on living organisms pair of identical or mirror-symmetrical telescopes mounted side-by-side and aligned to point accurately in the same direction, allowing the viewer to use both eyes (binocular vision) when viewing distant objects. Most are sized to be held using both hands Intended for treatment of minor injuries only. Typical contents include adhesive bandages, regular strength pain medication, gauze and lowgrade disinfectant. Binoculars First Aid Kit Compass A compass is an instrument used for navigation and orientation that shows direction relative to the geographic cardinal directions, or "points". Usually, a diagram called a compass rose, which shows the directions north, south, east, and west as abbreviated initials marked on the compass. Gloves Disposable gloves used specifically to protect hands from injury, toxins or bodily fluids. Stereoscope (dissecting microscope) view objects too large for the standard microscope; used for viewing during dissections; can view living specimens and whole organisms in greater detail; allows for good depth perception because a user can utilize both eyes Electronic balance Used to quickly determine the MASS of a sample; capable of automatic tare (the mass of the container) determination; number of significant digits predetermined and no estimation of the last digit is done; record the displayed mass “as is” Container designed for weighing liquid or powdered samples in the laboratory. The mass of the weigh boat is to be subtracted from the total mass of what you are weighing. Weigh Boat Or Weighing Boat Read each scenario and determine the equipment that would be needed using the work bank below. Binoculars Metric Ruler Test Tubes Compass Pipette Thermometer Electric Scale Probeware Timer Gloves x 4 Safety Goggles x 4 Triple Beam Balance Graduated Cylinder x 2 Stereoscope Weight Boat Hand Lens Test Tube Rack 1. You are out in the field observing flying patterns of birds including direction of flight, length of time in the air and the physical characteristics. Equipment needed: ________________________, ________________________, ___________________________ 2. After observing the birds in the wild you collect feathers to examine back in the laboratory to determine if they carry a particular parasite. You also check to see if there is a correlation between infection and feather length. Equipment needed for collection and observation: ______________________, _______________________, _____________________________, ____________________________, ____________________________ 3. The pond near the bird’s breeding site has been suspected of pollution causing the parasites to grow in population. You have been asked to collect water samples. Equipment needed: ________________________, ____________________________, ______________________________, ______________________________ 4. After collecting water you must test for dissolved oxygen, pH, and temperature back at the lab. In order to perform these tests, water needs to be measured in both large and small quantities. Equipment needed: _________________________, _______________________, ___________________________, ___________________________, ____________________________, __________________________ 5. After recording data you must disinfect the feathers using a solution of 35ml of water and 1.5 g of baking soda before disposing of them. Equipment needed: __________________________or _________________________, __________________________, ____________________________, ______________________________, ________________________________ Reading and Understanding a Materials Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) 6. What does MSDS stand for? _____________________________________________________ 7. What is the MSDS # and Revision Date for this chemical? ______________________________ 8. From your reading: Complete the table below using the MSDS sheet assigned to you. Question to Answer Information Found MSDS # assigned to you Complete name of chemical Synonyms for this chemical name What are the hazards of working with chemical? What should you do if this chemical spills on your skin? What is the reactivity of this chemical; is this high or low? What personal protection equipment should you wear when working with this chemical? What is the formula for this chemical (this is a property of the chemical)? If you spilled a large quantity of this chemical in a pond, what is its effect on aquatic life? 9. Why is it a requirement that this document be available for every chemical used in the lab? Section Found In Written in top right