End of Chapter Solutions Template
advertisement

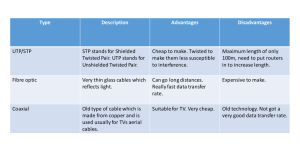
Lab Manual for CWNA Guide to Wireless LANs, Second Edition Lab Manual Solutions 1-1 Chapter 1 Solutions Activity Questions, Lab 1-1 1. Wireless network that provides Internet connection and virtual private network access from a given location. Answer: Hot spot 2. Telecommunications industry specification that describes how mobile phones, computers, and personal digital assistants (PDAs) can be easily networked using a short-range (about 30 feet) connection. Answer: Bluetooth 3. The act of locating and possibly exploiting connections to wireless networks while driving around. Answer: War driving 4. Converts radio-frequency fields (RF) into alternating current (AC) or vice versa. Answer: Antenna 5. Local area network in which a user can connect through a radio connection. Answer: WLAN 6. Formed when at least two devices, such as a portable PC and a cellular phone, connect using Bluetooth technology. Answer: Piconet 7. Refers to the transmission of modulated visible or infrared (IR) beams through the atmosphere to obtain broadband communications. Answer: FSO 8. Specification for a set of protocols that standardize the way that wireless devices, such as cellular telephones and radio transceivers, are used for Internet access. Answer: WAP 9. Incorporates the use of radio frequency to uniquely identify an object, animal, or person. Answer: RFID 10. A wireless computer data network that may extend over a large geographical area. Answer: WWAN 11. A language that allows the text portions of Web pages to be displayed on cell phones and PDAs wirelessly. Answer: WML 12. Wireless industry coalition whose members organized to advance the IEEE 802.16 standard, which will enable wireless networks to transmit up to 30 miles. Answer: WiMAX 13. A wireless network for interconnecting devices centered around an individual person’s workspace. Answer: WPAN 14. Software built into a wireless device that allows users to access and display specially formatted Internet content using a handset device. Answer: Microbrowser 15. A station that transmits and receives data and connects wireless users to the wired network. Answer: Access point 16. Term for certain types of wireless LANs that use specifications in the 802.11 family. Answer: Wi-Fi 17. A card that is inserted into a device to connect it to a wireless network. Answer: Wireless adapter Lab Manual for CWNA Guide to Wireless LANs, Second Edition Lab Manual Solutions 1-2 18. A WWAN technology used by cell phones and other handheld devices. Answer: GSM Review Questions, Lab 1-1 1. What is the fundamental difference between a WLAN, WPAN, and WWAN? Answer: The physical scope of the network 2. What is the difference between a regular Web browser and a microbrowser? Answer: A Web browser is used on computers and laptops; a microbrowser has been modified to work on handheld devices and is a lightweight version of a Web browser. 3. What is the difference between HTML and WML? Answer: WML is a lightweight version of HTML. 4. What is the difference between Wi-Fi and WiMAX? Answer: Wi-Fi is for WLANs; WiMAX is for WWANs. 5. What are the advantages and disadvantages to using a hot spot? Answer: The disadvantage is that it is not secure; the advantage is that it offers free, easy access to the Internet. Activity Questions, Lab 1-2 Advantage Interference Installation Wired or Wireless Wired has advantage Wireless Security Mobility Disaster recovery Reliability Health risks Wired Wireless Wireless Wireless Wired, maybe Explain As long as you don’t put UTP up against power sources, you should avoid interference. You don’t have to pull cable, except to form the switch to the access point. Wireless is unguided, so it is easier to tap into. It is not tethered by wires. You can set up a hot site more quickly. Many problems are cable-related. There is no concrete evidence against wireless yet, but there is some indication that long-term exposure could be risky. Review Questions, Lab 1-2 1. Interference is not a concern with wired networks. True or False? Answer: False 2. The primary advantage of wireless systems is mobility. True or False? Answer: True 3. Explain the difference between a hot site and a cold site. Answer: The hot site is ready to go. The cold site is just a facility—you need all the network infrastructure. 4. Why are wireless networks inherently less secure than wired networks? Answer: The transmission is unguided. 5. In your opinion, is wireless better than wired for regular desktop computing when mobility is not a factor? Why or why not? Answer: Opinion varies. Activity Questions, Lab 1-3 2. What are some of the latest Bluetooth devices? Lab Manual for CWNA Guide to Wireless LANs, Second Edition Lab Manual Solutions 1-3 Answer: Palm T-5 PDA, Nokia N-Gage gaming device, Sony Ericsson headset, Apple keyboard and mouse, Motorola RAZR phone/digital camera/mpeg 4. How is 802.15 related to Bluetooth? Answer: 802.15 is based on Bluetooth. 6. What is “Wi-Fi” short for? Answer: Wireless fidelity 7. To which IEEE standard did Wi-Fi originally apply? Answer: 802.11b What IEEE standards does Wi-Fi apply to now? Answer: 802.11b/a/g standard 8. What are Bluetooth devices designed to do? Answer: Replace cables between cell phones, notebooks, PDAs, printers, etc. What are Wi-Fi devices designed to do? Answer: Replace cables between computers, laptops, printers, etc., and an access point 9. What is the range of Bluetooth devices versus the range of Wi-Fi devices? Answer: Bluetooth’s range is 30 feet; 802.11’s range is 100 to 500 feet. 10. Bluetooth devices interfere with some Wi-Fi devices. Why is this true? Answer: Both are in the range of 2.4 GHz Review Questions, Lab 1-3 1. What is the IEEE standard for Bluetooth? Answer: 802.15 2. What is the IEEE standard for Wi-Fi? Answer: 802.11 3. In what way are Bluetooth and Wi-Fi competing standards? Answer: Both provide local area wireless connectivity. 4. In what way are Bluetooth and Wi-Fi not competing standards? Answer: Bluetooth is WPAN technology, and 802.11 is WLAN technology. 5. How do you feel about the prospects of Bluetooth? Why? Answer: Opinion varies.