Study Guide 1213
advertisement

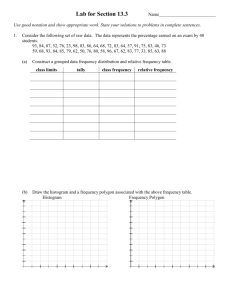
Environmental Science 303 Midterm Study Guide Chapters 2, 5, 15, & 11 Multiple choice, matching, and true and false questions 1 Graphing problem with given data Chapter 2 – Tools of Environmental Science Define the following words: observation, inference, hypothesis, independent variable, dependent variable, control group, constants 1. Read the story below. Then CIRCLE and LABEL parts in the story that relate to each of the terms listed above. We decided to get class guinea pigs. We noticed that it didn’t seem like they were eating very much of their food. We researched online and found 2 other brands. Some of the class thought the pigs would like Big Pig Food, the other ½ wanted to use Groovy Guinea Food. We decided that if they ate more BP, then they liked BP better, but if they ate more GG, then they like GG better. We divided the pigs into groups randomly. 1 group was fed BP, one group was fed GG and one group was fed the old kind of food. We gave the pigs the same amount of food in the bowls every day at the same time and weighed what was left in the bowls after 1 hour. We plotted the amount eaten (beginning weight- remaining weight) vs. kind of food on a graph. Then, we calculated the average amount eaten of each kind of food and plotted that against kind of food as well. 2. Why is it always better to test more samples? (For example, why would you want to test ten plants rather than 2 plants?) 3. Give an example of an observation and an inference. 4. What is the difference between an inference and a hypothesis? 5. What are the steps of the scientific process? DRAW a diagram. 6. Review your graphing notes. When would you use a bar graph? Line graph? Pie chart? 7. What are the independent variable, dependent variable and a good title for the graph? 8. DRAW a graph for the following information (be sure to include all the components, labels, title, etc.): Mrs. Loch noticed that the ant population always seems to go up when the aphid population is high. So she did an experiment to confirm her suspicions and prove to her classes that she was a brilliant scientist. She recorded her data in the table below: Month 1 Month 2 Month 3 Month 4 Ants 25 47 94 144 Aphids 50 73 139 210 Chapter 5- Energy Flow in Ecosystems Define the following words: abiotic, biotic, photosynthesis, producer, consumer, decomposer, cellular respiration, food chain, food web, trophic level Know the following: 1. Give an example of a biotic factor and an abiotic factor in the ecosystem. 2. COMPARE producers, consumers, decomposers, carnivores, omnivores, and herbivores. 3. What is the difference between a food web and a food chain? 4. DRAW an example of a food chain with 4 links. 5. Why is a food chain usually only 4 or 5 links? Think about the popcorn race. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. What percent of energy transfers to the next trophic level when the organism is eaten? Why would there be more food available if everyone became a vegetarian? What is taken in and given off during photosynthesis? How are cellular respiration and photosynthesis linked? What organisms recycle materials/nutrients through the ecosystem? Chapter 15 – Agriculture Define the following words: agriculture, topsoil, desertification, irrigation, fertile, pest, erosion, GMO, pesticide, persistent pesticide Know the following: 1. Make a t-chart to COMPARE traditional vs. modern agriculture. 2. What are some problems with factory farming? 3. What is pesticide resistance? 4. Pesticide resistance is driven by natural selection. Use the process of natural selection to describe how a pest might become resistant to a certain pesticide. 5. What makes soil? 6. What is topsoil made from? a. Why is it so important to farmers? 7. What nutrients are needed in soil for good plant growth? 8. What is an even mixture of clay, silt, and sand called? a. Why is this the best soil for growing plants? (Think particle sizes.) 9. How does no-till farming help to prevent erosion? 10. COMPARE the benefits and environmental impacts of pesticide use. 11. What are 2 biological strategies that could be used to control pests? 12. What are the advantages/disadvantages to using GMO’s vs. selective breeding? 13. What are the advantages to practicing Integrated Pest Management? 14. DDT is considered a persistent pesticide. What does this mean? 15. Pollutants like DDT also get magnified (increases) as you go up the food chain. Why? Which organisms will suffer the most? Chapter 11 – Water Define the following words: point source, non-point source, impervious surfaces, watershed, genetic pollution, thermal pollution, runoff, percolation, evaporation, condensation, transpiration, surface water, aquifer, reservoir, eutrophication, macroinvertebrate, desalination, indicator species, wastewater, sludge Know the following: 1. DRAW the water cycle and label the processes. 2. NAME two (2) examples of both nonpoint & point pollution. a. Which is more difficult to clean? b. More common? 3. What causes an algal bloom? EXPLAIN the steps, stating what happens to oxygen in the water. 4. What is a watershed? a. Which watershed do we live in? 5. Why is groundwater pollution more difficult to clean-up than surface water? 6. Algal blooms occur when there is an excess of which two nutrients? a. These nutrients are found in what everyday things that might get into the water? 7. Normally rapid growth of plants is a good thing. However rapid growth of algae (an algal bloom) is a bad thing. Why are algal blooms bad and how are they created? 8. Why are wetlands important? 9. What tests can you do to determine the quality (health) of a body of water? 10. Is it good or bad to find macroinvertebrates in the water? EXPLAIN how they help you determine the quality of the water. 11. You come across a stream and decide to conduct some tests to find out if it's clean. What results would you expect to find (think in terms of high/low) for the following tests: a. Phosphate and nitrate b. pH c. Dissolved oxygen d. Turbidity 12. Where does Upper Dublin get its drinking water from? 13. What are two things that naturally filter water? 14. DISCUSS 2 reasons why tap water is better than bottled water. 15. DRAW a Venn diagram to show the similarities and differences between wastewater and drinking water treatment. 16. What is the role of bacteria in wastewater treatment? 17. Most wastewater treatment plants don't do advanced treatment because it's too expensive. It would be best if they did because advanced treatment includes… 18. How much of the water in the world is fresh water? a. Why is the percentage that is actually available to us so much lower? 19. LIST the 3 biggest users of water in order from most to least. 20. What are 3 reasons that availability of freshwater is limited? 21. What are some things farmers could do to reduce the amount of water used? 22. What are 3 things YOU could do to reduce the amount of water used? 23. What is the BEST way to make sure there is enough water for everyone's needs?