File
advertisement

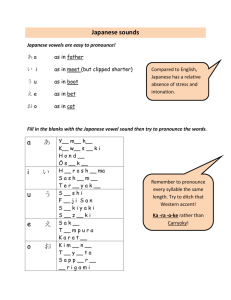
Name Date Japanese Reactions to Westernization The ________________________ Rebellion 1877 Many samurai were desperate with their situation and the loss of their former status. 60,000 __________________ troops faced 40,000 rebels, led by Takamori Saigo. It was a clash of _____________________ samurai weapons against a modern army. The samurai rebels were completely defeated in a bloody battle. Takamori Saigo was wounded and committed ________________ in samurai tradition. He became a hero for the Japanese 1. What Japanese traditions are depicted in this painting? 2. What aspects of this painting reflect western ideals? Explain. 3. How does this painting showcase the changing times of Japan? The ______________________________Company Some Samurai found new opportunities in political and business areas 1868- Iwasaki Yataro won government contracts for _____________________ lines and competed with British Created a loyal management group of former _________________ Expanded business to include shipbuilding, mining, transportation and banking _______________ families – Large firms that owned most private industry Strains of Modernization Poor living standards existed in crowded cities Political differences led to instability and assassinations of leaders Constant questioning and debate about Westernization Disgruntled ______________________________ class Need for raw materials to maintain industrial production Japanese Imperialism Joseon Dynasty: The Hermit Kingdom Considered China’s “younger brother” Looked to China for _________________________ Adopted Chinese language, civil service exams, government, and _________ policy. 1876 – Japanese______________ diplomacy forced Korea to sign the unequal Treaty of Ganghwa The Sino-Japanese War 1894-1895 Japanese troops took over Korean royal palace / fought Chinese troops in a series of land and naval battles. Total Japanese victory in 1895 – Treaty of Shimonoseki China acknowledged Korea’s full ________________________________ _________________________ in the East shifted from traditional China to modern Japan. Anti-Japanese Reaction • The Japanese assassinated Queen Min because she was reaching out to RUSSIA for help. • Japanese officials ordered Koreans to cut off ________________! The Russo-Japanese War 1904-1905 Russian expansion into Manchuria threatened Japan and Britain Russia obtained a 25-year lease on Port Arthur and permission to link __________________ Russians entered Korea despite Japanese objections. Led to Japanese attack on Russia. Japanese shocked the world and won many battles American Involvement U.S. President ______________________ helped to broker the Treaty of Portsmouth Russia had to acknowledge Japan’s superior political, military, and economic interest in Korea. Taft-Katsura Agreement: _____________agreement between U.S. and Japan (Philippines for Korea) Japanese Annexation of Korea – 1910: Japanese crushed Korean resistance killing 17,600 guerrillas “Subjugation” – The Dark Period 1910-1919 1. The Japanese took direct control of the Korean government 2. Banned all political organizations and even the right to assemble. 3. _______________________ Korean newspapers and magazines and burned over 200,000 books. 4. Police arrested intellectuals, religious leaders, and politicians - by 1912, over 50,000 arrests. March First Movement – 1919 U.S. President Woodrow Wilson’s “Doctrine of self-determination” inspired Korean Nationalists to seek Independence from Japan. 33 Nationalist Leaders gathered in a secret meeting to read their “Declaration of Independence” They were later arrested. Widespread demonstrations took place throughout Korea and sparked a nation-wide movement! The Japanese quickly crushed this Independence movement! “Cultural Accommodation” 1920-1931 1. After March First Movement, Japan needed to change their brutal image- began more “cooperative” policy toward Korea 2. Eased political, economic and social restrictions 3. Eased censorship of the press and the arts 4. Led to formation of _________________ consciousness – schools, literature, political organizations 5. Fostered a Korean Cultural Renaissance – novels, art, drama, cinema “Assimilation” 1931-1939 1. __________________________________ and increasing Chinese power led to Japan’s takeover of Manchuria in 1931. Japan mobilized Koreans to support its economic, political, and military campaigns 2. By 1934, “_________________________” focused on Japanese history, ethics and language. The Korean _______________ was eliminated from study and public use and students had to pray at Shinto Shrines. By 1939, Japan “encouraged” all Koreans to change their names to Japanese. Closing Thesis Statement: Despite astonishingly fast and successful modernization, the Meiji Restoration led Japan to aggressive and disastrous imperialist policies of the 1930s and 1940s.