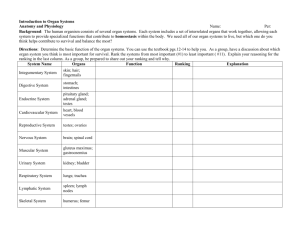
1 - 32
advertisement

1. Decreased blood supply to the organs causes hypoxia that activates fibroblasts function. Volume of what elements is increased in this case? A. Intercellular substance B. Lymphatic vessels C. Nerve elements D. Parenchymatous elements of the organ E. Vessels of microcircular stream 2. The increased intraocular tension is observed in the patient with glaucoma. Secretion of aqueous humor by the ciliar body is normal. Injury of what structure of the eyeball wall caused the disorder of flow-out from the anterior chamber? A. Venous sinus B. Ciliary muscle C. Ciliar body D. Posterior epithelium of cornea E. Choroid 3. The ventral roots of 5 frontal segment of spinal cord were cut during experiment in the animal. What changes will take place in the innervation region? A. Loss of movements B. Loss of proprioceptive sensitivity C. Loss of touch sensitivity D. Hypersensitivity E. Loss of temperature sensitivity 4. In the blood of a 26-year-old man it was revealed 18% of erythrocytes of the spherical ball-shaped, flat and horn-like shape. Other erythrocytes were in the form of the bi concave disks. How is such phenomenon called? A. Physiological poikilocytosis B. Pathological poikilocytosis C. Physiological anisocytosis D. Pathological anisocytosis E. Erythrocytosis 5. Lung of premature infant is presented on electronic photomicrography of biopsy material. Collapse of the alveolar wall caused by the deficiency of surfactant was revealed. Disfunction of what cells of the alveolar wall caused it? A. Alveocytes type II B. Alveolar macrophages C. Alveocytes type I D. Secretory cells E. Fibroblasts 6. Patient with injured muscles of the lower extremities was admittted to the traumatological department. Due to what cells is reparative regeneration of the muscle fibers and restoration of the muscle function possible? A. Satellite-cells B. Fibroblasts C. Myoblasts D. Myofibroblasts E. Myoepithelial cells 7. Moving of the daughter cromatids to the poles of the cell is observed in the mitotically dividing cell. On what stage of the mitotic cycle is this cell? A. Anaphase B. Telophase C. Prophase D. Interfase E. Metaphase 8. The cell of the laboratory animal was overdosed with Roentgen rays. As a result albuminous fragments formed in the cytoplasm. What cell organoid will take part at their utilization? A. Lysosomes B. Golgi complex C. Ribosome D. Emdoplasmic reticulum E. Cells centre 9. The specimens present sections of haemopoetic and immunogenetic organs. Organ has lymph tissue forming different structures (lobules, cortex and medulla, concentrically, arranged epithelioreticular cells). In what organ does antigen-independent proliferation and differantiation take place? A. Thymus B. Lymphatic nodes C. Hemolymph nodes D. Spleen E. Tonsil 10. A 2-year-old child experienced convulsions because of lowering calcium ions concentration in the blood plasma. Function of what structure is decreased? A. Parathyroid glands B. Hypophysis C. Pineal gland D. Thymus E. Adrenal Cortex 11. Middle part of cochlea of internal ear was destroyed in animal during the experiment. It will cause abnormalities of the sound perception of the following frequencies: A. Middle B. High C. No abnormalities D. Low E. High and low 12. Low level of albumins and fibrinogen was detected in the patient’s blood. Decreased activity of what organelle of the liver hepatocytes can cause it? A. Granular endoplasmatic reticulum B. Mitochondrions C. Agranular endoplasmatic reticulum D. Lysosomes E. Golgi complex 13. In the microspecimen of red bone marrow there were revealed multiple capillares through the walls of which mature blood cells penetrated. What type of capillares is it? A. Sinusoidal B. Somatic C. Fenestrated D. Visceral E. Lymphatic 14. During histological examination of the stomach it was found out that glands contain very small amount of parietal cells or they are totally absent. Mucose membrane of what part of the stomach was studied? A. Pyloric part B. Body of stomach C. – D. Cardiac part E. Fundus of stomach 15. In the ovary specimen colored with hematoxylin-eosin, follicle is determined where cuboidal follicular epithelial cells are placed in 1-2 layers, and pink covering (zona pellucida) is seen around ovocyte. Name this follicle: A. Primary B. Atretic C. Secondary D. Mature E. Primordial 16. The microscopic examination of wound lavage of a patient with acute woundy process of his skin revealed big contents of irregular extended-formed cells, with big nucleus, the basophilic cytoplasm of which includes many lysosomes, phagosomes and pinocytotic vesicles. What cells are found out in the wound? A. Connective tissue macrophages B. Fibroblasts C. Plasmocytes D. Fibrocytes E. Tissue basophils 17. After the radiactive exposure a patient has stem cells disorder. The regeneration of what cells of friable (loose) connective tissue will be damaged? A. Macrophages B. Fibroblasts C. Pericytes D. Adipocytes E. Pigment cells 18. A 39-year-old patient after radiotherapy because of hepatoma developed ulcer of small intestine. It was caused by the inhibition of mytotic activity of the cells, which are responsible for regeneration of small intestine surface epithelium. Inhibition of what cells mitotic activity does this patient have? A. Crypt columnar cells without brush border B. Caliciform exocrynocytes C. Endocrine cells D. Exocrynocytes with acidophilic granules E. Columnar cells 19. The auscultation of a patient with dry pleuritis has revealed plueral friction rub. What epithelium type can cause such signs? A. Simple flat (squamous) epithelium (mesothelium) B. Transitional epithelium C. Simple prismatic epithelium D. Laminated epithelium E. Simple cuboidal epithelium 20. The study of mitotic cycle phases of onion root revealed the cell, in which the chromosomes are situated in the equatorial plane, forming a monaster. What stage of the cell mitosis is it? A. Metaphase B. Telophase C. Anaphase D. Prophase E. Interphase 21. In the blood smear, stained according to Romanovsky-Giemsa method, there are 20% big (20 mcm in diameter), rounded cells with pale-basophilic cytoplasm and bean-shaped nucleus. How is this condition characterised clinically? A. Monocytosis B. Neutrophilosis C. Leukopenia D. Reticulocytosis E. Lymphocytosis 22. Because of present gallstone in the common bile duct, a patient has no bile excretion into duodenum. What disorder can it cause? A. Lipids digestion B. Proteins absorption C. Proteins digestion D. Carbohydrates digestion E. Carbohydrates absorption 23. During the postsynthetic period of mitotic cycle the synthesis of proteins – tubulines, which take part in the mitotic spindle formation, was destroyed. It can cause the impairment of: A. Chromosome separation B. Duration of mitosis C. Chromosome despiralization D. Chromosome spiralization E. Cytokinesis 24. A tissue sample of benign tumor was studied under the electron microscope. A lot of small (15-20 nm) spherical bodies, consisting of 2 unequal subunits were detected. These are: A. Ribosomes B. Mitochondria C. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum D. Microtubules E. Golgi complex 25. Oval and round organelles with double wall are seen at the electron micrograph. The outer membrane is smooth, the inner membrane folded into cristae contain enzyme ATPase synthetase. These are: A. Mitochondria B. Lysosomes C. Ribosomes D. Golgi complex E. Centrioles 26. After breathing with poisonous steams there is an increased quantity of slime (mucous) in respiratory passages of a chemical production worker. What of respiratory tract epithelial cells participate in mucosa moistening? A. Goblet cells B. Langergans cells C. Intercalated cells D. Fibroblasts E. Endocrine cells 27. The reason of occurrence of some diseases of an oral cavity is connected with structural peculiarities of its mucous membrane. What morphological attributes characterize these features? A. No muscularis mucosa, stratified squamous epithelium B. Simple columnar ciliated epithelium C. Transitional epithelium, no submucosa D. Transitional epithelium, no muscularis mucosa E. Well developed muscularis, no submucosa 28. There is the change of teeth at the 6-8-year-old children: deciduous are replaced by permanent. What embrionic tissues are the sources of formation of permanent teeth tissues? A. Ectodermal epithelium of a tooth plate and mesenhyme B. Mesodermal epithelium and mesenhyme C. Entodermal epithelium of a tooth plate and mesenhyme D. I, II brachial arches E. Entodermal epithelium and mesoderm 29. A 30-year-old woman was diagnosed with insufficiency of exocrine function of pancreas. Hydrolisis of what nutrients will be disturbed? A. Proteins, fats, carbohydrates B. Fats, carbohydrates C. Proteins, carbohydrates D. Proteins, fats E. Proteins 30. In the specimen of one of the parts of respiratory system a tubular organ was found. It has low epithelium, well developed muscular tunic, glands and cartilage are absent. Name this organ: A. Minor bronchus B. Median bronchus C. Major bronchus D. Trachea E. Larynx 31. Microspecimen of spinal cord contains a nucleus that should be analyzed. Its neurons form motor endings in the skeletal muscles. What nucleus of spinal cord is meant? A. Proper nucleus of the anterior horn B. Proper nucleus of the posterior horn C. Intermediate lateral nucleus D. Proper nucleus of gray substance E. Thoracic nucleus 32. During pubescence the cells of male sexual glands begin to produce male sex hormone testosterone that calls forth secondary sexual characteristics. What cells of male sexual glands produce this hormone? A. Leidig cells B. Sertoli’s cells C. Sustentocytes D. Spermatozoa E. Supporting cells 33. Labeled aminoacids alanine and tryptophane were introducted to a mouse in order to study localization of protein biosynthesis in its cells. Around what organelles will the accumulation of labeled aminoacids be observed? A. Ribosomes B. Golgi apparatus C. Agranular endoplasmic reticulum D. Cells center E. Lysosomes 34. Histological examination of a 40 y.o. man’s thymus revealed decreased part of parenchymatous gland elements, increased part of adipose and loose connective tissue, its enrichment with thymus bodies. The organ’s mass was unchanged. What phenomenon is it? A. Age involution B. Accidental involution C. Atrophy D. Dystrophy E. Hypotrophy 35. In course of indirect histogenesis of tubular bone tissue a plate is formed between epiphyseal and diaphyseal ossificcation centres that provides further lengthwise growth of bones. What structure is it? A. Metaphyseal plate B. Osseous plate C. Osteon D. Osseous cuff E. Layer of interior general plates 36. Vitamin A deficit results in the impairment of twilight vision. Name the cells that have the afore-mentioned photoreceptor function: A. Rod receptor cell B. Ganglion neurocytes C. Cone receptor cell D. Horizontal neurocytes E. Bipolar neurons 37. In course of an experiment a big number of stem cells of red bone marrow was in some way destructed. Regeneration of which cell populations in the loose connective tissue will be inhibited? A. Macrophages B. Fibroblast C. Pericytes D. Pigment cell E. Lipocytes 38. Examination of a 43 y.o. patient revealed that his stomach has difficulties with digestion of protein food. Gastric juice analysis revealed low acidity. Function of which gastric cells is disturbed in this case? A. Parietal exocrinocytes B. Main exocrinocytes C. Mucous cells D. Endocrine cells E. Cervical mucocytes 39. A 60 y.o. patient has a reduced perception of high-frequency sounds. what structures’ disorder of auditory analyzer caused these changes? A. Basilar membrane of cochlea near the oval window B. Basilar membrane of cochlea near helicotrema C. Muscules of middle ear D. Eustachian tube E. Tympanic membrane 40. In course of practical training students studied a stained blood smear of a mouse with bacteria phagocytozed by leukocytes. What cell organella completes digestion of these bacteria? A. Lisosomes B. Mytochondrions C. Ribosomes D. Golgi apparatus E. Granular endoplasmic reticulum 41. A teenager was irradiated with high radiation dose that resulted in serious damages of lymphoid system, lysis of many lymphocytes. Restoration of normal hemogram is possible due to the functioning of the following glands: A. Thymus B. Thyroid C. Adrenal D. Liver E. Pancreas 42. According to audiometry data a patient has a disturbed perception of mediumfrequency sounds. It might have been caused by a damage of: A. Middle part of cochlea B. Cochlear nuclei C. Quadritubercular structure D. Lateral geniculate bodies E. Spiral ganglion 43. An electron micrograph of a kidney fragment presents an afferent arteriole. Under its endothelium some big cells can be seen that contain secretory granules. What type of cells is it? A. Juxtaglomerular B. Smooth muscle cells C. Interstitial D. Juxtavascular E. Mesangeal 44. Histological specimen presents vessel the wall of which consists of endothelium, basal membrane and loose connective tissue. What type of vessel is it? A. Vein of non-muscular type B. Hemocapillary C. Lymphocapillary D. Vein of muscular type E. Artery 45. Ultramicroscopical examination of “dark” hepatocyte population in the cell cytoplasm detected a developed granular endoplasmic reticulum. What function has this organelle in these cells? A. Synthesis of blood plasma proteins B. Bile production C. Deintoxicative function D. Calcium ion depositing E. Carbohydrate synthesis 46. A histological specimen of spleen shows a vessel with a wall consisting of endothelium and subendothelial layer, median membrane is absent, external membrane inosculates with the layers of spleen connective tissue. What vessel is it? A. Vein of non-muscular type B. Artery of muscular type C. Capillary D. Vein of muscular type E. Arteriole 47. Life cycle of a cell includes the process of DNA autoreduplication. As a result of it monochromatid chromosomes turn into bichromatid ones. What period of cell cycle does this phenomenon fall into? A. S B. G2 C. G0 D. G1 E. M 48. A pathological process in bronchi resulted in epithelium desquamation. What cells will regenerate bronchial epithelium? A. Basal B. Intercalated C. Ciliated D. Goblet E. Endocrine 49. In embryo displays the process of dorsal mesoderm segmentation and somite formation is disturbed. What part of skin will have developmental abnormalities? A. Dermis B. Epidermis C. Sudoriferous glands D. Sebaceous glands E. Hair 50. In course of a conditional experiment the development of mesenchymal cells was completely inhibited. Development of the following muscular tissue will be disturbed: A. Smooth muscular tissue B. Cardiac muscular tissue C. Skeletal muscular tissue D. Neural muscular tissue E. Epidermal muscular tissue 51. Golgi complex exports substances from a cell due to the fusion of the membrane saccule with the cell membrane. The saccule contents flows out. What process is it? A. Exocytosis B. Facilitated diffusion C. Endocytosis D. Active-transport E. All answers arc false 52. During studying maximally spiralized chromosomes of human karyotype, the process of cell division was stopped in the following phase: A. Metaphase B. Telophase C. Interphase D. Anaphase E. Prophase 53. A sensitive neural ganglion consists of rounded neuron with one extension that divides into axon and dendrite at some distance from the perikaryon. What are these cells called? A. Pseudounipolar B. Multipolar C. Unipolar D. Apolar E. Bipolar 54. An endocrine gland with parenchyma consisting of epithelium and neural tissue is under morphological examination. Epithelial trabecules have two types of cells: chromophilic and chromophobic. Identify this organ: A. Hypophysis B. Hypothalamus C. Adrenal glands D. Thyroid gland E. Parathyroid gland 55. A patient ill with chronic gastritis went for endogastric pH-metry that allowed to reveal decreased acidity of gastric juice. It is indicative of diminished function of the following cells: A. Parietal exocrinocytes B. Accessory cells C. Endocrinocytes D. Cervical cells E. Chief exocrinocytes 56. A microspecimen of the submandibular salivary gland shows some basket-shaped cells concentrated around the acinis and excretory ducts. These cells surround bases of the serous cells and are called myoepi- theliocytes. These cells relate to the following tissue: A. Muscular tissue B. Special connective tissue C. Epithelial tissue D. Loose fibrous connective tissue E. Neural tissue 57. A histological specimen presents a receptor zone of a sensoepithelial sense organ. Cells of this zone are placed upon the basilar membrane and include the following types: external and internal receptor cells, external and internal phalangeal cell, stem cells, external limiting cells and external supporting cell. The described receptor zone belongs to the following sense organ: A. Acoustic organ B. Visual organ C. Gustatory organ D. Equilibrium organ E. Olfactory organ 58. Following exposure to radiation a lot of mutant cells appeared in a patient. Some time later most of them were detected and destroyed by the following cells of the immune system: A. T-lymphocytes-killers B. S-lymphocyte C. T-lymphocytes-supressors D. Plasmoblasts E. Stem cells 59. A 35-year-old patient complains about having severe rhinitis and loss of sense of smell for a week. Objectively: the nasal cavity contains a lot of mucus covering the mucous membrane and blocking olfactory receptors. In what region of the nasal cavity are these receptors located? A. Superior nasal concha B. Median nasal concha C. Common nasal meatus D. Vestibule of nose E. Inferior nasal concha 60. In a histological specimen parenchyma of an organ is represented by lymphoid tissue that forms lymph nodes; the latter are arranged in a diffuse manner and enclose a central artery. What anatomic formation has such morphological structure? A. Spleen B. Thymus C. Tonsil D. Lymph node E. Red bone marrow 61. A 32-year-old patient consulted by doctor about the absence of lactation after parturition. Such disorder might be explained by the deficit of the following hormone: A. Prolactin B. Vasopressin C. Glucagon D. Thyrocalcitonin E. Somatotropin 62. Examination of a patient admitted to the surgical department with symptoms of acute appendicitis revealed the following changes in the white blood cells: the total count of leukocytes is 16 • 109/l. Leukocyte formula: basophils - 0, eosinophils - 2%, juvenile young - 2%, band - 8%, segmented - 59%, lymphocytes - 25%, monocytes- 4%. The described changes can be classified as: A. Neutrophilia with regenerative left shift B. Neutrophilic leukemoid reaction C. Neutrophilia with hyperregenerative left shift D. Neutrophilia with degenerative left shift E. Neutrophilia with right shift 63. A patient was admitted to the hospital with an asphyxia attack provoked by a spasm of smooth muscles of the respiratory tracts. This attack was mainly caused by alterations in the following parts of the airways: A. Small bronchi B. Terminal bronchioles C. Respiratory part D. Large bronchi E. Median bronchi 64. An electronic microphotograph shows a macrophagic cell with erythrocytes at different stages of differentiation located along its processes. This is the cell of the following organ: A. Red bone marrow B. Spleen C. Tonsil D. Lymph node E. Thymus 65. A histological specimen shows a blood vessel. Its inner coat is composed by endothelium, subendothelium and internal elastic membrane. The middle coat is enriched with smooth myocytes. Such morphological characteristics are typical for the following vessel: A. Muscular-type artery B. Capillary C. Non-muscular vein D. Elastic-type artery E. Muscular-type vein 66. A histological specimen of a kidney shows a part of the distal tubule going between the afferent and efferent arteriole. The cells building the tubule wall have dense nuclei; basal membrane is absent. Such structural formation is called: A. Macula densa B. Juxtavascular cells C. D. Mesangial cells E. Juxtaglomerular cells 67. While examining the oral cavity a stomatologist revealed inflammation of papillae on the border of the median and posterior third of the back of tongue. What papillae are inflamed? A. Papillae vallatae B. Papillae filiforme C. Papillae conicae D. Papillae fungiforme E. Papillae foliatae 68. A middle-aged man went to a foreign country because he had been offered a job there. However he had been unemployed for quite a long time. What endocrine glands were exhausted most of all in this man? A. Adrenal glands B. Substernal gland C. Thyroid gland D. Seminal glands E. Parathyroid glands 69. The life cycle includes a process of self-doubling cell DNA. As a result, the monochromatic chromosomes become bichromatic. In what period of the cell cycle observed this phenomenon? A. S B. Go C. M D. G1 E. G2 70. On histological preparations represented lymphoid tissue, which forms the lymph nodules and contain a central artery. What anatomical formation is given in the morphological structure? A. Spleen B. Red bone marrow C. Thymus D. Lymph node E. Amygdala 71. The preparation of tubular structure colored with orsein, shows about 50 thick membranes, which have a wavy shape and form the basis of the tunica structure. What is the structure? A. Aorta B. The wall of the heart C. Esophagus D. Trachea E. Artery of muscular type 72. The preparation shows the hollow structure. The mucous membrane is covered with double-row ciliated epithelium, which goes into single row. Muscular layer is well developed in relation to the thickness of the entire wall. Cartilage and glands absent. Which body is represented in the slide? A. Middle bronchus B. Trachea C. Larynx D. Small airways E. Bladder 73. During exercise on a deck a gymnast lost balance and fell. Excitement of which receptors help to restore impaired posture? A. Otolith vestibuloreceptors B. Vestibuloreceptors C. Proprioceptors D. Ampullary vestibuloreceptors E. Receptors of the cochlea 74. The endocrine function of the follicular cells of the ovarian follicles was impared due to inflammation. Synthesis of which hormones will be depsessed? A. Estrogens B. Progesterone C. Luteotropin D. Follistatin E. Follicle-stimulating hormone 75. Histological slide of the kidney cortex represents the tubules lined with a single layer of cuboidal epithelium, the cytoplasm is stained oxyphilic. Which segment of the nephron is found in the slide? A. The proximal convoluted tubule B. Distal straight tubule C. Collecting ducts D. Loop of Henle E. Distal convoluted tubule 76. In electron micrographs spindle-shaped cells with rod-shaped nuclei are represented. In the cytoplasm there is a large number of intermediate microfilaments containing desmin. Which type of tissue is represented? A. Muscle B. Epithelial C. Connective D. Mesenchymal E. Nervous 77. Unlucky student suddenly met with the dean. The concentration of which hormone increases most rapidly in the blood of the student? A. Adrenaline B. Somatotropin C. Tireoliberin D. Cortisol E. Corticotropin 78. Malapsorption of proteins occurs in the patient with acute inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis). Due to the lack of synthesis and release of which enzyme this condition occuss? A. Trypsin B. Pepsin C. Lipase D. Amylase E. Dipeptidase 79. Blood count of an athlete is as follows: erythrocytes - 5,5*1012/l, Hb- 180 g/l, leukocytes – 7*109/l, neutrophils - 64%, basophils - 0,5%, eosinophils - 0,5%, monocytes - 8%, lymphocytes - 27%. First of all, such results indicate the stimulation of: A. Erythropoiesis B. Leukopoiesis C. Lymphopoiesis D. Immunogenesis E. Granulocytopoiesis 80. A sensory neural ganglion consists of roundish neurocytes with one extension that divides into axon and dendrite at a some distance from the perikaryon. What are these cells called? A. Pseudounipolar B. Multipolar C. Bipolar D. Unipolar E. Apolar 81. In course of a conditional experiment the development of mesenchyme cells was completely inhibited. Development of the following muscular tissue will be disturbed: A. Smooth muscular tissue B. Epidermal muscular tissue C. Cardiac muscular tissue D. Neural muscular tissue E. Skeletal muscular tissue 82. An electron microphotography of a fragment of proper gastric gland shows a big irregular round-shaped cell. There are a lot of intracellular tubules and mitochondria in the cytoplasm. Specify this cell: A. Parietal cell B. Mucous cell C. Endocrine cell D. Undifferentiated cell E. Principal cell 83. On an electron micrograph a scientist has identified a structure formed by eight histone proteins and a part of DNA molecule which makes about 1,75 coils around the molecules. Which structure has been identified? A. Nucleosoma B. Chromosome C. Elemetary fibril D. Half-chromatid E. Chromatid 84. A patient has been given high doses of hydrocortisone for a long time. This caused atrophy of one of the adrenal cortex zones. Which zone is it? A. Fascicular B. Reticular C. Glomerular and reticular D. Glomerular E. 85. Electronic microphotography of pulmonary alveole's wall presents a big cell. Its cytoplasm has a lot of mitochondria, developed Golgi apparatus, osmiophilie lamellated corpuscles. What is the main function of this cell? A. It produces surfactant B. It warms the air C. It is a component of blood-air barrier D. It absorbs microorganisms E. It purifies the air 86. The boy two years old suffers from respiratory diseases, stomatitis, skin lesions. Even minor damages of the gums and mucosa are complicated by long flowing inflammation. Found that immunoglobulins of all classes are almost absent in child's blood. Decrease of the functional activity of which cell population is the basis of this syndrome? A. B-lymphocytes B. Neutrophils C. NK – cells D. Macrophages E. T -lymphocytes 87. When autoradiographic study of the small intestine epithelium was performed, it was found that complete regeneration occurs for 3 days of active proliferation of undifferentiated cells. Specify their location: A. The bottom of the crypts B. The top of the villi C. The base of the villi D. Lamina propria of the mucosa E. The lateral surface of the villi 88. A child of 6 years old is in a hospital with a diagnosis of allergic rhinitis. In the blood: changes in the leukocyte formula. Number of which leukocytic cells can be increased? A. Eosinophils B. Neutrophils C. B- lymphocytes D. Basophils E. T- lymphocytes 89. On the slide of the pia mater vessel was found in the wall of which middle muscular layer is absent, the tunica externa is grow with the surrounding tissues, the tunica intima consists of a basement membrane and endothelium. What is this vessel? A. Unmuscular vien B. Artery of muscular type C. Artery of mixed type D. Vien of a muscular type with the weak development of muscular elements E. Arteriole 90. On the electronic image an organelle is visible that is a big poliproteaze complex consisting of tubular and two regulatory units located at both ends of the organelle. The organelle function is proteolysis. Name this organelle: A. Proteasome B. Golgi complex C. Inclusion D. Centriole E. Ribosome 91. Inflammation is characterized by the dilation of blood vessels at the site of injury, reduced blood flow, increased permeability of blood vessels. Which of the following cells play the major role in this? A. Tissue basophils B. Macrophages C. Plasma cells D. Eosinophils E. Fibroblasts 92. Patient with complaints of the appearance of acne on the face consulted by the cosmetician. An examination showed that the appearance of the acne is associated with the violation of secretion of the sebaceous glands. What type of secretion is characteristic for these glands? A. Holocrine B. Makroapocrine C. Merocrine and mikroapocrine D. Mikroapocrine E. Merocrine 93. The patient with complaints of on the pain in the eyes turned to oftalmologist. Erozion of the cornea - the absence of the superficial layer and spinosum of the epithelium was found. What cells are responsible for the regeneration of the damaged epithelium? A. Basal B. Cells of the granular layer C. Cells of the lucidium layer D. The cells of the stratum corneum E. The cells of the superficial 94. Experimental study of a new medicine founds a blocking effect on the assembly of protein tubulin, which is the basis of mitotic spindle in dividing cells. What stage of the cell cycle is disturbed with this drug? A. Anaphase of mitosis B. Synthetic period C. Telophase of mitosis D. Premitotic period of the interphase E. postmitotic period of the interphase 95. Nephrons, which lie on the border between the cortex and medulla, have the same diameter of afferent and efferent arterioles, are clearly visible on the slide of kidneys. What function would be disturbed if they are damaged? A. Shunting of the blood, when circulation is intensive B. Synthesis of the renin C. The activity of the sodium receptor D. Synthesis of the erythropoietin E. The synthesis of the prostaglandins 96. A 22-year-old female student was consulted by a physician about fever up to 38C, weakness, sore throat. Objectively: there is white coating of the tongue. What histological structures of the tongue are involved in the formation of the coating? A. Epithellium of the filiform papillae B. Epithellium of the foliate papillae C. Epithellium of the fungiform papillae D. Epithellium of the circumvallate papillae E. Connective-tissue base of all the lingual papillae 97. A microslide contains the preparation of a gland composed of several secretory saccule-shaped parts that open in the common excretory duct. What gland is it? A. Simple branched alveolar gland B. Compound branched alveolar gland C. Simple unbranched alveolar gland D. Compound unbranched alveolargland E. Simple branched tubular gland 98. In the course of an experiment adenohypophysis of an animal has been removed. The resulting atrophy of thyroid gland and adrenal cortex has been caused by deficiency of the following hormone: A. Tropic hormones B. Thyroid hormones C. Somatotropin D. Cortisol E. Thyroxin 99. As a result of an injury, the integrity of the anterior spinal cord root was broken. Specify the neurons and their processes that had been damaged: A. Axons of motor neurons B. Motor neuron dendrites C. Axons of sensory neurons D. Dendrites of sensory neurons E. Dendrites of association neurons 100. An electron micrograph shows a cell-to-cell adhesion consisting, in each cell, of an attachment plaque. The intercellular space is filled with electron-dense substance including transmembrane fibrillar structures. Specify this adhesion: A. Desmosome B. Synapse C. Tight junction D. Nexus E. Adherens junction 101. During the hystological study of cortical sheath, basophilic cells with developed synthesis organelles can be seen on the bone surface under the layer of fibers. These cells take part in bone tissue regeneration. What shaft layer are they located in? A. Periosteum B. Bone C. Osteon layer D. Outer lamellae of compact bone tissue E. Inner lamellae of compact bone tissue 102. There are cortical and medullary substances separated by connective tissue layer in the endocrine gland specimen. Parenchyma cells make up three zones in cortical substance, with rounded masses in the superficial zone, parallel chords in the middle one, reticular structure of cell chords in the deep one. What gland is it? A. Adrenal gland B. Thyroid gland C. Pituitary gland D. Epiphysis E. Hypothalamus 103. Histological specimen of a 10-day human embryo represents 2 contacting sacs (amniotic and yolk sacs). Specify the structure that separates the amniotic cavity from the yolk sac: A. Embryonic disk B. Amniotic stalk C. Floor of the amniotic sac D. Roof of the yolk sac E. Extraembryonic mesoderm 104. An electron micrograph shows a cell of neural origin. The terminal portion of the cell dendrite has cylindrical shape and consists of 1000 closed membrane disks. What cell is represented by the micrograph? A. Rod receptor cell B. Cone receptor cell C. Spinal node neuron D. Neuron of the cerebral cortex E. Neuron of the anterior horns of the spinal cord 105. A histologic specimen represents an organ with walls comprised of mucous, submucous, fibrouscartilaginous and adventitial membranes. Epithelium is multirowed and ciliated, muscular layer of mucous membrane is absent, submucous membrane contains serous-mucous glands, hyaline cartilage forms open circles. What organ has the described morphological features? A. Trachea B. Tertiary bronchi (segmental bronchi) C. Secondary bronchi (lobar bronchi) D. Terminal bronchiole E. Larynx 106. Study of the biopsy material of an embryo revealed a zone of developmental abnormality in a somite. The zone was located close to the endoderm and the notochord. What formations may have abnormal development in case of pregnancy continuation? A. Skeletal tissues B. Genito-urinary system C. Skeletal striated muscle tissue D. Cardiac striated muscle tissue E. Fibrous connective tissue of skin 107. A histological specimen of the eyeball shows a biconvex structure connected to the ciliary body by the fibers of the Zinn’s zonule and covered with a transparent capsule. Name this structure: A. Crystalline lens B. Vitreous body C. Ciliary body D. Cornea E. Sclera 108. A specimen shows an organ covered with the connective tissue capsule with trabeculae radiating inward the organ. There is also cortex containing some lymph nodules, and medullary cords made of lymphoid cells. What organ is under study? A. Lymph node B. Thymus C. Spleen D. Red bone marrow E. Tonsils 109. The cellular composition of exudate largely depends on the etiological factor of inflammation. What leukocytes are the first to get into the focus of inflammation caused by pyogenic bacteria? A. Neutrophil granulocytes B. Monocytes C. Myelocytes D. Eosinophilic granulocytes E. Basophils 110. Alveolar space of the acinus was invaded by some bacteria which interacted with the surfactant. This led to the activation of the cells that are localized in the alveolar walls and on the surface. What cells are these? A. Alveolar macrophages B. Alveolocytes type I C. Endothelial cells D. Clara cells E. Alveolocytes type II 111. A specimen of a parenchymal organ shows poorly delineated hexagonal lobules surrounding a central vein, and the interlobular connective tissue contains embedded triads (an artery, a vein and an excretory duct). What organ is it? A. Liver B. Pancreas C. Thymus D. Spleen E. Thyroid 112. Due to the use of poor-quality measles vaccine for preventive vaccination, a 1-year-old child developed an autoimmune renal injury. The urine was found to contain macromolecular proteins. What process of urine formation was disturbed? A. Filtration B. Reabsorption C. Secretion D. Reabsorption and secretion E. Secretion and filtration 113. A male working as a blacksmith has been tested for auditory acuity. The tests revealed 50% hearing loss in the low-frequency range and a near-normal auditory acuity in the high-frequency range. This condition has been caused by the damage to the following structures of the auditory system: A. Corti’s organ - closer to helicotrema B. Corti’s organ - closer to the oval foramen C. Median part of the Corti’s organ D. Muscles of the middle ear E. Eardrum 114. As a result of a mechanical injury an over 10 cm long portion of a peripheral nerve was damaged. This led to the impairment of the upper limb activity. The patient was offered nerve transplantation. What glial cells will participate in regeneration and provide the trophism of the injured limb? A. Schwann cells B. Fibrous cells C. Protoplasmic cells D. Microglia E. Ependymal cells 115. A specimen of an onion rootlet includes a cell in which the fully condensed chromosomes are located in the equatorial plane making the monaster. What phase of the mitotic cycle is the cell in? A. Metaphase B. Early telophase C. Prophase D. Interphase E. Late telophase 116. Human skin has a high breaking strength. It is known that the skin consists of epithelial tissue and two kinds of connective tissue. Which of the following tissues provides the skin strength? A. Unformed dense connective tissue B. Stratified squamous epithelium C. Loose connective tissue D. Single-layer epithelium E. Transitional epithelium 117. A 3-year-old child had eaten some strawberries. Soon he developed a rash and itching. What was found in the child’s leukogram? A. Eosinophilia B. C. D. E. Hypolymphemia Neutrophilic leukocytosis Monocytosis Lymphocytosis 118. Histologic slide of a kidney demonstrates the cells closely adjoined to the renal corpuscle in the distal convoluted tubule. Their basement membrane is extremely thin and has no folds. These cells sense the changes in sodium content of urine and promote renin secretion by juxtaglomerular cells. Name these cells: A. Macula densa cells B. Juxtaglomerular cells C. Mesangial cells D. Podocytes E. Glomerular capillary endothelial cells 119. During postembryonal haemopoiesis in red bone marrow the cells of one of the cellular differons demonstrate gradual decrease in cytoplasmic basophilia as well as increase in oxyphilia, the nucleus is being forced out. Such morphological changes are typical for the following haemopoiesis type: A. Erythropoiesis B. Lymphopoiesis C. Neutrophil cytopoiesis D. Eosinophil cytopoiesis E. Basophil cytopoiesis 120. A microspecimen of a heart shows rectangular cells from 50 to 120 micrometers large with central position of a nucleus and developed myofibrils. The cells are connected by intercalated discs. These cells are responsible for the following function: A. Function of heart contractions B. Function of impulse conduction C. Endocrine D. Protective E. Regeneratory 121. Atretic bodies and developed yellow body can be observed along with follicles at different developmental stages in an ovary slide. What stage of ovarian and menstrual cycle is characterized by the described ovary condition? A. Premenstrual B. Menstrual C. Postmenstrual D. Regeneration E. Follicle growth 122. A 12-year-old patient has white nonpigmented spots on the skin. The spots appeared when the patient has reached the age 10, and they constantly growing. This spots appeared due to the lack of the following skin cells:A. Melanocytes B. Adipocytes C. Fibrocytes D. Plasmocytes E. Labrocytes 123. Work in a mine to causes inhalation of large amounts of coal dust. Inhaled coal dust can be detected in thefollowing pulmonary cells: A. Alveolar macrophages B. Respiratory epithelial cells C. Secretory epithelial cells D. Capillary endothelial cells E. Pericapillary cells 124. Cells of healthy liver actively synthesize glycogen and proteins. What organelles are the most developed in this cells? A. Granular and agranular endoplasmic reticulum B. Cell center C. Lysosomes D. Mitochondria E. Peroxisomes 125. Alveolar space of acinus was invaded by bacteria that interacted with the surfactant. It leds to the activation of the cells that are localized in the alveolar walls and on the surface. Name these cells: A. Alveolar macrophages B. Alveolocytes type I C. Endothelial cells D. Clara cells E. Alveolocytes type II 126. A doctor examined a patient, studied the blood tests, and reached a conclusion, that peripheral immunogenesis organs are affected. What of the following organs had been affected? A. Tonsils B. Thymus C. Kidneys D. Red bone marrow E. Yellow bone marrow 127. On the slide of a parenchymal organ we can see: poorly delineated hexagonal lobulessurrounding a central vein, and the interlobular connective tissue containing triads (an artery, a vein and an excretory duct). What organ is it? A. Liver B. Pancreas C. Thymus D. Spleen E. Thyroid 128. An autoimmune renal injury was evolved a 1-year-old child due the using of poor-quality measles vaccine for preventive vaccination. It was detected macromolecular proteins in the urine. What process of urine formation was disturbed? A. Filtration B. Reabsorption C. Secretion D. Reabsorption and secretion E. Secretion and filtration 129. As a result of a mechanical injury an over 10 cm long portion of a peripheral nerve was damaged. This has led to an impairment of the upper limb activity. The patient was offered nerve transplantation. What glial cells will participate in regeneration and provide the trophism of the injured limb? A. Schwann cells B. Fibrous cells C. Protoplasmic cells D. Microglia E. Ependymal cells 130.A microslide shows a tissue withspherical cells, each of them contains alarge fat drop covered with thin cytoplasmlayer in its center. Nucleus is compressed and situated at the cell periphery. What tissue is it? A. White adipose tissue B. Brown adipose tissue C. Mucous tissue D. Pigmented tissue E. Reticular tissue 131. During autopsy of a 9-month-old girl’s body, who died due to severe pneumonia complicated with sepsis, lack of thymus is observed. In the lymph nodes the lymphoid follicles and cortical substance are absent; follicles of spleen are reduced in size with no light zones and plasma cells. What caused this structural changes? A. Accidental involution of thymus B. Thymus agenesis C. Thymus hypoplasia D. Thymus atrophy E. Thymus aplasia 132. In histological slide tissue is visible basic structural unit which is fiber. Fiber consists of symplast and satellites that are covered by basal membrane. For which tissue this structure is typical? Skeletal muscle Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Loose connective Reticular tissue 133. In the study of striated muscle fiber after the action of hydrolytic enzymes destruction of thin miofillaments is visible. What structures were damaged? Actin miofillaments Tonofibrilles Т-systems Sarcoplasmic reticulum Myosin miofillaments 134. In the phase of myocardial contraction (systole) calcium ion concentration increases sharply in the sarcoplasm of cardiomyocytes. What structures are involved in the deposit of calcium ions? Cisterns of smooth endoplasmic reticulum (s - system) Lysosomes Ribosomes Т-tube Nucleoli 135. In emergency room patient with lower limb muscle injury was hospitalized. Which cells take part in the reparative regeneration of muscle fibers and restoring of muscle function? Myosatellites Myoblasts Myofibroblasts Fibroblasts Myoepithelial cells 136. After a heart attack damage of the heart muscle area was. It is accompanied by massive deaths of the cardiomyocytes. What cells provide replacement formed defect in the structure of the myocardium? Fibroblasts Cardiomyocytes Myosatellites Epitheliocytes Smooth myocytes 137. In the study of striated muscle fiber after mechanical injury destruction of thick myofilaments is observed. Where pathological changes are localized? Disk A Disk I In half of the disk A Disk A and disk I In half of the disk I 138. On the microslides on heart rectangular cells from 50 to 120 microns, with a centrally located nucleus, welldeveloped myofibrils, linked by intercalated disks are visible. What function is associated with these cells? Contraction of the heart Conduction of impulses Endocrine Protective Regenerative 139. Cells in the electron micrograph are visible. Cells have rod-shaped nucleus, spindle shape, a large number of intermediate microfilaments composed of protein desmin. What is the tissue? Muscle Nerve Epithelial Loose connective Dense connective 140. Function of the myosatellites was activated under the action of the negative factors of the environment. Which process activation in muscle fibers can be expected? Regeneration of the muscle fibers Contraction of the muscle fibers Trophic of the muscle fibers Increased of a contractile thermogenesis Decrease of a contractile thermogenesis 141. In the illustration, structural unit of striated muscles myofibrils – sarcomere – is viisble. How to change the H-zone of the sarcomere at the maximum muscle contraction? Disappears Not changes Increases in two times Decreases in two times It takes the whole sarcomere 142. Striated skeletal muscle tissue is characterized by all of the features except: Cellular structure Ability to contract Presence of satellite cells Motor plaques The presence of layers of connective tissue 143. It is known that calcium ions provide muscle contraction. With what calcium nteracts during contraction? With protein troponin of thin fibrils With protein myosin of thick fibrils With protein actin of thin fibrils With actomyosin complex of sarcolemm With protein calsecvestrin 144. In the histological study of the cheek biopsy skeletal muscle tissue was observed. Name the structural unit of the tissue. Muscle fiber Cardiomyocyte Smooth myocyte Myosatellite Myofibril 145. In histological slide of a pyloric stomach bundles of spindle shape cells with rod-shaped centrally located nucleus are visible. What tissue these cells form? Smooth muscle Loose connective tissue Sceletal muscle Epithelial Reticular 146. Nucleated anastomosing fibers are visible in one of the layer of the hollow body. Fibers made up of cells which are connected by intercalated discs. What tissue forms this layer? Striated cardiac Striated skeletal Smooth muscle Loose fibrous connective Dense irregular connective 147. Morphology of the heart wall of the patient was restored after a heart attack. What tissue provide regeneration? Connective Smooth muscle Striated Epithelial Nerve 148. Toxic substance breaks mechanism of the transmission of nerve impulses from neuron to neuron in experiment. What structure provides this function? Synapse Neurolemma Neurofibrils Mitochondria Nissle substance 149. Degeneration of nerve fibers is possible in traumatic damage. It is accompanied by the breakdown of axons, myelin disintegration. What neural structures provide regeneration of myelin? Neurolemmocyte Mesaxon Perineurium Endoneurium Astrocytes 150. Damaged nerve fibers can regenerate. What glial cells take active part in this in the CNS? Oligodendrocytes Microglia Ependymocytes Fibrous astrocytes Protoplasmic astrocytes 151. Polio is characterized by damage of the spinal cord. Polio patient has skeletal muscle dysfunction. Destruction of which neurons occurs? Моtor Pseudounipolar Intercalated Pseudounipolar and intercalated Intercalated and motor 152. Sensitive nerve ganglion consists of spherical shape neurons with one process, which is divided into the axon and dendrite at a distance from the perikaryon. Which are cells? Pseudounipolar Unipolar Bipolar Multipolar Apolar 153. In certain cells of adult human mitosis is not observed and quantitative DNA content remain constant throughout the life. These cells: Neurons Endothelium Muscle (smooth) Epidermis Hematopoietic 154. The need to cut the nerve arose during surgery. Its integrity was restored after some time. Name the cells that provide regeneration. Neurolemmocytes Astrocytes Ependymocytes Microglia Mantle gliocytes 155. Choose one incorrect answer. For myelinated nerve fibers all the features are exhibited except: Several axial cylinders Single axial cylinder Nodes of Ranvier Neurofilament Neurolemmocytes 156. A large number of multipolar neurons are visible in the histological slide of a cross section of the cerebellum, in its gray matter. On which morphologically attributes these cells belong to multipolar? Number of processes Length of processes Shape of terminal axon extension Shape of perikaryon Cell size 157. On histological slide of nerve tissue is seen that the neurons are interconnected through the contacts that are specialized for one-way transmission of nerve impulse. What type of intercellular junction is seen in the slide? Synapsis Desmosome Simple Dense Nexus 158. A macrophage cell is visible on the electron microphotography. Along its processes erythrocytes on different stages of differentiation are arranged. Cell of what organ is represented? Red bone marrow Thymus Spleen Tonsil Lymph node 159. The transplant rejection begins after geterotransplantation of the organ. What blood cells provide this process? T-killers Т-helpers Т-supressors NK-cells T-memory cell 160. The cell with processes that contains differentiating lymphocytes in the deep invaginations of the plasmolemma is visible on the electron microphotography. To which organ this ultrastructure is characterized? Thymus Red bone marrow Spleen Tonsil Liver 161. In the reticular stroma of the organ mature blood cells and lymphoid follicles are visible. What organ is represented on the slide? Spleen Lymph node Tonsil Thymus Red bone marrow 162. In which organ lymphocytes form three types of lymphoid structures: lymphoid nodules, medullar cords and sinuses? Lymph node Spleen Thymus Tonsil Red bone marrow 163. The lobed organ contains stroma that consists of epithelial processing cells. What organ is represented on the slide? Thymus Red bone marrow Spleen Tonsil Lymph node 164. The medulla of the lobule of the hematopoietic organ has light color and contains epithelial bodies. Which organ has these morphological features? Thymus Lymph node Spleen Liver Kidney 165. The antibodies are released to the blood when re-enters of the antigens occurs. Which immunocompetent cells are responsible for this? Lymphocytes of memory Т - killers Т - supressors Macrophages Dendritic cells 166. The numerous plasmocytes were identified in the blood of the 16 year old girl that suffers an autoimmune inflammation of the thyroid gland. The proliferation and differentiation of which blood cells cause increasing of the number of plasma cells? В-lymphocytes Т-helpers Tissue basophils Т-killers Т-supressors 167. Antigen independing proliferation and differentiation of T-lymphocytes were studied on the child with impaired immune reactivity. Punctate what organ was taken for the study? Thymus Spleen Lymph node Red bone marrow Tonsil 168. The clusters of the round cells with large basophilic nucleus and a narrow rim of cytoplasm were detected in the lamina propria of the small intestine. The central part of these clusters is light and contains less cells than the peripheral. Which morphological structure is visible? Lymph node Nerve node Adipocytes Blood vessels Lymphatic vessels 169. On the slide of the bean-shaped organ cortex and medulla are visible. The cortex is represented by the single spherical nodules in diameter 0,5 - 1 мм, medulla – by medullary cords. From what organ histological section was made? Lymph node Kidney Thymus Adrenal glands Spleen 170. The histological section through the lymph node was made. On the slide expansion of the paracortical zone is visible. Proliferation of what kind of lymph node cells led to this process? Т-lymphocytes Fixed macrophages Plasmocytes Macrophages Reticulocytes 171. Two histological slides have given to the student. In both - organs with lymphoid nodules. On one of them only follicles are visible, on an another - follicles contain eccentric vessel. Which organs are visible on the slides? The first is lymph node, the second is spleen The first is red bone marrow, the second is spleen The first is thymus, the second is spleen The first is liver, the second is lymph node The first is liver, the second is spleen 172. After antigenic stimulation of the experimental animal on slide of the lymph node (in medullary cords) large number of the cells was found. The cells exhibit: basophilic cytoplasm, eccentric nucleus, chromatin in the shape of cart-wheel, perinuclear cytoplasm is very distinct. What are cells? Plasmocytes Macrophages Fibroblasts Adipocytes Tussue basophils (must cells) 173. Enlargement of the spleen and reduction of the number of erythrocytes in peripheral blood is observed in patient. Increased function of which spleen cells are involved in this phenomenon? Macrophages Lymphocytes Dendritic cells Plasmocytes Retyculocytes 174. Transplant rejection was detected after heterotransplantation. Which cells mainly provide this process? Т-killers Macrophages В-lymphocytes Т-helpers Т-supressors 175. The burn wound was closed by pig skin (heterotransplantation). What are the effector cells, which rejection the transplant (pig skin)? Т-killers Т-helpers Т-supressors В-lymphocytes Natural killers 176. The child has congenital immunodeficiency. Cellular immunity is damaged which causes frequent of the viral infection. Disorders in which the organ most likely caused by this pathology? Thymus Red bone marrow Lymph node Spleen Tonsil 177. A human bone marrow smear shows myeloid cells, adipocytes and stellate cells with oxyphilic cytoplasm processes of which contact each other. What are cells? Reticulocytes Fibroblasts Macrophages Dendritic cells Osteocytes 178. The foci of increased plasma cells genesis were found in the lymph node bioptate (in medullary cords). Antigen depending stimulation of which immune cells caused their formation? В-lymphocytes Т- lymphocytes Macrophages Dendritic cells Interdigitative cells 179. The crypts epithelium of which is infiltrated by the leukocytes were found in the histological preparation of the tonsil. From what epithelium this organ consists? Stratified squamous nonkeratinizing Simple columnar Stratified cuboidal Stratified squmous keratinizing Pseudostratified columnar 180. Activation of the immune reactions was found during the morphological studies of the spleen. In which structures of this organ antigen-dependent proliferation of the T- lymphocytes begins? Periarterial zone of the white pulp Central zone of the white pulp Mantle zone of the white pulp Мarginal zone of the white pulp Red pulp 181. The hemopoietic organ consisting of various shaped lobules is investigated in histological slide. The cortex and medulla are visible in each lobules. Which body has such features? Thymus Lymph node Spleen Tonsil Appendix 182. In the slides hematopoiesis and immunogenesis human organs are presented. This organs contain lymphoid tissue, forming different structures (lymphoid nodules, lobules, cords). In which organ antigen-independing proliferation and differentiation of lymphocytes occurs? Thymus Lymph node Spleen Hemolymphatic node Tonsil 183. It is known that the plasma cell produces antibodies specific for the antigen. With the introduction of the antigen the number of the plasma cells increases. Due to some of the blood cells there is an increase the number of plasma cells? В-lymphocytes Т-lymphocytes Моnocytes Basophils Eosinophils 184. With infectious diseases and intoxications number of reticuloepitheliocytes and Hassal bodies increases, area of the medulla becomes wider in the thymus lobules. How these changes of the thymus are called? Accidental involution Age involution Thymus -lymphatic status Т- immunodeficiency В- immunodeficiency 185. During the child vaccination in response to foreign antigens introduction humoral immunity reaction is developed. Describe the main spleen cells involved in the immune response. Macrophage, Т-helper, В-lymphocyte. Т-killer, Т-helper В-lymphocytes Т-supressor and helper, macrophage В-lymphocyte 186. The lobed organ is detected in the histological slide. Each lobules has a cortex and medulla. Lobules parenchyma is formed by lymphoid tissue in which T -cells are at different stages of development. Microenvironment is presented by epithelioreticular cells. Hassal bodies are determined in the medulla. What is organ? Тhymus. Kidney Lymph node Adrenal gland Spleen 187. Increase in the lymphoid tissue volume, which may indicate the activation of immune reactions is observed in the spleen and lymph nodes slides. Indicate in these organs locations where antigen-depending proliferation and differentiation of B-lymphocytes take place. Germinal center of lymph nodules Mantle zone Paracortical zone Medullar sinuses Periarterial zone 188. In order to diagnose biopsy of the hematopoietic organ parenchyma was taken and the megakaryocytes were found there. What is the organ of the following? Red bone marrow Spleen Thymus Lymph node Tonsil 189. In the afferent vessel of the experimental animal the vital stain was inducted. In which lymph node cells, it will be possible to detect particles of the stain? Typical macrophage and fixed macrophages Reticuloendothelial cells В-lymphocytes Plasmocytes Т-lymphocytes 190. In the red bone marrow developing blood cells are located by islands. Some islands are associated with the macrophages. What blood cells develop in these islands? Erythrocytes Precursors of T-and B-lymphocytes Monocytes Trombocytes Basophils 191. The patient 30 years old has malignant tumor of the skin. What epidermal cells involved in the immune response? Т-lymphocytes Keratinocytes Keratinocytes and Merkel cells Merkel cells Cells of the stratum spinosum 192. To the body of experimental animal antibodies against thymosins were inducted. Which cell differentiation broken in the first place? Т-lymphocytes Monocytes В-lymphocytes Macrophages Plasmocytes 193. In the histological slide the organ with the cortex and medulla is visible. Cortex consists of an outer zone with lymphoid nodules and paracortical zone. In the medulla cords, sinuses and trabeculae are located. What organ has this morphological features? Lymph node Adrenal gland Spleen Thymus Kidney 194. In the histological slide a parenchyma of the organ is represented by lymphoid tissue, which forms the lymph nodules. Nodules are diffusely and comprise a central artery. What organ has this morphological structure? Spleen Tonsil Lymph node Thymus Red bone marrow 195. Histological study of the thymus of the man aged 40 year showed: decreasing of parenchymal portion of the thymus, increasing of fat and loose connective tissue portion, increasing the number of thymus bodies at a constant total weight of the organ. How this phenomenon is called? Age involution of the thymus Accidental involution Thymus hypotrophy Thymus dystrophy Thymus atrophy 196. A newborn baby has thymus hypoplasia. What type of hematopoiesis is broken? Lymphopoiesis Monocytopoiesis Erythropoiesis Granulocytopoiesis Megakaryocytopoiesis 197. On slide the organ of immune sistem is represented. The organ exibits: the lobules surrounded by layers of connective tissue, the number of cells at the periphery of the lobules are significantly higher than in the center, the lymph nodules are absent. Which organ is represented? Thymus Red bone marrow Lymph node Spleen Tonsil 198. On the slide a organ is represented covered with a connective tissue capsule from which trabeculae depart. In the organ cortex is visible, which contains lymphoid nodules and medulla represented by strands of lymphoid cells. What organ is represented on the slide? Lymph node Thymus Spleen Red bone marrow Tonsil 199. The patient, 15 years old, has an angina and tonsils increasing. What histological structure of these organs are involved in the immune protection of the body in response to the streptococci penetration? Lymph nodules Stratified squamous keratinizing epithelium Stratified squamous nonkeratinizing epithelium Loose connective tissue Crypts 200. At the patient after grafting of a foreign kidney transplant rejection reaction has been developing. What are the main effector cells involved in the immune response? Т-killers В-lymphocytes Т-supressors Т-helpers Plasmocytes 201. To the body of experimental animal antibodies against thymus hormones were inducted. Which cell differentiation broken in the first place? Т-lymphocytes Monocytes В-lymphocytes Macrophages Plasmocytes 202. Processes of the erythropoiesis, granulocytopoiesis, monocytopoiesis, thrombocytopoiesis were violated at patient. What hematopoietic organ pathology can be detected? Red bone marrow Thymus Spleen Lymph node Tonsil 203. On the slide of the spleen red and white pulp were found. Stroma is presented by a special tissue. To what kind of tissue it belongs? Reticular connective tissue Dense connective tissue Adipose tissue Muscle tissue Nerve tissue 204. In the histological slide of a hematopoietic organ clusters of lymphocytes in the form of nodules and cords are distinguished, which together with the stromal elements form a cortex and medulla. What is the organ? Lymph node Spleen Red bone marrow Thymus Tonsil 205. To prevent the swine flu epidemic vaccine (foreign protein) was introduced into the human body. Which cells are included in the production of specific immunity? Lymphocytes Lypocytes Pigment cells Fibroblasts Adventitial cells 206. Damage of the epithelium of the mucosa was revealed by endoscopic examination of the stomach. What glandulotcytes are responsible for reparative regeneration? Undifferentiated cervical mucocytes Additional mucocytes Chief exokrinocytes Parietal exokrinocytes Surfaces glandular epithelium 207. Local stenosis of the esophagus due to scar formation occurred after chemical burn. What cells of the loose connective tissue are involved in the formation of scars? Mature specialized fibroblasts Young low-specialized fibroblasts Fibrocytes Myofibroblasts Fibroclasts 208. In histological slide cross-section of the hollow organ wall is presented. Its mucous membrane is covered by stratified squamous non-keratinizing epithelium. What organ is this? Esophagus Duodenum Colon Uterus Appendix 209. Pernicious anemia was developed in patients after gastrectomy. The absence of what cells of the gastric glands causes this pathology? Parietal Chief Cervical mucocytes Endocrinocytes Goblet 210. On histological slide submucosa of the small intestine is filled by secretory portions of protein glands. What department of the small intestine is presented in the slide? Duodenum Colon Jejunum Ileum Appendix 211. On histological slide of the small intestine wall groups of cells were found that are located at the bottom of the crypts, have basophilic cytoplasm and acidophilic secretory granules in the apical part. What are cells? Paneth cells Cells without brush border Endocrine cells Goblet cells Columnar with brush border 212. In histological slide parenchyma of the organ is represented by hexagonal lobules, which consist of anastomosing plates, between which radial sinusoidal capillaries are. What organ has this morphological structure? Liver Pancreas Thymus Spleen Lymph node 213. The patient has a violation of the endocrine function of the pancreas, which is manifested in the decrease of blood level of the hormone glucagon. The function of what gland cells is violated in this case? A-cells of the Langerhans islets B-cells of the Langerhans islets D-cells of the Langerhans islets D1-cells of the Langerhans islets PP-cells of the Langerhans islets 214. Patient since the 14 years has diabetes. What cells of the pancreas do not function? B – cells A – cells D – cells D1 cells PP – cells 215. Newborn has violation of digesting of the breast milk. Violation of what gastric glands cells is observed? Chief exocrinocytes Parietal exocrinocytes Cervical mucocytes Additional mucocytes Exocrinocytes 216. In the apical part of cytoplasm of the pancreatic cells the secretory granules appear and disappear in the secretory cycle. To which structural elements granules belong? Inclusions Microfilaments Lysosomes Exocytotic vacuoles Granular endoplasmic reticulum 217. Focal gastric epithelial damage occurred after exposures of the harmful factors. Which cells are responsible for regeneration? Cervical mucocytes Parietal exocrinocytes Chief exocrinocytes Endocrinocytes Mucocytes of glands body 218. On histological slide of the fundus glands large cells with acidophilic cytoplasm and complex system of intracellular tubules are visible. Which component of the gastric juice these cells form? Hydrochloric acid Pepsinogen Mucus Serotonin Gastrin 219. 50 years old patient has an elevated level of blood sugar. With dysfunction of which cell development of this disease is associated? B –cells A –cell Thyrocytes Pankreocytes Lipotropocytes 220. Long course of treatment with aspirin was appointed to the patients with rheumatic fever. Which structural component of the gastric mucosa will protect from damage in the greatest measure? Simple columnar glandular epithelium Connective tissue Muscle tissue Stratified ciliated epithelium Stratified squamous non-keratinizing epithelium 221. In histological slide of the glandular organ serous secretory units are determined only. Ducts whith doublelayered or stratified epithelium are visible in interlobular connective tissue. What organ is this? Parotid Submandibular gland Pancreas Sublingual salivary gland Liver 222. In the electron micrographs of the fundus gastric gland the large oval cell is visible. Cytoplasm contains a system of intracellular secretory tubules, numerous mitochondria. Call this cell. Parietal Chief Undifferentiated Mucous Exocrine 223. Changes in the soft palate and uvula were identified in a patient with diphtheria. What epithelium was injured? Stratified squamous Pseudostratified columnar Simple squamous Simple columnar Cuboidal 224. Surface epithelium of the stomach mucosa is damaged by inflammatory diseases. What type of the epithelium is damaged? Simple cylindrical glandular Simple squamous Simple cuboidal with microvilli Simple cuboidal Stratified cuboidal 225. Violation of digestion and absorption of proteins in the small intestine as a result of deficiency in intestinal juice dipeptidase were detected in patients with chronic enterocolitis (inflammation of the intestine). Which cells have been damaged? Paneth cells Columnar with a brush border Columnar without brush border Goblet Endocrinocytes 226. Suction (absorption) function is disrupted in diseases of the small intestine mucosa. What epithelium is responsible for this function? Simple columnar with brush border Simple cuboidal Simple columnar ciliated Stratified squamous Stratified cuboidal 227. Patient with diseases of the small intestine has a violation of the luminal and membrane digestions. Functions of what cells are violated? Columnar with brush border Columnar without brush border Goblet Paneth cells Endocrinocytes 228. Absence of specific structures of a relief of the small intestine is observed at endoscopic examination of the patient with chronic enterocolitis (inflammation of the intestine). What components determine the relief of the mucous membrane of the organ? The circular folds, villi and crypts Fields, folds, pits Gaustry, villi, crypts Spiral folds Fields, villi 229. Some diseases of the small intestine are associated with dysfunction of the exocrinocytes with acidophilic granules (Paneth cells). Where this cells are? At the bottom of intestinal crypts At the apical part of the intestinal villi On the lateral surfaces of the intestinal villi At the transition of the villi in the crypt In the upper part of intestinal crypts 230. Quantitative relationships between the epitheliocytes of the mucose are changed in some diseases of the large intestine. What types of cells predominate in the epithelium of the crypts of the large intestine is normal? Goblet cells Columnar villous epitheliocytes Endocrinocytes Cells with acidophilic granules Undifferentiated cells 231. Tumor that has origin from the mucose of the rectum (anal region) was detected during rectoromanoscopy. From what epithelium this tumor was formed? Stratified squamous non-keratinizing Simple columner glandular Simple columner with brush border Simple cuboidal Transitional epithelium 232. Anomaly of the liver development was detected during examination of the patient. What embryonic source was damaged? Endoderm of the middle part of primitive gut Endoderm of the dorsal wall of the primitive gut Foregut of the endoderm Mezonephric duct Endoderm of the hindgut 233. Blood circulation in classical lobules is disturbed by proliferation of connective tissue in the parenchyma of the liver (fibrosis) due to chronic disease. What is the direction of movement of the blood in the lobules? From the periphery to the center From the center to the periphery Around the lobules From the top to the bottom From the bottom to the top 234. Increase in the number of the glandulocytes with oxyphilic cytoplasm revealed by histological examination of the aspiration biopsy of the gastric mucosa in a patient suffering from peptic ulcer. Which component of the gastric juice these cells produce? Hydrochloric acid Mucus Pepsinogen Gastrin Secretin 235. Certain cells of the pancreas are in a state of tension in people who eat a lot of sweets. What cells are these? B –cells A –cell D-cells PP-cells Acinus 236. In histological slide organ of the digestive tract is visible. Its wall consists of four layers: mucosa, submucosa, muscle and serosa. The mucous has folds and pits. What organ has this relief? Stomach Esophagus Duodenum Small Intestine Appendix 237. In slide a section of the digestive tube wall is represented. Mucosal relief is presented by pits. The surface of the pits is covered by columnar epithelium, in which all cells lie on a basal membrane, the apical part of the cells is filled with droplets of mucoid secretions. What organ has this epithelium? Stomach Small Intestine Colon Esophagus Appendix 238. In histological slide organ is visible, in the lamina propria of which simple tubular glands, consisting mainly of chief, parietal, mucous and endocrine cells, are located. Indicate the type of the glands. Fundic glands of the stomach Pyloric glands of the stomach Cardiac glands of the stomach Esophagus glands proper Cardiac glands of the esophagus 239. In histological slide gland is visible. In the lobules acini, secretory cells of which have two zones: the base homogeneous basophilic and apical - zymogens oxyphilous, are presented. What body has these morphological features? Pancreas Liver Parotid gland Submandibular gland Sublingual salivary gland 240. Lobules with unclear borders, central vein inside and radially directed trabeculae, are the structural units of some organ. Lobule is limited by interlobular arteries, veins, and bile ducts (triad). Which organ is this? Liver Thyroid gland Pancreas Parotid gland Kidney 241. The patient with chronic atrophic gastritis has symptoms of hypochromic anemia. Violation of function of what cells of the gastric glands can explain the development of the anemia? Parietal cells Chief cells Additional cells Cervical cells Endocrine cells 242. The patient has a low gastric acidity. What cells of the gastric glands caused this condition? Parietal Chief Mucous Endocrine Cervical 243. Process of keratinization of the epithelium was found in biopsy of the mucous of a esophagus of the patient. Which of the following types of epithelium covering the mucous membrane of this organ is normal? Stratified squamous non-keratinizing Simple squamous Pseudostratified ciliated Simple columner Stratified squamous keratinizing 244. Significant impairment of a process of regeneration of a epithelium of a mucous membrane of a small intestine was found in cancer patients after radiotherapy. What cells of the epithelium were damaged? Columnar epitheliocytes without brush border in the crypts Columnar epitheliocytes with brush border Goblet exocrinocytes Endocrine cells Exocrinocytes with acidophilic graininess (Penneta) 245. Pernicious anemia developed in patient after radiation therapy for cancer of a stomach. Reason - damage to cells that produce intrinsic factor. Which of the cells of the gastric glands were damaged? Parietal cells Chief exocrinocytes Cervical mucocytes Endocrinocytes Additional mucocytes 246. Doctor found syndrome of acute enterocolitis (inflammation of the small intestine) with violation of the processes of digestion and absorption of the products in the patient. Damage of what intestinal epithelial cells are responsible for such violations? Columnar epitheliocytes with brush border Columnar epitheliocytes without brush border Goblet exocrinocytes Endocrine cells Exocrinocytes with acidophilic graininess 247. Proteins are poorly digested in the stomach of the patient. Analysis of gastric juice showed low acidity. The function of what stomach cells is broken in this case? Parietal cells Chief exocrinocytes Mucocytes Endocrinocytes Cervical mucocytes 248. Chemical burn of a upper surface of a tongue occurred in the girl 15 years old. What epithelium is damaged by this? Stratified squamous partially non-keratinizing Simple low columner Pseudostratified ciliated Transitional Simple squamous 249. Total hyperacidity was found in women 56 years old during pH-metry of gastric juice. With dysfunction of which cells of the gastric glands it can be connected? Parietal cells Chief exocrinocytes Cervical mucocytes Additional mucocytes Endocrinocytes 250. Ulcer formed in the small intestine of the patient after radiation therapy for tumors of the liver. Reason inhibition of mitotic activity of the cells that are responsible for the regeneration of the surface epithelium of the small intestine. Name these cells. Columnar epitheliocytes without brush border in crypts Columnar epitheliocytes Goblet exocrinocytes Endocrine cells Exocrinocytes with acidophilic graininess 251. The patient complains of pain in the stomach. Gastroscopy revealed the presence of small-sized ulcers in the fundus of the stomach. Violation of function of which cells of the gastric mucosa was one of the reasons of mucosal damage? Surface epithelium cell producing mucous secretion Parietal cells of the gastric glands that produce chloride and hydrogen ions Chief exocrinocytes producing pepsinogen Endocrinocytes producing somatostatin Endocrinocytes producing serotonin 252. The mucous epithelium of the esophagus of the patient has been damaged due to burn acetic essence. What cells of the surface epithelium are the source of reparative regeneration? Basal cells Squamous cells Spinosum cells Ciliated cells Endocrine cells 253. Furred tongue (excess of keratinization) was found in patients with chronic gastritis by external examination. The reason - amplification process of keratinization. In which tongue papillae epithelium can keratinizing? Filiform papillae Fungiform papillae Circumvallate papillae Foliate papillae Papillary layer 254. In histological slide a mucosa of the organ is represented. Columner cells with brush border and Goblet cells are defined on the surface of the villi in the epithelial layer. What organ has these cells? Small intestine Stomach Large intestine Ureteral Bronchus 255. Substantial reduction or full absence of parietal cells in the stomach glands was observed in patient biopsy material. Mucosa of what stomach area was studied? Pylorus Fundus Cardiac department Body of stomach Transition esophagus into the stomach 256. In histological slide a organ of a oral cavity is visible, its anterior surface is lined by stratified squamous non-keratinizing epithelium and a posterior surface - pseudostratified ciliated epithelium. What is this body? Soft palate Language Hard palate Lip Cheek 257. Extensive damage of the excretory acinar cells is defined in patients after acute pancreatitis. What cells are responsible for the regeneration? Cells of intercalated ducts Cells of islets of Langerhans Cells of intralobular ducts Stromal cells Vascular endothelium 258. Cells forming the wall of the bile capillaries were affected by viral infection. Its created the conditions for the getting of a bile into a blood of sinusoidal capillaries. What cells are damaged? Hepatocytes Kupffer cells Ito-cells Rit- cells Endotheliocytes 259. Well-developed granular endoplasmic reticulum is determined in the cytoplasm of the "dark" hepatocytes during ultramicroscopic study. What is the function of this organelle in these cells? Synthesis of plasma proteins Synthesis of carbohydrates Detoxification Production of bile Storage of calcium ions 260. Full update of the small intestine epithelium occurs within 3 days due to active proliferation of undifferentiated cells. Indicate their localization. Bottom of the crypts Top of the villi Base of the villi Lateral surface of the villi Lamina propria 261. Insulin injection for evaluation of the completeness of vagotomy is accompanied by a significant increase in the acidity of gastric juice. What cells of the gastric glands provide this process? Parietal Endocrine Chief Mucosal Cervical 262. Damage to the epithelium of the excretory ducts of the salivary glands is observed in chronic inflammatory processes. What epithelium will be damage in the striated ducts of the major salivary glands? Columner epithelium with basal striation Squamous epithelium with basal striation Cuboidal epithelium with basal striation Double layer with basal striation Stratified cuboidal 263. The baby gets breast milk. What histological structures of the oral cavity were adapted for stimulation of the nipple breast, causing reflex milk flow? Epithelial villi of the lips Stratified squamous keratinizing epithelium of the lips The connective papillae of the lips Fungiform papillae of the tongue Foliate papillae of the tongue 264. Tissue, located at the top of the tooth root and the point of branching of the roots, is visible in the thin section of tooth. The tissue contains cells with process lying in lacunae, and numerous collagen fibers having a radial or longitudinal direction. Call this tissue. Cellular cement Retikulofibrous bone tissue Dentin Enamel Dense connective tissue 265. Non-mineralizing areas that are places for penetration of the infection into the tooth meet at the boundary of the enamel with the dentin. How this areas to call? Enamel bundles Enamel prisms Enameloblasty Dentinoblasty Fibers of Toms 266. Depositions of hydroxyapatite crystals that look like globules are visible in histological slide of the tooth histogenesis. For which tooth tissue this type of mineralization is typical? Dentin Enamel Periodontal Cement Pulp 267. Epithelium of the stomach may change under the influence of various harmful factors that can cause stomach ulcers. What epithelium is damaged? Simple cylindrical glandular Stratified squamous non-keratinizing Simple squamous Simple cuboidal Pseudostratified columner 268. Which departments of the facial skull underdevelopment in the embryonic period leads to a malformation as "cleft palate"? Palatine processes Frontal process Frontal and maxillary processes Mandibular processes Mandibular and palatine processes 269. Wall of the organ of the digestive system is presented in the histological slide. Numerous lymphoid nodules are in the lamina propria and submucosa. Call this organ. Appendix Stomach Duodenum Jejunum Colon 270. Hepatic artery was damaged as a result of stab wounds. But the blood continues to flow into the hepatic lobule. What a vessel provides the blood flow in lobules? Portal venule (branche of the hepatic portal vein) Interlobular artery Portal arteriola Sublobular vienna Hepatic vienna 271. Granular EPS was destroyed in hepatocytes by the impact of hepatotropic poison. Synthesis of which substances will be broken in the epithelium of the liver? Albumins and fibrinogen Phospholipids Glycogen Cholesterol Vitamins 272. Group of cells are visible in histological slide of the pancreas. Some of them are situated centrally and has basophilic secretory granules. Their secret regulates carbohydrate metabolism. Call these cells. B –cells PP-cells A –cell Adipocytes D-cells 273. Striated muscle tissue of an organ of the digestive system is revealed by microscopic examination. From what organ biopsy was taken? Esophagus Stomach Jejunum Ileum Appendix 274. The inner layer of the epithelium of the enamel organ in the tooth germ was destroyed in animal experiment. The development of what tissue of a tooth is broken? Enamels Dentin Cement Pulp Periodontal 275. Granules containing dipeptidases and lysozyme have been found in the cytoplasm of epithelial cells of intestinal crypts by histochemical methods. Indicate these cells. Paneth cells Columnar epithelial cells Goblet exocrinocytes A –cells S-cells 276. The patient has a violation of taste sensation. The total sensitivity is maintained. What papillae are not damaged? Filiform papillae Circumvallate papillae Fungiform papillae Foliate papillae All 277. Canaliculi are visible in the dentin on longitudinal sections of the tooth. What is contained within the tubules? Processes of dentinoblasts Processes of enameloblasts Bodies of dentinoblasts Fibroblasts Elastic fibers 278. The patient is treated for chronic gastritis for a long time. Changes in the mucosal epithelium of the stomach are observed by endoscopy. What epithelium is changed? Simple columner glandular Simple columner with brush border Simple columner ciliated Pseudostratified columner Simple squamous 279. One of the organ of the oral cavity looks like a few folds of mucous membrane, in the lamina propria of which numerous lymphoid follicles are. What is the body? Palatine tonsils Tongue Parotid gland Sublingual glands Submandibular gland 280. As we know, the submandibular gland has mucous glandular portion, consisting of mucocytes. What features are characteristic for these cells? Flattened nuclei and clear cytoplasm Basophilic cytoplasm Rounded nuclei in the center of the cell Microvilli Basal striation 281. Analysis of biopsies of the gastric mucosa of a patient with gastritis showed a sharp decrease in the number of parietal cells. How does it effect on the following components of gastric juice? Decrease of acidity Increase of acidity Increase of gastric juice Reduction of gastric juice Decrease of mucus production 282. Morphological features of a gum are visible in the biopsy of a oral mucosa. What features of the structure of the mucous membrane of the gums can be observed in normal? Stationary adherent to the periosteum, lamina propria forms the high papillae, lack of muscle layer Low adherent to the periosteum, well defined muscle layer Absent of muscle layer, submucosa is well developed Property and muscle membranes are missing Holds a lot of small salivary glands 283. Some diseases of the salivary glands are caused by dysfunction of their excretory ducts. What types of the excretory ducts present in the major salivary glands? Intra-, interlobular ducts and common duct of the gland Lobular, striated and common ducts Intercalated, divided and common ducts Intra- and interlobular ducts Common duct 284. Structure of the oral cavity, which has a maxillary, mandibular and intermediate zone, is damaged by trauma. What structure is traumatized? Cheek Tongue Lip Hard palate Soft palate 285. The patient complains of deterioration of taste sensitivity. Doctor noticed mucosal atrophy of some areas of the oral cavity during examination. Where do morphological changes were observed more? On the upper surface of the tongue On the lower surface of the tongue At the root of the tongue In the hard palate On the gums 286. On slide structure of bone tissue, covered with a mucous membrane with keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium is presented. In all areas of the lamina propria collagen fibers form a powerful bundles, woven into the periosteum. Name the structure of the oral cavity? Hard palate Gums Lip Cheek Tongue 287. The patient went to the doctor with complains of fever up to thirty-eight degrees, weakness, a pain in the larynx. On examination revealed that the patient's tongue is with white coate. What are the histological structures of the tongue involved in the formation of excessive keratinization? Epithelium of the filiform papillae Epithelium of foliate papillae The epithelium of fungiform papillae Epithelium of circumvallate papillae Lamina propria of tongue papillae 288. The patient suffers from heart attacks. The doctor gave him a nitroglycerin under the tongue. What structural features of the oral mucosa are responsible for such a possibility of medication? Permeability of stratified squamous non-keratinizing epithelium Permeability of stratified squamous keratinizing epithelium Permeability of stratified squamous epithelium Presence of the tongue papillae Presence of salivary glands 289. The patient has an increased acidity of gastric juice. Hyperfunction of what cells in the glands of the gastric mucosa leads to this condition? Parietal exocrinocytes of own gastric glands Exocrinocytes of the gastric glands Additional mucocytes Goblet cells Exocrine pankreaocytes 290. Structure represented by mucosa and having a free portion and attached portion, which is tightly adherent to the periosteum defined in the oral cavity. Epithelium - stratified squamous keratinizing. Lamina propria forms a long, deep jutting out into the epithelium papillae. Call this structure. Gums Hard palate Lip Cheek Tongue 291. Cell, in cytoplasm of which granules that look like fruit pits (stones) are visible, presented at the electron micrograph of intralobular liver sinusoid. We know that this is a natural killer cell. Which cell is? Pit-cell Hepatocyte Endothelium of the sinusoid Stellate macrophage Perisinusoidal lipocyte 292. Sagittal line defect was detected in the palate after the birth of a child. In what process will this affect? Swallowing Chewing Digestion Breath Articulation