PHYSICS: First Semester BCcampus Open CCCS Overview
advertisement

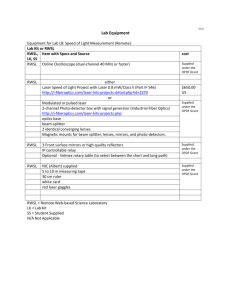
PHYSICS: First Semester BCcampus Open CCCS Overview: Introduction to Physics I and II are first year algebra-based courses. They are designed for those students that have a relatively weak background in physics. PHY 100 includes vectors, and scalars, kinematics, dynamics, energy, momentum, rotational motion, thermodynamics, fluids and wave motion. Laboratory work illustrates theoretical concepts and develops laboratory skills and techniques. Overview: This course enables the student to explore the truth about physical reality through reasoning, mathematics and experimentation. Examines kinematics, force, circular motion, energy, momentum, torque, rotational dynamics, simple harmonic motion, temperature, heat and thermodynamics. The concepts and theories presented are explored through demonstrations and handson experiments. It is a general physics course that is recommended for all of the health sciences and all other interested students. Text: Cutnell, J. (2010). Physics, 8th Edition. Wiley. Text: Serway, R. and J. Faughn (2003). College Physics, 7th edition. Scarborough, ON: Nelson Education. Topics: Introduction Vectors Kinematics Dynamics Work and Energy, Momentum Statics Rotational Motion Heat and thermodynamics Fluids Vibrations and Waves Sound Learning Outcomes: The student will understand the fundamental laws of mechanics and be able to apply the theory to solve related problems. Topics: A. Mechanics A. Units and Measurements B. Motion - One - and Two- Dimensional C. Newton`s Laws and Gravitation D. Static and Dynamic Equilibrium E. Circular Motion and Rotational Dynamics F. Work and Energy G. Impulse and Momentum H. Fluids and Solids I. Simple Harmonic Motion J. Sound and Vibration B. Heat A. Temperature and Expansion B. Heat Transfer C. First and Second Laws of Thermodynamics Learning Outcomes: Define each of the related vocabulary words. Recognize appropriate symbols used. State the concepts introduced. Distinguish between different concepts within a topic. Translate mathematical formulae into charts, tables, or graphs. Interpret graphs or tables. Collect and organize data in a systematic manner. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Measurements and experimental errors (Lab Kit) One dimensional motion (RWSL) Resolving forces (Lab Kit) Conservation of energy (RWSL) Conservation of momentum (RWSL) Torque and rotational equilibrium (Lab Kit) The simple pendulum (Lab Kit) Oscilloscope speed of sound (RWSL) LABS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. Present data by construction of charts and graphs. Evaluate the relevancy of data. Write a formal report. Set up and solve problems using geometry, algebra, and trigonometry as required. Demonstrate prescribed problem-solving methods. Read, analyze and apply concepts to new situations. Demonstrate the ability to select and apply contemporary forms of technology to solve problems or compile information in the study of physics. Experimental Errors and Uncertainty Measurement Trigonometric Measurements Data Collection Acceleration Friction Simple machine: lever Simple Machine - Pulleys Pendulum and the Calculation of g Centripetal Acceleration Hooke's Law Determining the Speed of Sound Specific Heat Capacity of Metals PHYSICS: Second Semester BCcampus Open CCCS Overview : This is the second of the Introduction to Physics courses. PHY 101 deals with geometrical and wave optics, Coulomb’s Law, electric fields, electric energy and potential, capacitance, current resistance, magnetism, inductance, LC oscillations, transformers, AC circuits, modern physics, nuclear physics, and radioactivity. Laboratory work is used to reinforce theoretical concepts and develop laboratory skills and concepts. Overview : This course is the second in a two-semester introduction to algebrabased physics. It expands upon PHY 111 and covers electric fields, electric circuits, magnetic fields, optics, and modern physics. It explores the concepts and theories presented in class through demonstrations and hands-on experiments. Mathematical techniques used in the course include algebra, geometry, and trigonometry, but not calculus. The material in this course will be oriented around fundamental concepts and principles, which are especially powerful for successfully explaining nature's behavior. Text: Cutnell, J. (2010). Physics, 8th Edition. Wiley. Text: Serway, R. and J. Faughn (2003). College Physics, 7th edition. Scarborough, ON: Nelson Education. Topics Electricity Magnetism Light Optics Relativity Quantum physics Learning Outcomes The student will understand the fundamental laws of mechanics and be able to apply the theory to solve related problems. Topics I. Electric Fields II. Magnetic Fields III. Optics and Light IV. Special Relativity & Particles V. Nuclear Physics Learning Outcomes Define each of the related vocabulary words. Recognize appropriate symbols used. State the concepts introduced. Distinguish between different concepts within a topic. Translate descriptive material to mathematical formulae. Translate mathematical formulae into charts, tables, or graphs. Interpret graphs or tables. Collect and organize data in a systematic manner. Present data by construction of charts and graphs. Evaluate the relevancy of data. Write a formal report. Set up and solve problems using geometry, algebra, and trigonometry as required. Demonstrate prescribed problem solving methods. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Wave Optics (RWSL) Convex Lenses (RWSL) Basic Electrical Circuitry (Lab Kit) Kirchhoff's Rules (Lab Kit) Capacitance (Lab Kit) Electron EM Ratio (RWSL) Magnetic Forces (RWSL) Atomic Spectra (RWSL) LABS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Read, analyze and apply concepts to new situations. Demonstrate the ability to select and apply contemporary forms of technology to solve problems or compile information. Static Electricity Electric Fields Intro to Electric Circuits Resistors in Series & Parallel Circuits Semiconductor Temperature Sensor Capacitance Electric Motor Reflection & Refraction Diffraction Grating Polarized Light Radioactive Decay