Animation: Sodium-Potassium Exchange Pump (Quiz 1 and 3)

Carol Suh Period 3
Animation: Sodium-Potassium Exchange Pump (Quiz 1 and 3)- 100%
1.
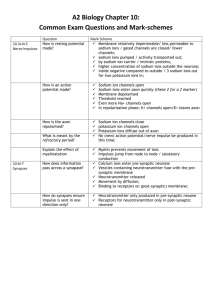
The sodium-potassium pump functions to pump a.
sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell. b.
sodium ions into the cell and potassium ions out of the cell. c.
sodium and potassium ions into the cell. d.
sodium and potassium ions out of the cell. e.
sodium and potassium ions in both directions across the cell membrane.
2.
What is the source of energy used to power the sodium-potassium pump? a.
breakdown of ATP b.
formation of ATP c.
transport of ATP by the pump d.
breakdown of GTP e.
transport of GTP by the pump
3.
During one cycle, the sodium-potassium pump binds and moves. a.
1 Na + and 2 K + . b.
2 Na
+
and 2 K
+
. c.
2 Na
+
and 3 K
+
. d.
3 Na
+
and 2 K e.
3 Na
+
and 3 K
+
+
.
4.
The sodium-potassium pump is a trans-membrane protein. a.
True b.
False
5.
The binding and release of sodium or potassium ions are due to conformational changes in the protein a.
True b.
False
Animation: Sodium-Potassium Exchange Pump (Quiz 2)- 100%
1.
Which of the following statements are not true about the sodium potassium pump? a.
The ions from the intracellular fluid plus an ATP molecule bind to the carrier protein on the inside of the cell membrane. b.
ATP is broken down into ADP and potassium to supply the energy. c.
The carrier protein changes shape as it transports ions from the intracellular fluid to the extracellular fluid. d.
The ions from inside the cell are transported across the cell membrane. e.
The ions are then released into the extracellular fluid.
2.
Which of the following statements are not true about the sodium potassium pump? a.
After releasing ions into the extracellular fluid, the carrier protein exhibits a new conformation. b.
With this new conformation, the carrier protein can now bind to different ions in the extracellular fluid. c.
The ions in the extracellular fluid bind to the carrier protein, and the potassium attached to the carrier protein is released. d.
The carrier protein then changes shape again. e.
The ions from the extracellular fluid are then transported across the cell membrane to the inside of the cell.
3.
The sodium potassium exchange pump is an example of… a.
diffusion. b.
facilitated diffusion. c.
active transport. d.
osmosis. e.
filtration.
Carol Suh Period 3
4.
The sodium potassium exchange pump moves three potassium ions out of the cell and two sodium ions into the cell with each cycle. a.
True b.
False
5.
Active transport moves substances from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration of that substance. a.
True b.
False
Animation: Chemical Synapse (Quiz 1)- 100%
1.
An action potential arriving at the presynaptic terminal causes...
a.
sodium ions to diffuse into the cell.
b.
sodium ions to diffuse out of the cell c.
calcium ions to diffuse into the cell. d.
acetylcholine to diffuse into the cell.
e.
ligand-gated sodium channels to open.
2.
As a result of question number one...
a.
synaptic vessels migrate to the plasma membrane and release acetylcholine. b.
acetylcholine is actively transported from the pre-synaptic neuron.
c.
acetylcholine is actively transported to the post synaptic neuron.
d.
ligand-gated sodium channels open.
e.
sodium ions diffuse into the cell.
3.
Acetylcholine has which effect on the post-synaptic neuron?
a.
Ligand gated calcium channels open and calcium diffuses in.
b.
Ligand gated sodium channels open and sodium diffuses in. c.
Terminal vessels migrate to the plasma membrane.
d.
Voltage gated calcium ion channels open and calcium diffuses in.
e.
Voltage gated sodium ion channels open and sodium diffuses in.
4.
If the post-synaptic membrane potential reaches threshold level, an action potential will be produced.
a.
True b.
False
5.
Acetylcholine is actively transported from the pre-synaptic membrane to the post - synaptic membrane.
a.
True b.
False
Animation: Chemical Synapse (Quiz 2)- 100%
1.
An action potential arriving at the presynaptic terminal causes...
a.
voltage-gated sodium ion channels to open, and sodium ions to diffuse into the cell.
b.
voltage-gated sodium ion channels to open, and sodium ions to diffuse out of the cell.
c.
voltage-gated calcium ion channels to open, and calcium ions to diffuse into the cell. d.
acetylcholine to diffuse into the cell.
e.
ligand-gated sodium channels to open, and sodium ions to diffuse out of the cell.
2.
As a result of question number one...
a.
synaptic vessels migrate to the plasma membrane and release acetylcholine. b.
acetylcholine is actively transported from the pre-synaptic neuron.
c.
acetylcholine is actively transported to the post synaptic neuron.
d.
ligand-gated sodium channels open.
e.
sodium ions diffuse into the cell.
3.
Acetylcholine has which effect on the post-synaptic neuron?
a.
Ligand gated calcium ion channels open and calcium diffuses in.
b.
Ligand gated sodium ion channels open and sodium diffuses in.
Carol Suh Period 3 c.
Terminal vessels migrate to the plasma membrane.
d.
Voltage gated calcium ion channels open and calcium diffuses in.
e.
Voltage gated sodium ion channels open and sodium diffuses in.
4.
If the post-synaptic membrane potential reaches threshold level, an action potential will be produced.
a.
True b.
False
5.
Acetylcholine is actively transported from the pre-synaptic membrane to the post-synaptic membrane.
a.
True b.
False
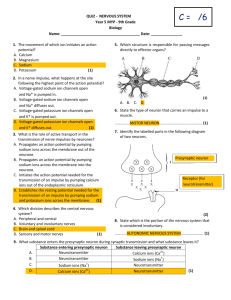
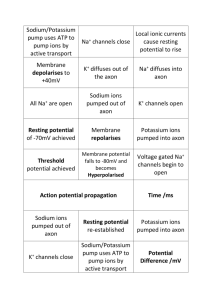
Animation: The Nerve Impulse- 100%
1.
Which of the following statements about the resting membrane potential is TRUE?
a.
the exterior of the cell has a net negative charge and the interior has a net positive charge.
b.
the exterior of the cell has a net negative charge and the interior is neutral c.
the exterior of the cell has a net positive charge and the interior has a net negative charge d.
the exterior of the cell has a net positive charge and the interior is neutral e.
the exterior of the cell is neutral and the interior has a net negative charge
2.
During depolarization, which of the following statements about voltage-gated ion channels is TRUE a.
K
+
gates open before Na
+
gates b.
Na
+
gates open before K
+
gates c.
Na
+
and K
+
gates open at the same time d.
Na + gates open while K + gates remain closed e.
K
+
gates open while Na
+
gates remain closed
3.
Depolarization occurs because a.
more K + diffuse into the cell than Na + diffuse out of b.
more K
+
diffuse out of the cell than Na
+
diffuse into it c.
more Na
+
diffuse into the cell than K
+
diffuse out of it d.
more Na
+
diffuse out of the cell than K
+
diffuse into it e.
both Na + and K + diffuse into the cell
4.
The sodium-potassium pump is involved in establishing the resting membrane potential.
a.
True b.
False
5.
The nerve impulse is an electrical current that travels along dendrites or axons.
a.
True b.
False
Animation: Transmission Across a Synapse- 100%
1.
The primary neurotransmitter at the neuromuscular junction is a.
dopamine.
b.
adrenaline.
c.
acetylcholine. d.
histamine.
e.
serotonin
2.
Arrange the following in the proper order in which they occur at the pre-synaptic side of a neuromuscular junction.
1. Calcium ions are released
2. Action potential arrives at the presynaptic terminal
3. Neurotransmitter is released a.
1, 2, 3 b.
2, 1, 3 c.
2, 3, 1
Carol Suh d.
3, 2, 1
Period 3 e.
3, 1, 2
3.
Arrange the following in the proper order in which they occur at the post-synaptic side of a neuromuscular junction.
1. Action potential is propagated over the muscle cell membrane
2. Depolarization of the post-synaptic membrane
3. Sodium ions move into muscle cell a.
1, 2, 3 b.
2, 1, 3 c.
2, 3, 1 d.
3, 2, 1 e.
3, 1, 2
4.
The area between the pre-synaptic nerve cell and the post-synaptic muscle cell is termed the synaptic cleft.
a.
True b.
False
5.
Receptors that bind the neurotransmitter at the post-synaptic cell membrane are voltage-gated.
a.
True b.
False
Animation: Voltage-Gated Channels and the Action Potential (Quiz 1)- 100%
1.
Depolarization occurs because...
a.
potassium ions continue to diffuse out of the cell after the inactivation gates of the voltage-gated sodium ion channels begin to close.
b.
the extra efflux of potassium ions causes the membrane potential to become slightly more positive than the resting value.
c.
the increased potassium ion permeability lasts slightly longer than the time required to bring the membrane potential back to its resting level d.
more sodium ions diffuse into the cell than potassium ions diffuse out of it. e.
the inactivation gates of the voltage-gated sodium ion channels begin to open and the diffusion of sodium ions decreases
2.
Repolarization occurs because...
a.
potassium ions continue to diffuse out of the cell after the inactivation gates of the voltage-gated sodium ion channels begin to close. b.
the extra efflux of potassium ions causes the membrane potential to become slightly more positive than the resting value.
c.
the increased potassium ion permeability lasts slightly longer than the time required to bring the membrane potential back to its resting level.
d.
more sodium ions diffuse into the cell than potassium ions diffuse out of it.
e.
the inactivation gates of the voltage-gated sodium ion channels begin to open and the diffusion of sodium ions decreases.
3.
Hyperpolarization, or afterpotential occurs because...
a.
potassium ions continue to diffuse out of the cell after the inactivation gates of the voltage-gated sodium ion channels begin to close.
b.
the extra efflux of potassium ions causes the membrane potential to become slightly more positive than the resting value.
c.
the increased potassium ion permeability lasts slightly longer than the time required to bring the membrane potential back to its resting level. d.
more sodium ions diffuse into the cell than potassium ions diffuse out of it.
e.
the inactivation gates of the voltage-gated sodium ion channels begin to open and the diffusion of sodium ions decreases.
Carol Suh Period 3
4.
After the passage of the action potential, the sodium-potassium pump reestablishes the resting membrane potential.
a.
True b.
False
5.
The sodium-potassium pump uses bulk transport to move the sodium and potassium ions.
a.
True b.
False
Animation: Voltage-Gated Channels and the Action Potential (Quiz 2)- 80%
1.
At resting membrane potential, which of the following statements about the voltage-gated sodium ion
(Na
+
) channels is TRUE?
a.
activation gates are closed and inactivation gates are open b.
activation gates are open and inactivation gates are closed c.
activation and inactivation gates are open d.
activation and inactivation gates are closed e.
activation and inactivation gates alternate between open and closed
2.
During depolarization, which of the following statements about voltage-gated ion channels is TRUE?
a.
K
+
gates open before Na
+
gates b.
Na
+
gates open before K
+
gates c.
Na
+
and K
+
gates open at the same time d.
K
+
gates open while Na
+
gates remain closed
3.
Depolarization occurs because a.
more K
+
diffuse into the cell than Na
+
diffuse out of it.
b.
more K
+
diffuse out of the cell than Na
+
diffuse into it.
c.
more Na + diffuse into the cell than K + diffuse out of it. d.
more Na
+
diffuse out of the cell than K
+
diffuse into it. e.
both Na
+
and K
+
diffuse into the cell.
4.
The sodium-potassium pump is involved in establishing the resting membrane potential.
a.
True b.
False
5.
The voltage-gated potassium channels close before the membrane potential is brought back to its resting level.
a.
True b.
False
Animation: Action Potential Propagation in an Unmyelinated Axon (Quiz 1)- 100%
1.
An action potential a.
prevents the neuron cell membrane from altering its charge. b.
causes the inside of the neuron cell membrane to become positive and the outside negative. c.
causes the inside of the neuron cell membrane to become positive and the outside neutral. d.
causes the outside of the neuron cell membrane to become positive and the inside negative. e.
causes the outside of the neuron cell membrane to become positive and the inside neutral.
2.
An action potential generates local currents that tend to ________ the membrane immediately adjacent to the action potential. a.
depolarize b.
repolarize c.
hyperpolarize d.
stabilize e.
neutralize
3.
The absolute refractory period is the period of time during which a.
a second action potential cannot be generated.
Carol Suh Period 3 b.
a second action potential is generated. c.
the action potential ceases. d.
the action potential decreases in magnitude. e.
the action potential changes direction.
4.
Action potential propagation occurs in both directions along the axon. a.
True b.
False
5.
Threshold is the minimum current required for the cell membrane to generate an action potential. a.
True b.
False
Animation: Action Potential Propagation in an Unmyelinated Axon (Quiz 2)- 100%
1.
An action potential... a.
causes the neuron cell membrane to become unable to alter its charge. b.
causes the outside of the neuron cell membrane to become positively charged in reference to the inside. c.
causes the inside of the neuron cell membrane to become positively charged in reference to the outside. d.
causes the inside of the neuron cell membrane to become negatively charged in reference to the outside. e.
causes the inside of the neuron cell membrane to become neutrally charged in reference to the outside.
2.
An action potential generates local currents that tend to _____ the membrane immediately adjacent to the action potential. a.
depolarize b.
repolarize c.
hyperpolarize d.
stabilize e.
neutralize
3.
Absolute refractory period causes... a.
action potential propagation to cease b.
action potential propagation to begin c.
action potential propagation to increase d.
action potential propagation to occur in both directions e.
action potential propagation to occur in one direction
4.
Action potentials can travel in both directions on the axon. a.
True b.
False
5.
Threshold is the minimum current required for the cell membrane to generate an action potential. a.
True b.
False