Key Concept - dpsscience
advertisement
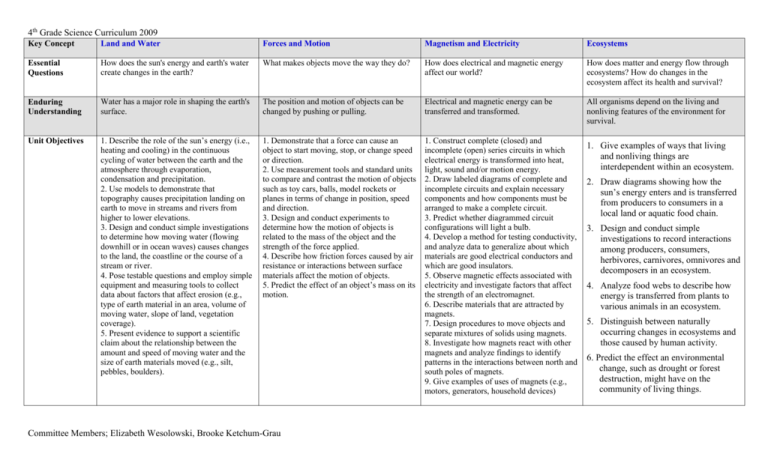
4th Grade Science Curriculum 2009 Key Concept Land and Water Forces and Motion Magnetism and Electricity Ecosystems Essential Questions How does the sun's energy and earth's water create changes in the earth? What makes objects move the way they do? How does electrical and magnetic energy affect our world? How does matter and energy flow through ecosystems? How do changes in the ecosystem affect its health and survival? Enduring Understanding Water has a major role in shaping the earth's surface. The position and motion of objects can be changed by pushing or pulling. Electrical and magnetic energy can be transferred and transformed. All organisms depend on the living and nonliving features of the environment for survival. Unit Objectives 1. Describe the role of the sun’s energy (i.e., heating and cooling) in the continuous cycling of water between the earth and the atmosphere through evaporation, condensation and precipitation. 2. Use models to demonstrate that topography causes precipitation landing on earth to move in streams and rivers from higher to lower elevations. 3. Design and conduct simple investigations to determine how moving water (flowing downhill or in ocean waves) causes changes to the land, the coastline or the course of a stream or river. 4. Pose testable questions and employ simple equipment and measuring tools to collect data about factors that affect erosion (e.g., type of earth material in an area, volume of moving water, slope of land, vegetation coverage). 5. Present evidence to support a scientific claim about the relationship between the amount and speed of moving water and the size of earth materials moved (e.g., silt, pebbles, boulders). 1. Demonstrate that a force can cause an object to start moving, stop, or change speed or direction. 2. Use measurement tools and standard units to compare and contrast the motion of objects such as toy cars, balls, model rockets or planes in terms of change in position, speed and direction. 3. Design and conduct experiments to determine how the motion of objects is related to the mass of the object and the strength of the force applied. 4. Describe how friction forces caused by air resistance or interactions between surface materials affect the motion of objects. 5. Predict the effect of an object’s mass on its motion. 1. Construct complete (closed) and incomplete (open) series circuits in which electrical energy is transformed into heat, light, sound and/or motion energy. 2. Draw labeled diagrams of complete and incomplete circuits and explain necessary components and how components must be arranged to make a complete circuit. 3. Predict whether diagrammed circuit configurations will light a bulb. 4. Develop a method for testing conductivity, and analyze data to generalize about which materials are good electrical conductors and which are good insulators. 5. Observe magnetic effects associated with electricity and investigate factors that affect the strength of an electromagnet. 6. Describe materials that are attracted by magnets. 7. Design procedures to move objects and separate mixtures of solids using magnets. 8. Investigate how magnets react with other magnets and analyze findings to identify patterns in the interactions between north and south poles of magnets. 9. Give examples of uses of magnets (e.g., motors, generators, household devices) Committee Members; Elizabeth Wesolowski, Brooke Ketchum-Grau 1. Give examples of ways that living and nonliving things are interdependent within an ecosystem. 2. Draw diagrams showing how the sun’s energy enters and is transferred from producers to consumers in a local land or aquatic food chain. 3. Design and conduct simple investigations to record interactions among producers, consumers, herbivores, carnivores, omnivores and decomposers in an ecosystem. 4. Analyze food webs to describe how energy is transferred from plants to various animals in an ecosystem. 5. Distinguish between naturally occurring changes in ecosystems and those caused by human activity. 6. Predict the effect an environmental change, such as drought or forest destruction, might have on the community of living things. 4th Grade Science Curriculum 2009 *** at the end of each lesson, discuss the relationship between the lesson and the enduring understanding*** STC Land and Water Unit Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 Lesson 6 Lesson 7 Lesson 8 Lesson 11 Lesson 13 Lesson 14 *** at the end of each lesson, discuss the relationship between the lesson and the enduring understanding*** STC Force and Motion Lesson 1 & 2 taught together Lesson 3 Lesson 4 Lesson 5 Lesson 6 Lesson 7 Lesson 8 Lesson 9 Lesson 10 Lesson 14 *** at the end of each lesson, discuss the relationship between the lesson and the enduring understanding*** Delta Magnetism and Electricity Lessons; Investigation 1: Parts 1-3 (3-4 class sessions) Investigation 2: Parts 1-4 (4 class sessions) Investigation 3: Parts 1-3 (4-5 class sessions) Investigation 4: Parts 1-3 (4 - 5 sessions) Follow WebQuest found on http://knaughton.wordpress.com/4th-gradescience-lessons/ Two class periods: 1st - Choosing individual investigation question and planning the investigation. 2nd - Completing the investigation and drawing conclusions. Teacher uses rubric to score. ***Students should reflect back to their Journal questions for guidance*** Found within Lesson 14: Performance Assessment CMT Embedded Task http://knaughton.wordpress.com/4th-gradescience-lessons/ Found within WebQuest: Visual Project of the Food Web and Letter Writing Unit Vocabulary water cycle, evaporate, condense, precipitation, erosion, valley, floodplain, delta motion, force, speed, gravity, friction, mass, inertia, energy electric current, energy source, battery, contact, complete (closed) circuit, incomplete (open) circuit, conductor, insulator, user, path, generator ecosystem, organism, abtiotic factors, nutrient, producer, consumer, herbivore, carnivore, omnivore, decomposer, food chain, food web Supplemental Resources The Magic School Bus: Wet All Over, A Book About the Water Cycle by Scholastic A Drop of Water by Walter Wick Forces and Motion by Sally Hewitt, Forces and Motion: From Push to Shove by Christopher Cooper, A Crash Course in Forces and Motion with Max Axiom, Super Scientist by Emily Sohn, Extreme Zone: Force and Motion by Paul Mason What is Electricity? By Lisa Trumbauer, Where Does Electricity Come From? By C. Vance Cast Amazing Magnetism (Magic School Bus) by Rebecca Carmi and John Speirs What Makes a Magnet? By Franklyn M. Branley Switch On, Switch Off by Melvin Berger Food Chain Frenzy (Magic School Bus) By Anne Capeci Living Sunlight: How Plants Bring the Earth to Life by Penny Chisholm Who Eats What? Food Chains and Food Websby Patricia Lauber One Day in the Woods by Jean Craighead George Desert is Theirs by Byrd Baylor Gets Eaten: A Book About Food Chains by Assured Experiences Performance Assessments See Food Chains/Web Webquest See Go with the Flow Committee Members; Elizabeth Wesolowski, Brooke Ketchum-Grau 4th Grade Science Curriculum 2009 Scholastic Technology Resources www.brainpop.com United Streaming Video: The Sun, Water Cycles and Climate from the Series"Water Smart"(includes teacher's guide and video quiz), United Streaming Viideo: River Flight (2 parts) http://www.physics4kids.com/files/motion_f orce.html http://www.idahoptv.org/dialogue4kids/seaso n9/forcesmotion/facts.cfm http://www.learningscience.org/psc2bmotion forces.htm http://pbskids.org/fetch/games/dishitout/inde x.html http://pbskids.org/zoom/activities/sci/#forces energy http://www.phun.com Committee Members; Elizabeth Wesolowski, Brooke Ketchum-Grau http://www.pge.com/microsite/pge_dgz/wires /game.html, http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/scienceclips/ag es/8_9/science_8_9.shtml http://www.quia.com/rr/35935.html http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/podsmission/el ectricity/annie02.shtml http://www.engineeringinteract.org/resources /siliconspies.htm http://pbskids.org/eekoworld/index.html?load =environment http://www.mbgnet.net/ (Look for “What’s it like where you live?”) http://www.earthmatters4kids.org/main.html http://www.epa.gov/owow/estuaries/kids/