STANDARD 4 COMPONENT 10 Objective: a. Analyze the cyclic
advertisement

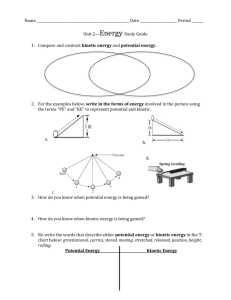
STANDARD 4 COMPONENT 10 Objective: a. Analyze the cyclic nature of potential and kinetic energy (e.g., a bouncing ball, a pendulum). Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. kinetic/mechanical energy : The energy an object has due to its motion. energy : Ability to do work or cause change gravitational potential energy : The energy stored in an object due to its height above the Earth cyclic : The tendency of something to repeat over and over. potential energy : Energy that is stored and available to be used later Learning Activities The Triangle of Doom Class Activity and Notes-See me for these. Standard 4 COMPONENT 10 Essential Questions 1.) Describe how a pendulum shows the change from gravitational potential energy to kinetic energy. 2.) Fill out the similarity difference matrix below. Definition 2 examples Synonym/restate Similarities Kinetic Energy Differences Gravitational Potential Energy 3.) If you dug a hole all the way through the Earth from one side to another and dropped a mass in one end what would happen to the mass? How would it behave? Standard 4 COMPONENT 10 Practice Vocabulary Quiz 1. The energy an object has due to its motion. a. kinetic/mechanical energy b. gravitational potential energy c. cyclic d. potential energy 2. Ability to do work or cause change a. kinetic/mechanical energy c. energy b. gravitational potential energy d. potential energy 3. The energy stored in an object due to its height (position) above the Earth a. kinetic/mechanical energy c. energy b. gravitational potential energy d. potential energy 4. The tendency of something to repeat over and over. a. kinetic/mechanical energy c. cyclic b. gravitational potential energy d. potential energy 5. Energy that is stored and available to be used later a. kinetic/mechanical energy c. cyclic b. gravitational potential energy d. potential energy Standard 4 COMPONENT 10 Practice Content Quiz 1. Using the picture below. Where in the balls path is its potential energy the most? a. A b. B c. C d. D 2. Using the picture above. What is happening to the ball’s potential and kinetic energy between points “B” and “C”? a. potential energy is decreasing and kinetic energy is increasing b. both kinetic and potential energy first increase then decrease c. both kinetic and potential energy first decrease then increase d. kinetic energy is decreasing and potential energy is increasing 3. Where is kinetic energy the greatest in the picture above? a. A b. B c. C d. D 4. Which statement best describes the energy conversions taking place as the ball is first tossed up and then comes down? a. kinetic and potential energy are equal going up and coming down b. energy transfers from kinetic to potential and back to kinetic c. energy transfers from potential to kinetic and back to potential d. energy transfers back and forth between potential and kinetic going up and coming down 5. Use the pendulum to answer the following question. How much gravitational potential energy is contained at position E? a. 500 J b. 375 J c. 125 J d. 0 J Standard 4 COMPONENT 10 Essential Questions Key 1.) Describe how a pendulum shows the change from gravitational potential energy to kinetic energy. When the pendulum is raised high it stores only gravitational potential energy. There is not kinetic because it is not moving yet. When the pendulum is released and gains speed the gravitational energy decreases and is changed into kinetic energy. As it moves faster there is less and gravitational because it is getting lower and going faster. However, because of the increased speed the kinetic energy is increasing. This happens until it is at its lowest point, where it is traveling the most, and has the most kinetic energy and no gravitational potential energy. The process is then repeated as the pendulum swings forward and up on the other side. An important note is that if the pendulum is considered frictionless then the kinetic added to the gravitational energy will always add up to the amount you started with. 2.) Fill out the similarity difference matrix below. Kinetic Energy Definition 2 examples The energy an Moving car object has due to its Synonym/restate Energy of motion, the faster Similarities They are both types of energy. motion. Gravitational Potential Energy Running person The energy stored in an object due to its height above the Earth A rock perched high on a cliff. A skydiver about to jump out of a plane something is moving the more kinetic energy it has. Energy of height. The higher something is and the larger it is the more stored gravitational energy it has. The pendulum has some value for each type of energy at each position. Differences Kinetic is because of the motion of mass and gravitational potential is because of height. 3.) If you dug a hole all the way through the Earth from one side to another and dropped a mass in one end what would happen to the mass? How would it behave? When you drop the mass in one of the holes it would accelerate to the center of the Earth. It would then pass pst the center of the Earth, but begin to slow down as it reached the other opening on the other side. At this point it would momentarily stop and then begin falling back to the center of the Earth and repeat the process. Assuming no friction this cyclic falling back and forth would continue for ever. Standard 4 COMPONENT 10 Practice Vocabulary Quiz Key 1. The energy an object has due to its motion. a. kinetic/mechanical energy c. cyclic b. gravitational potential energy d. potential energy 2. Ability to do work or cause change a. kinetic/mechanical energy c. energy b. gravitational potential energy d. potential energy 3. The energy stored in an object due to its height (position) above the Earth a. kinetic/mechanical energy c. energy b. gravitational potential energy d. potential energy 4. The tendency of something to repeat over and over. a. kinetic/mechanical energy c. cyclic b. gravitational potential energy d. potential energy 5. Energy that is stored and available to be used later a. kinetic/mechanical energy c. cyclic b. gravitational potential energy d. potential energy Standard 4 COMPONENT 10 Practice Content Quiz Key 1. Using the picture above. Where in the balls path is its potential energy the most? a. A b. B c. C d. D 2. Using the picture above. What is happening to the ball’s potential and kinetic energy between points “B” and “C”? a. potential energy is decreasing and kinetic energy is increasing b. both kinetic and potential energy first increase then decrease c. both kinetic and potential energy first decrease then increase d. kinetic energy is decreasing and potential energy is increasing 3. Use the picture above. Where is kinetic energy the greatest? a. A b. B c. C d. D 4. Which statement best describes the energy conversions taking place as the ball is tossed up and comes down? a. kinetic and potential energy are equal going up and coming down b. energy transfers from kinetic to potential and back to kinetic c. energy transfers from potential to kinetic and back to potential d. energy transfers back and forth between potential and kinetic going up and coming down 5. Use the pendulum to answer the following question. How much gravitational potential energy is contained at position E? a. 500 J b. 375 J c. 125 J d. 0 J