live protist lab
advertisement

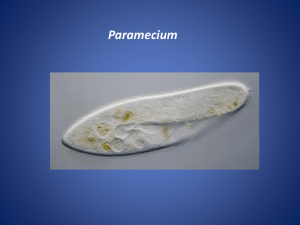
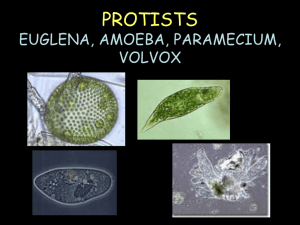
LIVE PROTIST LAB PART 1: EUGLENA A. Place a drop of Euglena culture on the depression slide B. Using proper microscope procedure, locate the Euglena under low power (4x objective lens) C. Once located, rotate the nosepiece to medium power (10x) and watch the Euglena move slowly through the field of view. D. In the field of view on your answer sheet, draw your Euglena at medium power and label the following parts (you may use your book as a reference page 74) Pellicle, flagellum, nucleus, chloroplasts ON THE LINE BELOW THE FIELD OF VIEW, WRITE THE NAME OF THE ORGANISM YOU ARE LOOKING AT, AS WELL AS THE TOTAL MAGNIFICATION. E. Answer the following questions on your answer sheet PART 1. 1. Euglena is a microscopic, single-celled a. animal b. plant c. protist d. worm 2. Euglena contain ________________ in order to produce food. a. chloroplasts b. cilia c. pseudopods 3. What is the purpose of the eyespot Answer TRUE or FALSE 4. A euglena culture should be kept in a dark place. 5. Euglena without chlorophyll could still make food. Part 2 AMOEBA A. Place a drop of amoeba culture on a depression slide. B. Using the proper microscope procedure, find an amoeba using low power (4x). Look for a gray-like blob that moves slowly across your field of view. C. Change to medium power (10x) for a more detailed view. D. In the field of view on your answer sheet draw your amoeba and label the following parts: (use your book as a reference page 64) Cell membrane, nucleus, and a pseudopod ON THE LINE BELOW THE FIELD OF VIEW, WRITE THE NAME OF THE ORGANISM YOU ARE LOOKING AT, AS WELL AS THE TOTAL MAGNIFICATION. E. After carefully observing your amoeba for several minutes, answer the following questions on your answer sheet PART 2. 6. Does it move? a. yes b. no 7. How does the movement take place? a. swims b. by cilia c. by flagella d. by pseudopod 8. The amoeba obtain food by a. pouncing on it b. attracting it with an odor c. engulfing it 9. The function of the contractile vacuole is to 1. 2. 3. 4. regulate water contents to the cell prevent the cell membrane from collapsing digest food take in food 10. Amoeba are difficult to see because ______________________________. PART 3 PARAMECIUM A. Place a drop of protoslo in the depression on the slide. B. Place a drop of paramecium culture on the depression slide. C. Using proper microscope procedure, locate the paramecium under low power (4x) – the paramecium move very fast D. Once located, change to the medium objective lens (10x), and watch the paramecium move slowly through the field of view E. In the field of view on your answer sheet, draw your paramecium. You may use your book as a reference to draw the paramecium. F. Label the following parts Use your book to help page 66: pellicle, cilia, nucleus ON THE LINE BELOW THE FIELD OF VIEW, WRITE THE NAME OF THE ORGANISM YOU ARE LOOKING AT, AS WELL AS THE TOTAL MAGNIFICATION. G. Answer the following questions on your answer sheet PART 3. (use your book and notes) 11. How does the paramecium move? a. swims b. cilia c. flagella d. pseudopods 12. Does it move faster or slower than the amoeba? a. faster b. slower c. about the same rate 13. What is the purpose of “protoslo”? Write True or False to the following questions: (use your book and notes) 14. Paramecium have large numbers of flagella. 15. Paramecium can be considered to have a permanent shape. 16. Cilia cover the entire surface of the paramecium. 17. Food vacuoles are found in the cytoplasm of the paramecium. 18. Paramecium has a “permanent” mouth opening. 19. A paramecium’s contractile vacuole is used to capture food. 20. Paramecium makes its own food by photosynthesis. 21. Paramecium has more than one nucleus. 22. Cilia brush food particles into a paramecium’s mouth opening. 23. Paramecium obtain food like an animal, rather than like a green plant.