Plant Hormone
advertisement

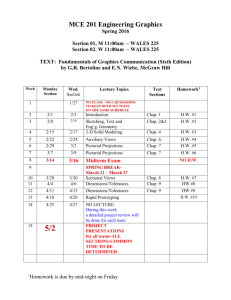
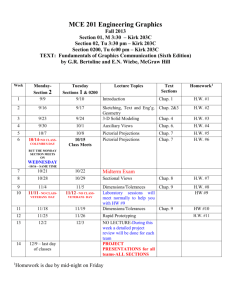
Plant Hormone 植物荷爾蒙 課程代碼: 3296 Dr. CHIN HO LIN Life science, NCHU 1. Define (a). Plant hormone (b). Plant growth regulator (Chap.1. 高) 2. Is plant development regulated by changes in the concentration of growth substances or by changes in the sensitivity to growth substances? State and compare Trewavas’s view on sensitivity to growth substances vs. Cleland’s view on changes of hormone concentration. *Ref.:p.322. Salisbury & Ross. 1985.Plant Physiology. 3rd edition. 3. Define: totipotency , diagram and explain F.C. Steward’s work (1964, Science 143:20-24) on carrot cell regeneration as example. 4. IAA biosynthesis and decomposition pathway in higher plant. What is the precursor of IAA synthesis? *reference:1. (S&R)Plant Physiology. Wodwrorth, Co. 2. L. Taiz and E.Zeiger. Plant Physiology. The Benjamin/ Cummings Publishing Co., Inc. (T&Z) 5. Diagram and explain chemiosmotic hypothesis of IAA polar transport.( p406. T&Z ) 6. Summerize (a) two stages of GA biosynthesis. (b) List 3 types of GA biosynthesis inhibitors, explain their respective mode of inhibition. *reference:1. Salisbury and Ross.1985. pp:321. 2. Taiz and Zejger. 1991. pp:426-433. 3. 林金和,王麗華.1992. GA 生合成抑制劑之生理探討. Weed Sci, Bull.13(1):31-39. 4. (高 Chap 3 P56) ★ Homework: 1. 2. 3. 4. 6. 7. 10. 11. 12. 13. 15. 21. 24. 26. 28 7. List 2 types of GA functions, relate their chemical-structural relationship. *reference: R.P. Pharis. Chap.16. pp:166-178. In Gibberellins. Takahashi et al. 1991. Springer Verlag. 8. Explain microdrop bioassay of GA using dwarf rice. *reference: Taiz and Zeiger.1991. pp:433-435. 9. List the chemical structure and classify natural cytokinin from synthetic cytokinin (高,Chap 4) 10. Relate, Agrobacterium, crown gall turmor, auxin and cytokinin synthetic capability. What’s mechanism of Agrobacterium induced crown gall tumor? 11. (a) Briftly summarize ABA discovery. (b) Major pathway of ABA synthesis and its synthesis inhibitor. (c) Major product of ABA degradation. 12. (a) Morphological symptom of seedlings in response to ethylene treatment. (b) Triple response. (c) Importance of methionine and CH3S and ACC in ethylene synthesis. (d) Climacteric vs. non-climacteric rise of fruit ripening. (高,pp:115-116) (e) Regulation of ethylene action. (f) At appropriate steps mark what treatment (physical、chemical) can stimulate or inhibit ethylene biosynthesis. 13. (a) Named and classify polyamine. (b) Competition between polyamine synthesis and other hormone and what is the impact of this competition. (c) List the polyamine synthesis inhibitor. (d) What’s relation between polyamine and K+ in plant tissue. (e) Explain the transport of polyamine. 14. List and explain Jasmonic acid or methyl Jasmonate, show their plant hormone activity (Quote the reference) (Chap 9,Kao) 15. (a) What is a Fusicoccin (b) Explain how Fusicoccin stimulate growth (see. acid growth, chap 15,Kao) (c) How does Fusicoccin cause leaf wilting and dehydration in Fusicoccum amygdali infested plant?(chap,10 Kao) 16. (a) short day plant (b) long day plant (c) day neutral plant (d) critical day length (e) dark reversion and inversed dark reversion of phytochrome (f) draw the chemical structure of a phytochrome (g) What is the precursor of phytochrome chromophore (h) localization of phytochrome within the cell (i) Explain mode of action of phytochrome (chap 11, Kao) 17. Explain epinasty 18. Elaborate GA biosynthesis pathway? 19. What is acid growth theory? 20. What’s growth mechanism of adventitious root upon cutting? 21. List 3 types of substances which may considered as new hormone and briefly explain their structure and function. 22. The change of hormone after flooding. 23. Elaborate mechanism of monocotyledon seed germination? 24. Following listed physiological phenomenon, which are caused by plant hormone?Explain it. (1) leaves fall (2) apical dominance (3) cell growth (4) photoperiodism 25. Elaborate mechanism of castor bean seed germination? 26. Diagram the change of ethylene and CO2 concentration in climacteric fruit ripening. 27. Describe mechanism of cell growth. 28. List 3 practical agricultural use of each plant hormone (5 kinds).