the endocrine system
advertisement

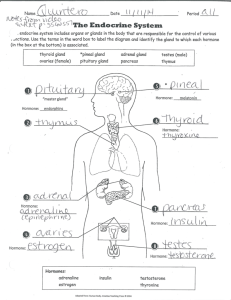
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The endocrine is a body control system. It affects bodily activities by releasing chemical messages, hormones, into the blood stream. It contains 2 types of glands, the endocrine and exocrine glands. The endocrine glands form what is generally referred to as a system, yet the fact that they are not directly inter-connected seems to contradict this classification. These glands occur through the body at various sites secreting special products called hormones directly into the surrounding tissues. Hormones are like chemical agents, which help to organize and control the function of various other glands and activities such as growth, metabolism, menstruation and immune function. Exocrine glands secrete their products into ducts. The ducts then carry the secretions into body cavities or to the body's surface. They include sweat, sebaceous, mucous and digestive glands. Endocrine glands are ductless glands and secret their products directly into the blood. They include the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroids, adrenal, and pineal glands as well as the pancreas, ovaries, and testes. Hormones are chemical substances that function to maintain the homeostasis (balance) of the body by stimulating changes in the cells in body organs. Pituitary gland regulates many body activities and is nicknamed the 'master gland'. It is located at the base of the brain, in an area called the hypothalamus. It produces many hormones the main one being the Human Growth Hormone (HGH), which causes growth of cells and the body. Thyroid gland is situated just below the larynx and has two lobes on either side of the trachea. It is a shield shaped gland. The principal hormone it produces is called thyroxine. Thyroxine controls metabolism by increasing the rate at which carbohydrates are burned and proteins and fats are broken down. It also helps regulate growth. Parathyroid glands are four small glands attached to the outer surface of the thyroid gland. They release the parathyroid hormones (PTH). PTH control the homeostasis of the blood, especially calcium and phosphate. The adrenal glands are small, triangular shaped glands located just above each kidney. They are divided into the outer adrenal cortex and the inner adrenal medulla. The adrenal cortex secretes hormones called corticosteroids, which have many functions including anti-inflammatory functions. The adrenal medulla secretes i) adrenalin and ii) noradrenaline both of which affect the central nervous system. The pineal gland is located in the brain. It secretes at least one hormone, melatonin, which appears to affect the secretion of hormones by the ovaries. Its other functions are somewhat obscure but has an effect on the sleeping cycle. The pancreas is both an exocrine and endocrine gland. The endocrine portion consists of clusters of cells called the Islets of Langerhans. It secrets insulin, a hormone which controls the blood sugar level. Endocrine System Page 1 of 4 The gonads are the ovaries and the testes. The ovaries secrete oestrogens and progesterone, and the testes secrete testosterone. HYPO AND HYPER SECRETION - Hypersecretion is oversecretion while hyposecretion is undersecretion of hormones. Each condition can cause many disorders. Glands: Pituitary gland The root word is pituita and the combining form is -pituitar- Thyroid The root word is thyr and the combining form is thyr/o, -thyroid- Parathyroid The root word is parathyr and the combining form is parathyr/o, -parathyroidAdrenal The root word is adren and the combining form is adren/o Pineal Endocrine System FSH,(follicle stimulating hormone) LH, (leutinising hormone) HGH, (human growth hormone) ACTH (adrenocorticotrophic hormone), TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone), ADH (anti-diuretic hormone) Master Gland. Regulates growth, metabolism, kidneys and sex Hypersecretion: (1) Gigantism and (2) Acromegaly (where the bones of the face, hands and feet are enlarged) Hyposecretion: Dwarfism and Acromicria Hyposecretion of ADH leads to diabetes insipidus Thyroxin Regulated by the pituitary gland - metabolic rate. Hyperthyroidism or Grave’s disease characterised by an increased basal metabolic rate and increased pulse, also exophthalmos which is the distension of the eyeballs. Thyrotoxicosis - syndrome due to excessive amounts of thyroid hormones in the blood Hypothyroidism or Goitre - enlargement of the thyroid gland which can lead to the need for a thyroidectomy. Myxoedema causes swelling of the face, limbs, and hands, slow metabolism and mental dullness. Congenital myxoedema is called cretinism Parathyroid hormone - Calcium metabolism, regulates calcium for use in bone growth, muscle tone, & nervous activity. Hyperparathyroidism causes softening of the bone Hypoparathyroidism leads to spasmodic twitching and contractions of muscles which is called tetany. Adrenaline, Cortisol, Regulated by the pituitary. Secretes steroid and helps the body cope with stress. Regulates balance between salt and water Hypersecretion: Cushing’s syndrome (hypercortisolism) characterised by protein loss, fatigue, osteoporosis, diabetes insipidus and oedema. Hyposecretion: Addison’s disease (hypocortisolism) characterised by weight loss, low blood sugar, low blood pressure, depression and salt cravings. Produces melatonin, a hormone which modulates wake/sleep patterns and the gonads. It regulates both sleeping cycles and the hormonal changes that usher in sexual maturity during adolescence. Page 2 of 4 Pancreas The root word is pancreat and the combining form is pancreat/o Gonads Hypothalamus Thymus Endocrine – insulin controls level of sugar in the blood Exocrine – Pancreatic enzymes to aid in digestion High insulin levels - hyperglycaemia. Diabetes Mellitus results in excess sugar in the blood - Causes damage to blood vessels and organs kidneys and eyes. Low insulin levels – hypoglycaemia - characterised by fainting and coma Regulated by the pituitary. Sex glands, Ovaries - oestrogen and progesterone. Testes - Testosterone Regulates the autonomic nervous system - integration of endocrine and nervous systems Doubles in size at puberty, shrinks in an adult. Immunological role, initiates antibody formation in the blood Terms and word parts: aden/o adren/o adrenocortic/o andr/o -crine end/o -globulin glyc/o -gyne hormone hyperhypoinsulin/o kal/i ket/o -micria natr/i oestr/o parathyroid/o pituitar-plasia progest/o -ptosis thyroid/o -trophic -tropic Endocrine System gland adrenal gland adrenal cortex male to secrete within protein sugar woman a specific chemical that regulates other cells or organs above, excessive below, insufficient insulin potassium ketones condition of small size sodium oestrogen parathyroid gland pituitary condition of growth/formation of (cells) progesterone falling / displacement / prolapse thyroid gland pertaining to nourishment pertaining to affinity for / stimulating Page 3 of 4 Abbreviations: BSL BSS FBS GTT HRT blood sugar level blood sugar series fasting blood sugar glucose tolerance test hormone replacement therapy Diabetes: Diabetes Type I IDDM Insulin Dependent - pancreas doesn't make enough insulin. Formerly called Juvenile Onset Diabetes. Due to beta cell destruction. Diabetes Type II NIDDM Non-insulin dependent - pancreas makes enough insulin, but the patient's cells do not use insulin properly. Formerly called Mature Onset Diabetes Activity: Build a word which means: 1. process of secreting above normal levels of thyroid hormone ______________ 2. enlarged adrenal gland 3. condition of too little sodium in the blood ______________________________ 4. process of producing too much insulin ________________________________ 5. incision into the thyroid cartilage ____________________________________ _________________________________________ Find the meaning of the following words: 1. thyroparathyroidectomy _________________________________________ 2. pituicyte _________________________________________ 3. hypernatraemia _________________________________________ 4. androblastoma _________________________________________ 5. adrenocorticohyperplasia _________________________________________ Endocrine System Page 4 of 4