Teaching - CST Home
advertisement

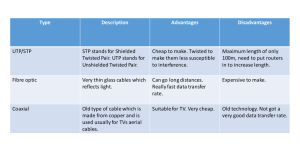
CWNA Guide to Wireless LANs, Second Edition Chapter 1 It’s a Wireless World At a Glance Instructor’s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives Teaching Tips Quick Quizzes Class Discussion Topics Additional Projects Additional Resources Key Terms 1-1 CWNA Guide to Wireless LANs, Second Edition 1-2 Lecture Notes Overview In this chapter, the students will first explore how wireless is used in everyday life, and then take a peek at some popular wireless technologies. They will see how different sectors of the economy are using wireless technology, and learn about its advantages and disadvantages. Chapter Objectives Describe how wireless technology is used in daily activities Tell how wireless local area networks are used in applications such as education, business, travel, construction, and other areas Explain the advantages and disadvantages of wireless technology Teaching Tips A Day in the Life of a Wireless User 1. Provide an overview of the ways in which wireless technology has embedded itself in everyday life. Define the term hotspot. Home 1. Provide an overview of WLANs. Explain how they can increase productivity by allowing users to connect to a network from a variety of locations without wires. Mention some example of devices that can be interfaced via wireless networks. Car 1. Provide an overview of Bluetooth technology, and explain how it is use in small devices over short distances. Teaching Tip Over 2,000 different computer, telephone, and peripheral vendors have agreed to create products based on the Bluetooth standard. Office 1. Discuss the concept of fixed broadband wireless. Explain that it is used to transmit data wireless between immobile entities, such as office buildings. Briefly mention the infrastructure, such as antennas, involved in fixed broadband wireless. 2. Introduce the concept of free space optics. CWNA Guide to Wireless LANs, Second Edition 1-3 Teaching Tip Atmospheric effects such as scintillation (the "waves of heat" pattern you sometimes see over dark surfaces) can have an affect on free space optics transmissions. Teaching Tip With FSO, transmissions fade rapidly in certain kinds of weather—fog, in particular. Field 1. Discuss how handheld devices can be used to communicate wirelessly. Explain that these devices typically connect to the nearest cell tower, which then connect to the local telephone company. On Site 1. Describe the purpose and use of RFID tags. Explain the differences between RFID tags and traditional barcodes. A Look at Wireless Technologies 1. Provide a brief introduction to wireless technologies. Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) 1. Discuss the characteristics of Wi-Fi. Explain that there are many wireless standards, each with different characteristics. 2. Discuss the purpose and functionality of wireless NICS. Illustrate with Figure 1-1. If possible, pass a wireless NIC around to the students. 3. Discuss the purpose and functionality of an Access Point. Illustrate with Figure 1-2. If possible, pass an access point around to the students. 4. Explain that a patch cable connects an AP to a wired LAN or to the Internet. Discuss how the interface between a wireless and wired LAN allows wireless users to access entities on the wired LAN, such as printers. Illustrate with Figure 1-3. 5. Illustrate a home wireless LAN with Figure 1-4. Bluetooth 1. Provide an overview of Bluetooth technology. Explain the purpose of a radio module and a link manager. 2. Mention the transmission capabilities of the Bluetooth standard. Illustrate a Bluetooth device with Figure 1-5. If possible, pass a Bluetooth device around to the students, and demonstrate a Bluetooth connection. CWNA Guide to Wireless LANs, Second Edition 1-4 3. Explain that when two Bluetooth devices come within range of each other, they automatically make a connection. Discuss the role of the master and slave(s) in this connection. Define the term piconet. Teaching Tip Bluetooth is named after the 10th-century Danish King Harald Bluetooth, who was responsible for unifying Scandinavia. Teaching Tip Bluetooth support is integrated into Microsoft Windows XP Service Pack 2 (SP2). Telecommunications Links 1. Discuss some of the telecommunication methods in use today. characteristics of ISDN and T-1 transmission methods. Explain the 2. Briefly discuss DSL and Cable transmission. 3. Describe the transmission capabilities of WiMax and FOS. Explain that these are lineof-site transmission methods. Discuss the configurations necessary to utilize these transmission methods, emphasizing the differences between WiMax and FOS. Illustrate with Figure 1-7. Cellular Telephony 1. Discuss the characteristics of Global Systems for Mobile (GSM) communications technology. Stress that information transmitted over GSM may be based on the Wireless Application Protocol (WAP). Explain that WAP provides a standard way to transmit, format, and display Internet data for devices like cell phones and handheld devices. 2. Using Figure 1-8 to illustrate, discuss the communication mechanism between computers and servers when browsing the Internet. Teaching Tip Make sure that the students understand that when a Web server sends a Web page back to a PC, it is only sending HTML code; the Web browser is responsible for interpreting that code and displaying the results on the screen. 3. Explain that a WAP cell phone runs a microbrowser that uses Wireless Markup Language (WML) instead of HTML. Mention that a WAP gateway is used to translate HTML to WML. Illustrate the WAP model with Figure 1-9. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) 1. Describe the difference between RFID tags and standard barcodes in detail. 2. Discuss the transmission characteristics of RFID. 3. Describe the physical characteristics of an RFID tag. Use Figure 1-10 to illustrate. CWNA Guide to Wireless LANs, Second Edition 1-5 Teaching Tip No RFID Tag can read through metal. Teaching Tip Different RFID tags operate at different frequency ranges. These frequency ranges are often used for different applications. Wireless Technology Categories 1. Using Table 1-1 as a guide, discuss each of the various wireless technology categories. Mention that WLANs will be the focus of this text. Quick Quiz 1 1. ____________________ wireless refers to wireless transmissions between devices that cannot be mobile. Answer: Fixed broadband 2. ____________________ is an alternative to high-speed fiber optic transmissions. Answer: Free space optics (FSO) 3. True or False: It is not necessary to connect an AP to a wired LAN or to the Internet. Answer: False 4. A Bluetooth device uses a(n) ____________________, which is special software that helps identify other Bluetooth devices, creates the links between the devices, and sends and receives data. Answer: link manager 5. ____________________ provides a standard way to transmit, format, and display Internet data for devices like cell phones and handheld devices. Answer: Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) Wireless LAN Applications 1. Explain that wireless LAN applications can be found in every industry with employees who need the freedom to conduct business without being confined to a specific location. Education 1. Explain that wireless LANs are an ideal technology for colleges and schools. Discuss why educational institutions were some of the first organizations to adopt WLANs on a wide-scale basis. 2. Use Figure 1-11 to illustrate a typical campus map that identifies wireless access points. CWNA Guide to Wireless LANs, Second Edition Teaching Tip 1-6 Some, if not most, of the students may not understand how difficult it was to gain internet access at educational institutions prior to the adoption of wireless technology. Try to convey to them what it was like to have to wait for computer access in the computer lab, and sit in a computer lab for hours on end. Explain that most dorms at most universities did not even have hard-wired internet access until the mid-1990s. 3. Stress the ways that wireless technology has reduced the cost of computer at universities, such as reduced need for wiring and infrastructure. Business 1. Explain some of the ways that wireless technology has changed how business is conducted. Stress that the ability to access data to make decisions whenever and wherever the need arises is critical, and wireless technology facilities easier and quicker access to data. 2. Explain why and how wireless technologies allow businesses to create an office in a space where the traditional infrastructure doesn’t exist. Teaching Tip Because WLANs are becoming so widespread, computer giant IBM and cell phone vendor Nokia are teaming up to make it easier for a company’s employees to move from a WLAN hotspot to an area of GSM coverage transparently while remaining connected to the network. Travel 1. Explain that the travel industry has perhaps adopted wireless technologies more than any other sector of the economy. Mention the wireless capabilities that have been installed in most airports and on some airlines. 2. Mention that wireless technology goes beyond serving just the passenger. Explain the ways that airlines incorporate wireless technology into the everyday tasks inherent to that industry, such as maintenance. 3. Mention that some airlines are using wireless data transmission to send messages to and receive message from aircraft in flight. Construction 1. Discuss the reasons why the construction industry has benefited greatly from wireless technology, such as ability to quickly reschedule and quick filing of paper work. 2. Explain how wireless technology has been used to create “smart” construction equipment. Specifically discuss the use of GPS on construction equipment. Warehouse Management 1. Discuss the importance of proper inventory and knowing the location of items within a warehouse. CWNA Guide to Wireless LANs, Second Edition 1-7 2. Explain how a WMS coordinates warehouse management activities, and explain how wireless technology can be used in conjunction with a WMS. 3. Discuss the use of RFID tags on inventory or palettes of inventory. Explain how this can alleviate or solve many warehouse management issues, and mention how the WMS manages and coordinates warehouse activities using the RFID tags. Public Safety 1. Explain how WLAN and GSM technologies are being used in public safety facilities and equipment. Mention that APs can be installed on municipal building, and can be used to download large volumes to information to properly equipped public safety vehicles. Health Care 1. Provide an overview of the administrative tasks in a medical setting that can be made easier via wireless technology. Specifically mention the administration of medication. 2. Explain that wireless LAN point-of-care computer systems allow medical staff to access and update patient records immediately. Discuss the medical administration processes that can be assisted by wireless technology. 3. Stress that wireless healthcare systems can immediately verify that medication is being administered to the correct patient in the correct dosage, which eliminates potential errors and documentation inefficiencies. Mention that the documentation process now takes place at the bedside where care is delivered, improving accuracy. Also mention that all hospital personnel now have real-time access to the latest medication and patient status information. 4. Explain that wireless technology is also used in other medical areas. example of a video pill. Illustrate with Figure 1-12. Present the Wireless Advantages and Disadvantages 1. Explain that with any technology, there are advantages and disadvantages to be considered, and WLANs are no exception. Advantages 1. Provide a brief overview of the advantages of wireless LANS. Mobility 1. Explain that the primary advantage of wireless technology is mobility. Mention that many occupations that require workers to be mobile. 2. Explain that an increasingly mobile workforce is one characteristic of today’s business world. Discuss how WLANs fit into this business environment, stressing that with a wireless network, workers can access information from almost anywhere. 3. Discuss the concept of “flat” organizations. Explain that wireless networks give teambased workers the ability to access the network resources that they need while collaborating in a team environment. CWNA Guide to Wireless LANs, Second Edition 1-8 Easier and Less Expensive Installation 1. Explain that installing network cabling in older buildings can be difficult and costly. Discuss the hurdles that might be encountered while trying to outfit a building with a wired network infrastructure. 2. Stress that the elimination of the need for cabling can substantially reduce the cost of installing and maintaining a network. Mention how wireless LANs can also reduce the time cost of installing a network. 3. Mention that wireless networks provide flexibility in terms of setting up and organizing an office space. Increased Reliability 1. Discuss the reasons why cable failure may occur, and explain how a wireless LAN can reduce the likelihood that cable failure would adversely affect a network. Stress that this increases overall network reliability. Disaster Recovery 1. Explain that a documented disaster recovery plan is vital to every business if it is to get back on its feet quickly after a calamity. Define the term hot site, and explain how a hot site is used in the event of a disaster. 2. Define the term cold site, and discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using a cold site rather than a hot site. Explain that using a WLAN at a cold site means that very little cabling is required to get the cold site running. Teaching Tip Typically, a business has an annual contract with a company that offers hot site services with a monthly service charge. Some services also offer data backup so that all company data is available regardless of whether a hot site or cold site is used. Disadvantages 1. Provide a brief overview of the disadvantages of wireless LANS. Security 1. Explain that wireless signals are broadcast over open air, making security a major issue. 2. Using the list on pages 20 and 21 of the text as a guide, discuss the unique challenges inherent to wireless security. Define the terms war driving and rouge access point. Teaching Tip Wireless security will be covered in detail in Chapters 8 and 9. CWNA Guide to Wireless LANs, Second Edition 1-9 Radio Signal Interference 1. Explain that signals from other devices can disrupt wireless transmissions, or the wireless device may itself be the source of interference for other devices. Discuss the types of devices that might cause radio signal interference. 2. Explain that the only solution is to this issue is to locate the source of interference and remove it, or move the wireless access point to a position where the interference will not occur. Health Risks 1. Explain that wireless devices emit a low level of RF radiation, as do cell phones. Mention that high levels of RF radiation are know to cause biological damage, but it is not know if low level can cause damage as well. Teaching Tip Most wireless devices also emit very low levels of RF energy even when in stand-by mode. However, these levels are considered non-significant and do not appear to have health consequences. Teaching Tip Questions have been raised about the safety of hand-held mobile phones with a built-in antenna positioned close to the user’s head when speaking on the phone. In mobile devices, the antenna is the primary source of RF. The safety of cordless phones, which have a base unit connected to the telephone wiring in a house and which operate at far lower power levels and frequencies, has not been questioned. Quick Quiz 2 1. ____________________ institutions were some of the first adopters of WLANs. Answer: Educational 2. True or False: Wireless technologies also allow businesses to create an office in a space where the traditional infrastructure doesn’t exist. Answer: True 3. True or False: The use of wireless technology in a medical setting is limited to medical administration. Answer: False 4. A(n) ____________________ is generally run by a commercial disaster recovery service that allows a business to continue computer and network operations to maintain business continuity. Answer: hot site CWNA Guide to Wireless LANs, Second Edition 1-10 5. An employee who purchases an access point and secretly brings it into the office in order to provide personal wireless access has installed what is known as a(n) ____________________. Answer: rogue access point Class Discussion Topics 1. Do any of the students have a wireless LAN installed in their homes? Did they install it themselves? How did they choose the equipment necessary to install it? 2. Can the students think of any other major industries, other than the ones mentioned in this chapter, that would benefit from wireless technology? Additional Projects 1. Beyond the two Wi-Fi hot spot locating tools explored in Projects 1-1 and 1-2, many other Web sites offer this service. Have the students research online and locate two or three other such Web sites. Have them perform the same search on the Web site that they find, Wi-Fi.org, and Yahoo maps. Does one service provide better results than the others? When the students have completed this assignment, compile their results into a master list that can be redistributed to the class. 2. Have the students research online to find the typical cost of wireless equipments, such as wireless NICS and wireless access points. Then, have them research the cost of regular NICS. How do the per unit costs compare? If wireless equipment is more expensive, ask the students whether they think this cost is offset by the reduced cost of cabling. Additional Resources 1. Wifi411: Online Wi-Fi Hot Spot Locator: http://www.wifi411.com/ 2. WLAN links: http://wi-fiplanet.webopedia.com/TERM/W/WLAN.html 3. Official Bluetooth Web Site: http://www.bluetooth.com/ 4. FSO White Papers: http://www.freespaceoptic.com/White_Papers.htm 5. Free Space Optics Primer: http://www.baselinemag.com/article2/0,1397,1778374,00.asp 6. The Wi-Fi Alliance Home Page: http://www.wi-fi.org/OpenSection/index.asp 7. WiMAX Forum: http://www.wimaxforum.org/home 8. Introduction to Cellular and GSM Communications: http://www.gsmfavorites.com/introduction/ 9. WAP Resource Center: http://www.palowireless.com/wap/ CWNA Guide to Wireless LANs, Second Edition 1-11 10. Wireless Markup Language Tutorial: http://www.computerworld.com/news/2000/story/0,11280,42991,00.html 11. RFID Frequencies Tutorial: http://www.rfidinc.com/tutorial.html 12. Planes and Trains: Wireless on the Move: http://www.techworld.com/mobility/features/index.cfm?featureid=512&Page=2&pageP os=2 13. WLANs Spreading to Hospitals: http://www.wi-fiplanet.com/news/article.php/1581811 Key Terms Access point (AP): A wireless device that acts as a base station to receive signals from and transmit signals to wireless network interface cards in other wireless devices. Bluetooth: A low-power wireless data and voice transmission technology. Cable modem: A telecommunications technology that sends data over television cable. Cold site: A remote site that provides only office space in the event of a disaster. Digital subscriber lines (DSL): A telecommunication technology that uses telephone lines. Fixed broadband wireless: A wireless wide area network technology for transmissions between buildings. Free space optics (FSO): A fixed broadband wireless technology that uses lowpowered infrared beams and transmits at speeds up to 1.25 Gbps over a distance of up to 6.4 kilometers (4 miles). An alternative to high-speed fiber optic transmissions. Gbps: Billions of bits (gigabits) per second. Global Systems for Mobile (GSM) communications: A wireless wide area network technology used by cellular telephones and handheld devices. Hot site: A remote site that contains redundant equipment, supplies, and telecommunications infrastructure for a business, and is ready immediately in the event of a disaster. Hotspot: Location where wireless data service is available. Integrated Services Digital Networks (ISDN): A wide area network technology that transmits at 256 Kbps. Kbps: Thousands of bits (kilobits) per second. Link manager: Bluetooth software that helps identify other Bluetooth devices, creates the links with them, and sends and receives data. Master: A Bluetooth device that controls wireless traffic. Mbps: Millions of bits (megabits) per second. Microbrowser: A small browser program that runs on a cellular telephone or a handheld device. Piconet: A Bluetooth network that contains one master and at least one slave. Radio frequency identification (RFID): Small tags that function like electronic barcodes. Radio module: Bluetooth radio transceiver built onto a microprocessor chip. Rogue access point: A WLAN access point installed without permission. Slave: A Bluetooth device that takes commands from the master device. T-1: A wide area network technology that transmits at 1.544 Mbps. WAP gateway: A device that translates between WML and HTML. CWNA Guide to Wireless LANs, Second Edition 1-12 WAP proxy: Same as WAP gateway. War driving: Driving around with a wireless device searching for a wireless signal. Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity): Another name for a wireless local area network. WiMax: A fixed broadband wireless technology that sends and receives signals between antennas over longer distances. Wireless adapter: Another name for a wireless network interface card (NIC). Wireless Application Protocol (WAP): A standard way to transmit, format, and display Internet data for devices like cell phones or handheld devices. Wireless local area network (WLAN): A local area network (LAN) in which the devices are not connected by wires. Wireless Markup Language (WML): A programming language designed to display text-based Web content on the small screen of a cell phone or handheld device. Wireless network interface card (wireless NIC): A card that is inserted into a device that enables it to communicate on a wireless network. Wireless personal area network (WPAN): Wireless technologies that have a limited transmission range of up to 3.3 meters (10 feet). Wireless wide area network (WWAN): Wireless technologies that have a transmission range from 152 meters (500 feet) to 120 kilometers (75 miles) or more.