The following form contains information supplied by company
advertisement

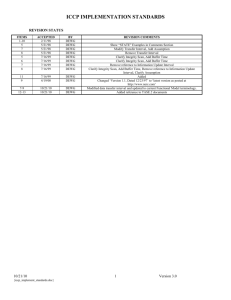
Association Information Exchange Form
The attached ICCP Association Information Exchange Form has been created to
facilitate ICCP associations between ICCP nodes. ICCP node administrators should fill
out this form using their own setup information. Thus the form will contain information
supplied by company-A to company-B detailing the parameters needed during companyB’s ICCP association configuration. Note that similar information needs to be supplied
by company-B to company-A.
The fields are marked as Mandatory, Recommended, or Optional. Mandatory
fields are required in order to create an association. Recommended fields should
generally be filled in if applicable. For example, an OSI NSAP is only required if using
an OSI stack. Optional fields can be filled in for instance to help with troubleshooting if
connection or data transmission errors occur.
July 15, 1999
{iccp_aief.doc}
Ver 2.0
1
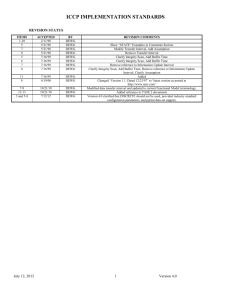
ICCP Association Information Exchange Form
Date:
Company-A:
Contact for Company-A:
Company-B:
Contact for Company-B:
General Notes:
Table 1: Company-wide / Server independent information
1.
ICCP vendor and platform
The name of the Company-A’s ICCP vendor, vendor
software version, as well what operating system and
hardware platform used for the ICCP servers.
2. Number of possible ICCP servers:
This is the total number of ICCP servers that may be
available to a remote client to associate with. Include
backup servers if they have unique addresses. This
number should equal the number of copies of Table 2
included in this form. Typically 1 - 10.
3. Company A’s domain name:
The domain name which company-B will use to access
data on Company-A’s ICCP node. Recommended to
be the 4 character ISN node name of Company-B.
July 15, 1999
{iccp_aief.doc}
2
M
R
M
Ver 2.0
ICCP Association Information Exchange Form
4.
Requested Company B’s domain name:
The domain name on Company B’s ICCP node which
company-A requests to be created. This is only a
request as this name is designated by company-B.
Recommended to be the 4 character node name of
company-A. Note: This is the only entry on these forms
that refers to Company B’s ICCP node.
5. Association type
O
“Single direction Client-Server”: Enter this if Company
A’s and Company B’s ICCP nodes act as either Client
or Server over one association. Information can be sent
in only one direction per association. The client must
initiate the association.
R
“Dual direction Client-Server”: Enter this if Company
A’s and Company B’s ICCP nodes act as Client and
Server over one association. Information can be sent in
either direction per association. The association type is
determined by prior agreement between the two users.
Typically “Dual direction Client-Server”.
6. Association Initiation:
This field is only used if the association type is “Dual
direction Client-Server” and indicates which ICCPnode
shall initiate the association (e.g. company-A). The
initiator of the association is determined by prior
agreement between the two users.
7. Bilateral table ID:
R
Company A’s bilateral table name used when Company
B is accessing Company A’s data (e.g. “1.1”).
8. Supported ICCP services:
M
A list of the conformance blocks supported by the
server (e.g. Blocks 1,2).
9. ICCP version:
M
The version of ICCP running on the server (e.g.
TASE.2 Version 1996-08).
10. Shortest periodic interval:
M
Time in seconds at which Company A’s data is being
updated. Typically 10 seconds.
11. ISN style NSAP’s:
O
A collection of NSAP’s have been assigned by ICI for
use by ISN ICCP nodes. These all use a particular
addressing scheme called ISN style NSAP’s.
Alternatively, some ICCP nodes are using TCP/IP only
or are using their own NSAP addressing scheme.
Typically “yes”.
July 15, 1999
{iccp_aief.doc}
3
R
Ver 2.0
ICCP Association Information Exchange Form
12. OSI routing Company A’s router:domain of
If you are using ISN style NSAP’s, this 4 byte number
is part of the company-B’s router configuration and
consists of a 2 byte Domain ID and a 2 byte Area ID.
If you are using OSI, but not using ISN style NSAP’s
then enter the full hex string. If you are using TCP/IP,
then leave this blank.
13. IP address of the WAN port on Company A’s router.
If you are using TCP/IP, this field is either a fully
qualified domain name or a 12 integer number
delimited with periods.
14. Transport Layer Ack Time:
R
R
This field indicates a maximum time in seconds that can
elapse between receipt of a TPDU by Transport from
the network layer and the transmission of the
corresponding acknowledgment. Typically 5 seconds.
15. Transport Layer Retransmission Time:
O
This field indicates the maximum time in seconds
Transport will wait for an acknowledgment before
retransmitting a TPDU. Typically 10 seconds.
16. Transport Layer Window Time:
O
This field indicates a maximum time in seconds that
Transport will wait before retransmitting up-to-date
window information. Typically 10 seconds.
17. Number of Retries:
O
This field indicates the maximum number of attempts to
retransmit a TPDU before issuing a Disconnect
Request. Typically 6.
18. Maximum MMS PDU size.
O
Size in bytes of the maximum MMS protocol data unit.
Typically 8k bytes or more.
July 15, 1999
{iccp_aief.doc}
4
O
Ver 2.0
ICCP Association Information Exchange Form
Table 2: ICCP Server specific information
(This table should be duplicated for each ICCP server installed)
1.
Server name:
The name by which company-A refers to this server.
This field is not electronically transmitted during any
ICCP transactions, but is only here to facilitate verbal
communication between Company A and Company B.
2. Server number:
O
“1” if this is the primary server, “2” if this is the first
backup, etc.
3. IP network address:
R
If you are using TCP/IP, this optional field is the IP
address for this ICCP server if TCP/IP can be used as
the network transport.
4. AP Title:
R
Object identifier representing the Application Process
Title given to this application. The standardized format
of the AP Title is found in Appendix B.
5. AP Invoke ID
M
A long integer used to identify an invocation instance of
the application process. Typically not specified.
6. AE Qualifier
O
A long integer (32 bit signed) is used to qualify the
application entity.
7. AE Invoke ID
O
Used to identify an invocation instance of the
application entity. Typically not specified.
8. Presentation Selector (PSEL)
O
2 or 4 byte number used to select the correct instance of
the presentation layer (e.g. 00 09 or 00 00 00 09).
9. Session Selector (SSEL)
M
2 or 4 byte number used to select the correct instance of
the session layer (e.g. 00 09 or 00 00 00 09).
10. Transport Selector (TSEL)
M
2 or 4 byte number used to select the correct instance of
the session layer (e.g. 00 09 or 00 00 00 09).
11. Complete NSAP
M
A number that represents the OSI network address for
Company A’s ICCP node. The NSAP can be up to 20
bytes long. For ISN nodes, the first 7 bytes should be
(in hex): 39 840f 80 113826. For a more detailed
discussion of NSAP’s see Appendix A.
July 15, 1999
{iccp_aief.doc}
5
R
Ver 2.0
ICCP Association Information Exchange Form
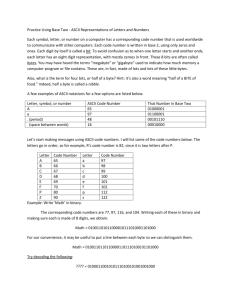
Appendix A: Explanation of ISN Style NSAP’s
ISN Style NSAP have the following form (in hex):
39 840f 80 113826 0000 rrrr aaaa dddddddddddd nn
The first byte contains the Authority Format ID (AFI) where 39 is for ISO
The next two bytes contain Initial Domain ID (IDI) where 840F is for USA
The next byte contains the Domain Format ID (DFI) where 80 is for GOSIP style format
The next three bytes contain the organization ID where 113826 is for NERC
The next two bytes is a reserved field and should be set to 0000
rrrr = Routing Domain ID (Contact NERC for this value)
aaaa = Area (Contact NERC for this value)
dddddddddddd = Station ID (see below)
nn = NSEL (see below)
ISN Style Station ID Addressing Standard
The next to last 6 bytes of the NSAP contain the Station ID. The Station ID format is:
Bytes 1-4
ASCII code in hex of the registered SiteID of the ISN (or other ICCP)
Node with padded underscore(s) as needed.
Byte 5
ASCII code in hex of the node number on which the server is running. For
example, if the node number is equal to ‘1’ then byte 5 should contain hex
31.
Byte 6
ASCII code in hex indicating the application specification of the Protocol:
Hex 49 for ICCP
Examples:
SC__1I
ECAR1I
ECAR2I
53
45
45
43
43
43
5F
41
41
5F
52
52
31
31
32
49
49
49
ASCII to Hex and Conversion Table for Station ID’s:
ASCII
Hex ASCII
Hex ASCII
_
5F
9
39
I
1
31
A
41
J
2
32
B
42
K
3
33
C
43
L
4
34
D
44
M
5
35
E
45
N
6
36
F
46
O
7
37
G
47
P
8
38
H
48
Q
Hex
49
4A
4B
4C
4D
4E
4F
50
51
ASCII
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
Hex
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
5A
Note: NSAP’s are always specified in hex while the AP Title standard in Appendix B
consists of a set of decimal numbers. Use this table to translate your site id into hex for
the station ID portion of your NSAP’s.
July 15, 1999
{iccp_aief.doc}
6
Ver 2.0
ICCP Association Information Exchange Form
The Network Selector or NSEL is the last byte of the NSAP and is used to select the
correct instance of the Network layer. Some DECnet/OSI systems will automatically
assign this a value (20 hex for Phase IV NSP transport, 21 hex for OSI transport TP4).
Other OSI stacks do not impose this requirement. The recommended value for systems on
which it is not automatically assigned is 01.
July 15, 1999
{iccp_aief.doc}
7
Ver 2.0
ICCP Association Information Exchange Form
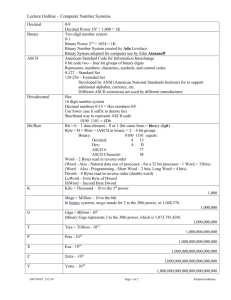
Appendix B: Mandatory AP Title Standard
The AP Title is used by some ISO applications to determine what application is calling
since NSAP’s, TSEL’s, SSEL’s and PSEL’s of the caller may not passed to applications
upon association. The AP Title consists of 9 16 bit decimal numbers:
Field Name
Field format
1
2
3
One single 16 bit One 16 bit
Seven 16 bit decimal integers
decimal integer) decimal integer
Required value
2
16 (country 3826 XXXX XXXX XXXX XXXX YYYY
in decimal
(joint-iso-ccitt) based naming
0073
hierarchy)
(3826 is the abbreviated NERC org ID used
to specify ISN applications), XXXX XXXX
XXXX XXXX is for the registered ISN node
ID in decimal (one 16 bit decimal number for
each ASCII character in the site ID including
padding underscores), YYYY is the for the
node number (one 16 bit decimal number),
the last 16 bit number is an application
specification where decimal 0073 indicates
ICCP.)
For example, an ICCP application at MAIN1 would have an AP Title of:
0002 0016 3826 0077 0065 0073 0078 0049 0073
Note: Some ICCP vendors do not provide a user interface for setting AP Titles. In this
case the user may be required to manually edit a Directory Information Base ASCII file.
ASCII to Hex and Decimal Conversion Table:
ASCII
Dec
ASCII
Dec
ASCII
Dec
ASCII
_
95
9
57
I
73
R
1
49
A
65
J
74
S
2
50
B
66
K
75
T
3
51
C
67
L
76
U
4
52
D
68
M
77
V
5
53
E
69
N
78
W
6
54
F
70
O
79
X
7
55
G
71
P
80
Y
8
56
H
72
Q
81
Z
Note: Only use this ASCII conversion table to calculate the AP Title.
Dec
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
July 15, 1999
Ver 2.0
{iccp_aief.doc}
8
ICCP Association Information Exchange Form
Revision history:
Version Date Comments
1/16/98
Added transport layer parameters
Added AP Title and NSAP appendices
1/23/98
Fixed IP addressing and association
parameter errors
Changed AP Title standard
2/24/98
Added ICCP vendor information
5/20/98
Added more instructions to help user
fill out forms.
5/26/98
Added cover page
Added M,R,O column
9/25/98
Moved rows (formerly labeled 2.3 –
2.8 now labeled 1.3 – 1.8). Deleted
row (formerly labeled 1.5)
12/1/98
In table 2, changed fields 4, 8, 9, and
10 from “Recommended” to
“Mandatory”
1/19/99
Fixed typographical errors
5/13/99
Moved Association type and initiator
from Table 2 to Table 1. Updated
version number and date in header/
footer. [kbp]
7/15/1999
Made AP Titles mandatory per
Version 2.0
Appendix B. Removed John
Gillerman as document owner.
Upgraded document to Version 2.0.
July 15, 1999
{iccp_aief.doc}
9
Ver 2.0