ch01 - WordPress.com
advertisement

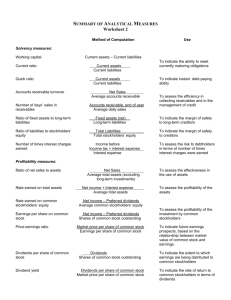
CHAPTER 1 THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Use accounting vocabulary for decision making Apply accounting concepts and principles Use the accounting equation to describe an organization Evaluate a company’s operating performance, financial position, and cash flows Explain the relationships among the financial statements QUESTIONS ON OPENING VIGNETTE 1. The income statement for Yum! Brands’ details the firm’s earned revenues and net income. What is the meaning of these accounting terms? Solution: Revenues are increases in retained earnings from delivering goods and services to customers or clients. Net income is the difference between the revenues earned during the accounting period and the expenses incurred to earn the revenues. (easy, L.O. 1) 2. Who are investors and what information does a potential investor need from Yum! Brands? Solution: Investors (along with creditors) provide money to finance the operations of Yum! Brands. They need relevant and reliable information regarding the amount they can expect to earn from their investment in Yum! Brands. (medium, L.O. 4) TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS 3. Bookkeeping is a type of accounting used primarily by sole proprietorships. (medium, L.O. 1, false) 4. The three forms of business organizations are sole proprietorships, partnerships, and notfor-profit organizations. (easy, L.O. 1, false) 5. Relevant and reliable accounting information is required to convince an investor to invest money in a particular company. (easy, L.O. 1, true) 6. All business owners are personally liable for the debts of their businesses. (easy, L.O. 1, false) 1-1 7. From both an accounting and a legal viewpoint, a proprietorship is a distinct and separate entity from the proprietor. (moderate, L.O. 1, false) 8. Generally accepted accounting principles, or GAAP, are the rules and procedures established by the Financial Accounting Standards Board, or the FASB. (easy, L.O. 2, true) 9. The stable monetary unit concept means that the type of currency used for the financial statements is not expected to change. (moderate, L.O. 2, false) 10. The objectivity principle states that assets and services should be recorded at their actual cost, since cost is a reliable measure to use in financial accounting. (moderate, L.O. 2, false) 11. The accounting equation expresses the idea that Resources = Outsider claims + Insider claims. (difficult, L.O. 3, true) 12. The accounting equation must always be in balance. (easy, L.O. 3, true) 13. Liabilities are divided into "outsider claims" and "insider claims." (moderate, L.O. 3, false) 14. Stockholders’ equity is often referred to as "net assets" and represents the residual amount of business assets which can be claimed by the owners. (moderate, L.O. 3, true) 15. Common stock and net income are the main components of paid-in capital. (moderate, L.O. 3, false) 16. Retained earnings represent cash that is available to a company for future operations and expansion. (difficult, L.O. 3, false) 17. Net income appears on both the income statement and the balance sheet. (medium, L.O. 3, false) 18. The statement of retained earnings is organized in terms of the organization’s operating, investing, and financing activities. (medium, L.O. 3, false) 19. Expenses are decreases in retained earnings that result from operations. (moderate, L.O. 3, true) 20. For business purposes, dividend payments are classified as expenses. (moderate, L.O. 3, false) 1-2 21. The computation of ending retained earnings considers current net income or net loss and dividends. (moderate, L.O. 3, true) 22. The owners’ equity of proprietorships and partnerships is different. (medium, L.O. 3, true) 23. The statement of cash flows reports on where cash came from and how it was used. (moderate, L.O. 4, true) 24. In accounting, the word "net" means after a subtraction. (moderate, L.O. 4, true) 25. The owners’ equity of a partnership includes both partner stock and partner earnings. (difficult, L.O. 4, true) 26. A balance sheet reports the company’s financial position at a specific point in time. (medium, L.O. 4, true) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 27. The two types of accounting are: a. financial and managerial b. internal and external c. bookkeeping and decision-oriented d. profit and nonprofit (medium, L.O. 1, a) 28. According to the author, potential investors need information that is: a. fair and future-oriented b. accurate and truthful c. relevant and reliable d. audited and complete (medium, L.O. 1, c) 29. Who ultimately controls a corporation? a. the chief executive officer b. board of directors c. president d. the stockholders (medium, L.O. 1, d) 1-3 30. Financial statements are: a. reports issued by outside consultants who are hired to analyze key operations of the business b. reports created by management that states it is responsible for the acts of the corporation c. standard documents that tell us how well a business is performing and where it stands in financial terms d. standard documents issued by outside consultants who are hired to analyze key operations of the business in financial terms (easy, L.O. 1, c) 31. For which form of business ownership are the owners of a business legally distinct from the business? a. proprietorship b. partnership c. corporation d. all of the above (easy, L.O. 1, c) 32. All of the following are forms of business organizations except: a. proprietorship b. partnership c. restaurant d. corporation (easy, L.O. 1, c) 33. The largest organization of professional accountants in the United States is the: a. American Institute of Certified Public Accountants b. Securities and Exchange Commission c. Financial Accounting Standards Board d. Auditing Standards Board (moderate, L.O. 1, a) 34. The Financial Accounting Standards Board is responsible for establishing: a. the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants b. the Securities and Exchange Commission c. generally accepted accounting principles d. the code of professional conduct for accountants (moderate, L.O. 2, c) 35. The acronym GAAP stands for: a. government audited accounting pronouncements b. generally accepted accounting principles c. government authorized accountant principles d. generally acceptable authorized pronouncements (moderate, L.O. 2, b) 1-4 36. All of the following are characteristics of useful accounting information except: a. relevant b. informative c. consistent d. reliable (moderate, L.O. 2, b) 37. The objectivity principle of accounting: a. maintains that each organization or section of an organization stands apart from other organizations and individuals b. ensures that accounting records and statements are based on the most reliable data available c. holds that the entity will remain in operation for the foreseeable future d. enables accountants to ignore the effect of inflation in the accounting records (moderate, L.O. 2, b) 38. The stable-monetary-unit concept of accounting: a. maintains that each organization or section of an organization stands apart from other organizations and individuals b. ensures that accounting records and statements are based on the most reliable data available c. holds that the entity will remain in operation for the foreseeable future d. enables accountants to ignore the effect of inflation in the accounting records (moderate, L.O. 2, d) 39. The going-concern concept of accounting: a. maintains that each organization or section of an organization stands apart from other organizations and individuals b. ensures that accounting records and statements are based on the most reliable data available c. holds that the entity will remain in operation for the foreseeable future d. enables accountants to ignore the effect of inflation in the accounting records. (moderate, L.O. 2, c) 40. The principle which states that assets acquired by the business should be recorded at their actual price is the: a. objectivity principle b. stable dollar principle c. cost principle d. reliability principle (easy, L.O. 2, c) 41. The reliability principle is also called the: a. full and fair principle b. truthfulness concept c. relevance concept d. objectivity principle (moderate, L.O. 2, d) 1-5 42. Which of the following statements below is false? a. The informed opinion of owners is an important source of objective evidence. b. Reliable data may be supported by objective evidence. c. An independent appraisal, conducted by a licensed professional, is usually considered reliable. d. Reliable data are verifiable. (moderate, L.O. 2, a) 43. The relevant measure of value of the assets of a company that is going out of business is its: a. historical cost b. recorded value c. book value d. current market value (moderate, L.O. 2, d) 44. The CEO of a business owns a residence in Phoenix. The company the CEO works for owns a residence in Tucson used for strategic planning meetings by its executives. Which of these properties is considered assets of the business? a. the Phoenix residence only b. the Tucson residence only c. both the Phoenix and Tucson residences d. neither the Phoenix nor Tucson residences (moderate, L.O. 2, b) 45. An Oklahoma City business paid $25,000 cash for equipment used in the business. At the time of purchase, the equipment had a list price of $30,000. When the balance sheet was prepared, the value of the equipment later rose to $32,000. What is the relevant measure of the value of the equipment? a. historical cost, $25,000 b. fair market cost, $30,000 c. current market cost, $32,000 d. $25,000 on the day of purchase, $32,000 on balance sheet date (moderate, L.O. 2, a) 46. The accounting equation can be stated as: a. Assets + Liabilities = Stockholders’ equity b. Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders’ equity c. Assets = Liabilities - Stockholders’ equity d. Assets + Stockholders’ equity = Liabilities (easy, L.O. 3, b) 47. Which of the following best describes a liability? a. Liabilities are a form of paid-in capital. b. Liabilities are future economic benefits to which a company is entitled. c. Liabilities are accounts receivable of the corporation. d. Liabilities are economic obligations to creditors to be paid at some future date by the corporation. (easy, L.O. 3, d) 1-6 48. The owners’ interest in the assets of a corporation is known as: a. long-term assets b. stockholders’ equity c. operating expenses d. common stock (moderate, L.O. 3, b) 49. Claims held by the stockholders of a corporation are alternately known as: a. retained earnings b. paid-in capital c. earned income d. paid-in capital plus retained earnings (difficult, L.O. 3, d) 50. Payables are classified as: a. increases in earnings b. assets c. decreases in earnings d. liabilities (easy, L.O. 3, d) 51. Receivables are classified as: a. increases in earnings b. assets c. decreases in earnings d. liabilities (easy, L.O. 3, b) 52. The sum of "outsider claims" plus "insider claims" equals: a. total assets b. net income c. total stockholders’ equity d. total liabilities (difficult, L.O. 3, a) 53. Revenues are: a. increases in liabilities resulting from delivering goods or services to customers b. increases in retained earnings resulting from delivering goods or services to customers c. decreases in assets resulting from delivering goods or services to customers d. decreases in retained earnings resulting from delivering goods or services to customers (moderate, L.O. 3, b) 54. How do revenues for a period relate to the beginning and ending balances in retained earnings? a. Revenues will increase the beginning balance of retained earnings for the period. b. Revenues will decrease the beginning balance of retained earnings for the period. c. Revenues less expenses will either increase or decrease the beginning balance of retained earnings for the period. d. None of these answers are correct. (moderate, L.O. 3, c) 1-7 55. Expenses are: a. increases in assets resulting from operations b. increases in retained earnings resulting from operations c. increases in liabilities resulting from purchasing assets d. decreases in retained earnings resulting from operations (moderate, L.O. 3, d) 56. Dividends: a. always affect net income b. are distributions to stockholders of assets (usually cash) generated by net income c. are expenses d. are distributions to stockholders of assets (usually cash) generated by a favorable balance in retained earnings (moderate, L.O. 3, b) 57. A corporation’s paid-in capital consists of a. assets and liabilities b. revenues and expenses c. net income and dividends d. common stock and retained earning (moderate, L.O. 3, d) 58. Net income is computed as: a. revenues – expenses b. revenues + expenses c. revenues – expenses + dividends d. revenues – expenses – dividends (moderate, L.O. 3, a) 59. Which of the following must be added to beginning Retained Earnings to compute ending Retained Earnings? a. revenues b. expenses c. dividends d. All of these answers are correct. (moderate, L.O. 3, a) 60. At the end of the current accounting period, account balances were as follows: Cash, $150,000; Accounts Receivable, $50,000; Common Stock, $10,000; Retained Earnings, $60,000. Liabilities for the period were: a. $ 80,000 b. $130,000 c. $140,000 d. $190,000 (moderate, L.O. 3, b) 1-8 61. On January 1, 2004, total assets for Liftoff Technologies were $125,000; on December 31, 2004, total assets were $145,000. On January 1, 2004, total liabilities were $110,000; on December 31, 2004, total liabilities were $115,000. What is the amount of the change and the direction of the change in Liftoff Technologies' stockholders’ equity for 2004? a. decrease of $15,000 b. increase of $15,000 c. increase of $30,000 d. decrease of $30,000 (moderate, L.O. 3, b) 62. Revenues were $150,000, expenses were $70,000, and cash dividends were $30,000. What was the net income and the change in retained earnings for the period? Net Income a. $50,000 b. $80,000 c. $80,000 d. $250,000 (moderate, L.O. 3, b) Change in Retained Earnings $50,000 $50,000 $80,000 $250,000 63. At the beginning of the period assets were $400,000 and stockholders’ equity was $150,000. During the year assets increased by $30,000, liabilities increased by $50,000, and stockholders’ equity was unchanged. Beginning liabilities must have been: a. $230,000 b. $250,000 c. $280,000 d. $300,000 (difficult, L.O. 3, b) 64. If assets increase $120,000 during a given period and liabilities decrease $25,000 during the same period, stockholders’ equity must: a. increase $95,000 b. decrease $145,000 c. decrease $95,000 d. increase $145,000 (difficult, L.O. 3, d) 65. If liabilities increase $120,000 during a given period and stockholders’ equity decreases $25,000 during the same period, assets must: a. decrease $145,000 b. increase $145,000 c. increase $95,000 d. decrease $95,000 (difficult, L.O. 3, c) 1-9 66. Stockholders’ equity for Commerce-GA Corporation on 01/01/2006 and 12/31/2006 were $60,000 and $75,000, respectively. Assets on 01/01/2006 and 12/31/2006 were $115,000 and $105,000, respectively. Liabilities on 01/01/2006 were $55,000. What is the amount of liabilities on 12/31/2006? a. $40,000 b. $15,000 c. $30,000 d. The amount is indeterminable from the given information. (difficult, L.O. 3, c) 67. Dividends appear on the: a. retained earnings statement b. income statement c. balance sheet d. both the retained earnings statement and the income statement (moderate, L.O. 4, a) 68. Assets appear on the: a. balance sheet b. income statement c. retained earnings statement d. statement of cash flows (easy, L.O. 4, a) 69. Common stock appears on the: a. balance sheet b. income statement c. statement of cash flows d. retained earnings statement (easy, L.O. 4, a) 70. A company’s gross profit for the period is reported on the: a. balance sheet b. statement of cash flows c. income statement d. statement of retained earnings (easy, L.O. 4, c) 71. Gains and losses appear on which of the financial statements listed below? a. the balance sheet b. the income statement c. the retained earnings statement d. the statement of cash flows (easy, L.O. 4, b) 1-10 72. The ending balance in Retained Earnings appears on the: a. balance sheet only b. balance sheet and statement of retained earnings c. statement of retained earnings only d. income statement (moderate, L.O. 4, b) 73. Cash dividends: a. decrease revenue on the income statement b. increase expenses on the income statement c. decrease retained earnings on the retained earnings statement d. decrease operating activities on the statement of cash flows (moderate, L.O. 4, c) 74. Which of the following financial statements shows the net increase or decrease in cash during the period? a. balance sheet b. statement of operations c. statement of retained earnings d. statement of cash flows (easy, L.O. 4, d) 75. An investor wishing to assess a company’s financial position at the end of the period would probably examine a. the statement of cash flows b. the income statement c. the balance sheet d. the statement of retained earnings (moderate, L.O. 4, c) 76. A potential investor interested in evaluating a company’s financial performance for the current period would probably examine which of the following financial statements? a. balance sheet b. income statement c. statement of cash flows d. retained earnings statement (moderate, L.O. 4, b) 77. Which statement summarizes the revenues and expenses of an entity? a. balance sheet b. statement of cash flows c. statement of retained earnings d. statement of operations (moderate, L.O. 4, d) 1-11 78. Which financial statement provides a "snapshot photo" of one moment in time? a. balance sheet b. income statement c. statement of retained earnings d. statement of cash flows (moderate, L.O. 4, a) 79. The income statement: a. reports the results of operations since the inception of the business b. covers a defined period of time c. is not dated d. may cover a period of time or only one day in time, like a snapshot photograph (moderate, L.O. 4, b) 80. The income statement presents a summary of the: a. revenues and expenses of an entity for a specific time period b. assets and liabilities of an entity c. cash inflows and outflows of an entity d. changes that occurred in the stockholders’ equity of an entity (easy, L.O. 4, a) 81. Operating expenses appear on the income statement: a. directly after gross profit b. directly after cost of goods sold c. directly after revenue d. Operating expenses do not appear on the income statement. (moderate, L.O. 4, a) 82. Cost of goods sold: a. appears on the income statement as a deduction from gross profit b. appears on the balance sheet as a deduction from sales c. appears on the income statement as a deduction from sales d. appears on the retained earnings statement as an addition to beginning retained earnings (moderate, L.O. 4, c) 83. A retail store buys t-shirts for $25 and sells them for $60. The store’s cost of goods sold would be: a. $25 b. $35 c. $60 d. None of these answers are correct. (easy, L.O. 4, a) 1-12 84. Net income is: a. deducted from beginning retained earnings on the retained earnings statement b. added to beginning retained earnings on the retained earnings statement c. added to assets on the balance sheet d. deducted from net sales on the income statement (moderate, L.O. 4, b) 85. A net loss occurs when: a. total revenues exceed total expenses b. total expenses exceed total revenues c. total revenues and dividends exceed total expenses d. total revenues exceed total expenses and dividends (moderate, L.O. 4, b) 86. The balance sheet is alternately known as the: a. operating statement b. assets statement c. statement of financial position d. statement of profit and loss (moderate, L.O. 4, c) 87. The balance sheet reports information about: a. liabilities, equity, and expenses b. assets, revenues, and liabilities c. assets, liabilities, and equity d. revenues, expenses, and equity (easy, L.O. 4, c) 88. Assets are generally classified as: a. current assets and producing assets b. producing assets and consumable assets c. long-term assets and consumable assets d. current assets and long-term assets (easy, L.O. 4, d) 89. Current assets are assets expected to be converted to cash, sold, or consumed: a. within the next 12 months or within the business’s normal operating cycle if less than a year b. within the next 12 months or within the business’s normal operating cycle if longer than a year c. within the next 6 months d. within the next 24 months (moderate, L.O. 4, b) 1-13 90. Notes receivable due in 60 days would be classified as a: a. long-term asset on the balance sheet b. current asset on the balance sheet c. current liability on the balance sheet d. long-term liability on the balance sheet (easy, L.O. 4, b) 91. Equipment would appear on the: a. income statement with the revenues b. balance sheet with the long-term assets c. balance sheet with the current assets d. income statement with the operating expenses (easy, L.O. 4, b) 92. Depreciation is normally associated with which asset on the balance sheet? a. land b. accounts receivable c. inventory d. equipment (moderate, L.O. 4, d) 93. Accounts receivable would appear on the: a. income statement with the revenues b. retained earnings statement with the net income c. balance sheet with the current assets d. balance sheet with the current liabilities (easy, L.O. 4, c) 94. Notes payable (due in 60 days) would appear on the: a. income statement with the expenses b. retained earnings statement with the dividends c. balance sheet with the current assets d. balance sheet with the current liabilities (easy, L.O. 4, d) 95. Income taxes owed to the federal government would be classified as a(n): a. current asset on the balance sheet b. current liability on the balance sheet c. expense on the income statement d. financing activity on the statement of cash flows (moderate, L.O. 4, b) 96. Purchases and sales of long-term assets are examples of: a. investing activities b. accrual activities c. financing activities d. operating activities (moderate, L.O. 4, a) 1-14 97. Stockholders’ equity increases as a result of: a. owner investments b. a net loss during the period c. a net income during the period d. both a and c (moderate, L.O. 4, d) 98. When treasury stock is purchased by a company it: a. increases the amount of owners’ equity b. decreases the amount of owners’ equity c. decreases the amount of total liabilities d. increases the amount of total liabilities (difficult, L.O. 4, b) 99. The statement of cash flows is divided into which three categories? a. planning, executing, and evaluating activities b. operating, investing, and financing activities c. increasing, decreasing, and noncash activities d. developing, producing, and marketing activities (easy, L.O. 4, b) 100. What is the proper order for the statement of cash flows? a. financing activities, investing activities, and operating activities b. operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities c. operating activities, financing activities, and investing activities d. investing activities, financing activities, and operating activities (moderate, L.O. 4, b) 101. Cash received from the sale of stock would appear: a. as an operating activity on the statement of cash flows b. as a noncash financing activity on a statement of cash flows c. as an investing activity on the statement of cash flows d. as a financing activity on the statement of cash flows (moderate, L.O. 4, d) 102. The repayment of a note payable would be classified as a(n): a. investing activity on a statement of cash flows b. financing activity on a statement of cash flows c. operating activity on a statement of cash flows d. current asset on the balance sheet (difficult, L.O. 4, b) 103. The issuance of stock for cash would be classified as a(n): a. investing activity on a statement of cash flows b. financing activity on a statement of cash flows c. operating activity on a statement of cash flows d. current asset on the balance sheet (difficult, L.O. 4, b) 1-15 104. Cash collected from customers would appear on the statement of cash flows as a(n): a. operating activity b. financing activity c. investing activity d. activity that would not appear on the statement of cash flows. (moderate, L.O. 4, a) 105. The payment of salaries would appear: a. on the statement of cash flows with the operating activities b. on the statement of financial position with the current liabilities c. on the statement of earnings with the revenues d. on the statement of operations as part of cost of goods sold (difficult, L.O. 4, a) 106. The income statement is prepared to determine: a. the change in retained earnings due to the results of operations b. the change in cash due to results of operations c. the change in assets and liabilities due to the results of operations d. All of these answers are correct. (difficult, L.O. 5, a) 107. Which of the following statements should be prepared before the balance sheet is prepared? a. statement of retained earnings b. statement of cash flows c. statement of financial position d. Both the statements of retained earnings and cash flows are correct. (difficult, L.O. 5, a) 108. The amount of net income shown on the income statement also appears on the: a. balance sheet b. statement of assets c. statement of financial position d. statement of retained earnings (moderate, L.O. 5, d) 109. The balance sheet contains: a. the amount of net income b. the beginning balance in retained earnings c. the ending balance in retained earnings d. the amount of dividends paid to stockholders (moderate, L.O. 5, c) 110. What is one component of stockholders’ equity? a. common stock b. notes payable c. property, plant, and equipment d. cash (easy, L.O. 5, a) 1-16 111. Which financial statement must be prepared before the others? a. income statement b. balance sheet c. statement of cash flows d. retained earnings statement (moderate, L.O. 5, a) 112. The SEC Edgar file contains information on: a. all profitable US companies b. all companies on the SEC "watch list" c. recommended US and international companies d. all publicly traded companies in the US (moderate, L.O. 5, d) 113. The main source of cash for a business stems from: a. current assets b. operating activities c. financing activities d. investing activities (moderate, L.O. 5, b) 114. Retained earnings appear on which of the following financial statements? a. statement of retained earnings, statement of cash flows, and income statement, but not the balance sheet b. statement of retained earnings and balance sheet, but not the income statement or statement of cash flows c. statement of retained earnings, statement of cash flows, and balance sheet, but not the income statement d. statement of retained earnings and statement of cash flows, but not the income statement or balance sheet (difficult, L.O. 5, b) 115. An investor who wished to answer the question, "Can the company sell its products?" should investigate the a. current and projected inventory levels b. sales revenue trend c. net income for the current period and projected net income for the next period d. operating activities section of the cash flow statement (moderate, L.O. 5, b) 1-17 PROBLEMS AND CRITICAL THINKING EXERCISES 116. A company’s management makes three major types of decisions on an ongoing basis: decisions regarding operating activities, decisions regarding investing activities, and decisions regarding financing activities. Discuss each of these three types of activities, including examples of each type. Solution: Operating activities relate to deciding how to operate the business and involve decisions such as what products and/or services to sell, what prices to sell those products and services for, and how to market those products and services. Investing activities relate to deciding what kinds of investments to make and involve decisions such as what types of long-term assets to buy. Financing activities relate to deciding how to finance the company’s operations and involve decisions such as whether to obtain cash by selling stock or by borrowing from a bank. (moderate, L.O. 1) 117. Why is accounting often referred to as "the language of business?" How is accounting different from bookkeeping? Solution: Accounting is the system that measures business activities, processes that information into reports, and communicates the results to decision makers. Accounting, as an information system, provides the elements necessary for management and others to make decisions and estimates how well a company may perform in the future. Accounting is the common "language" used by managers, investors, and others to communicate information about a business. Bookkeeping is simply the procedural element of accounting that processes the accounting data. Accounting is an information system, of which bookkeeping is a component. (easy, L.O. 1) 118. What are the three forms of business organizations? How do they differ? Solution: A proprietorship has a single, or sole, owner who is responsible for the business and its operations. A partnership has two or more individuals who operate together as co-owners of the business. In both of these forms of organization, the owners are individually liable for the debts of the business. A corporation is a business owned by stockholders, who may or may not have a part in the day-to-day operations of the business. The stockholders of a corporation are not legally liable for the debts of the business. It is easier to sell one’s ownership of a corporation, since the ownership is evidenced by shares of stock, which can be traded. There are legal rules to be considered when a partner wishes to sell his or her interest in a partnership. Such rules make it more difficult to sell a partnership interest. A sole proprietor who sells his or her business may encounter difficulty since the business owner may be the business itself (such as a consultant or other independent contractor). (moderate, L.O. 1) 1-18 119. List and define three generally accepted accounting concepts/principles discussed in Chapter 1. Solution: Entity concept — An accounting entity is an organization or a section of an organization that stands apart from other organizations and individuals as a separate, identifiable economic unit. From an accounting perspective, sharp boundaries are drawn around each entity so as not to confuse its affairs with those of other entities, such as the owner of a business and the business itself. This allows an objective measurement of accounting data to be taken and turned into useful information. Reliability principle — Accounts records and statements are based on the most reliable data available so that they will be as accurate and as useful as possible. This principle is also called the objectivity principle. Cost principle — This principle states that acquired assets and services should be recorded at their actual cost. The cost of an asset should be maintained in the accounting records for as long as the business holds the asset. Going-concern principle — This principle holds that the entity will remain in operation for the foreseeable future. This principle allows certain assumptions to be made by management, investors, and other interested parties about the business and its operations into future accounting periods. Stable-monetary-unit concept — This concept assumes that the dollar’s purchasing power is relatively stable and thus ignores the effect of inflation in the accounting records. (moderate, L.O. 2) 120. Your friend has asked you to review and analyze the financial status of her company before she goes to the bank to request a loan. Answer the following questions: a. What will you need to review to make a sound decision? b. What will the bank be looking for? Be specific. Solution: a. A decision maker would like to have access to all the financial statements of a company for several years, including the income statement, balance sheet, statement of retained earnings, and statement of cash flows. b. The bank will be looking at the company’s ability to repay the loan. The bank will look at the amount of income generated by the company for the past several years as well as whether or not it has been increasing or decreasing. The amount of debt already owed by the company will also be an issue. The bank would like to see that stockholders’ equity exceeds total liabilities at the time of the loan request. Also, dividends paid to the owner should not exceed the net income in any given period. These are indications that the owner is as much at risk as the bank would be if the loan were granted. (difficult, L.O. 4) 1-19 121. Listed below are several account titles. List the type of account listed by the account title. The first item is listed as an example. Account Title Account Type Equipment Asset Notes Payable Merchandise Inventory Prepaid Insurance Common Stock Land Accounts Receivable Accounts Payable Retained Earnings Solution: Account Title Account Type Equipment Asset Notes Payable Liability Merchandise Inventory Asset Prepaid Insurance Asset Common Stock Equity Land Asset Accounts Receivable Asset Accounts Payable Liability Retained Earnings Equity (easy, L.O. 3) 1-20 122. Following is an alphabetical list of the assets, liabilities, revenues, and expenses of Great Smoky Bar-B-Que, Inc. Prepare an income statement for the year ended November 30, 2005. Accounts payable Accounts receivable Advertising expense Cash Cost of goods sold Inventory Interest expense $ 2,800 5,400 2,600 9,100 29,800 7,900 800 Note payable Rent expense Salary expense Salary payable Sales revenue Supplies expense Utilities expense Solution: Great Smoky Bar-B-Que, Inc. Income Statement For the Year Ended November 30, 2005 Revenues: Sales revenue Expenses: Cost of goods sold Rent expense Salary expense Advertising expense Supplies expense Interest expense Utilities expense Net income $78,800 $29,800 10,200 12,100 2,600 1,800 800 700 (moderate, L.O. 4) 1-21 58,000 $20,800 $ 4,000 10,200 12,100 900 78,800 1,800 700 123. Northwestern Express Enterprises gathered together the following information at the end of its first year of operations, September 30, 2006: Rent expense Truck Supplies Salary expense Accounts receivable Note payable Common stock $ 7,500 14,600 2,500 19,400 8,200 11,000 25,000 Dividends Accounts payable Service revenue Salary payable Utilities expense Interest expense Cash $10,200 6,700 45,500 1,200 5,000 1,500 20,800 Prepare an income statement for Northwestern Express Enterprises for the year ended September 30, 2006. Solution: Northwestern Express Enterprises Income Statement For the Year Ended September 30, 2006 Revenues: Service revenue Expenses: Salary expense Rent expense Utilities expense Interest expense Net income $45,500 $19,400 7,500 5,000 1,500 33,400 $12,100 (moderate, L.O. 4) 1-22 124. The following accounts were extracted from the accounting records of Teutonic Enterprises following its second year of operations, June 30, 2006: Rent expense Truck Supplies Salary expense Accounts receivable Note payable Common stock $ 7,500 13,600 2,500 19,400 8,200 10,000 25,000 Dividends Accounts payable Service revenue Salary payable Utilities expense Interest expense Cash $10,200 6,700 45,600 2,200 5,000 1,200 21,900 Retained earnings at the end of the first year of operations was $15,000. Prepare an income statement and a statement of retained earnings for Teutonic Enterprises. Solution: Teutonic Enterprises Income Statement For the Year Ended June 30, 2006 Revenues: Sales revenue Expenses: Salary expense Rent expense Utilities expense Interest expense Net income $45,600 $19,400 7,500 5,000 1,200 33,100 $12,500 Teutonic Enterprises Statement of Retained Earnings For the Year Ended June 30, 2006 Retained earnings, June 1, 2006 Add: Net income $15,000 12,500 $27,500 10,200 $17,300 Deduct: Dividends Retained earnings, June 30, 2006 (moderate, L.O. 4) 1-23 125. Bruce’s Auto Transport Service gathered together the following information regarding the asset, liability, stockholders’ equity, revenue, and expense accounts as of the end of its first year of operations, April 30, 2006: Accounts payable Accounts receivable Cash Common stock Dividends Interest expense Note payable $ 6,700 8,200 23,800 25,000 8,300 1,200 11,000 Rent expense Salary expense Salary payable Service revenue Supplies Truck Utilities expense $ 6,500 19,400 1,200 45,500 2,500 14,600 5,000 Prepare a statement of retained earnings for Bruce’s Auto Transport Service for the year ended April 30, 2006. Solution: Bruce’s Transport Service Statement of Retained Earnings For the Year Ended April 30, 2006 Retained earnings, May 1, 2005 Add: Net income Deduct: Dividends Retained earnings, April 30, 2006 $ 0 13,400 13,400 8,300 $ 5,100 (moderate, L.O. 4) 1-24 126. The following information was extracted from the accounting records of Hamilton Corporation as of December 31, 2007. Prepare a balance sheet for Hamilton Corporation. Accounts payable Accounts receivable Cash Common stock Equipment $11,200 40,000 21,600 50,600 24,600 Inventory Note payable Retained earnings Salary payable Supplies $23,500 31,000 17,100 2,300 2,500 Solution: Hamilton Corporation Balance Sheet December 31, 2007 Assets Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Supplies Equipment Total assets $21,600 40,000 23,500 2,500 24,600 $112,200 Liabilities Accounts payable $11,200 Note payable 31,000 Salary payable 2,300 Total liabilities 44,500 Stockholders’ equity Common stock 50,600 Retained earnings 17,100 Total stockholders’ equity 67,700 Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity $112,200 (moderate, L.O. 4) 1-25 127. Following is an alphabetical list of the assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity accounts of Waterloo-Ag Products, Inc. Prepare a balance sheet dated April 30, 2006. Accounts payable Accounts receivable Cash Common stock Inventory $10,200 17,000 30,900 32,400 34,000 Note payable Retained earnings Salary payable Supplies $15,000 27,500 10,700 13,900 Solution: Waterloo-Ag Products, Inc. Balance Sheet April 30, 2006 Assets Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Supplies Total assets $30,900 17,000 34,000 13,900 Liabilities Accounts payable Note payable Salary payable Total liabilities $95,800 Stockholders’ equity Common stock Retained earnings Total stockholders’ equity Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity (moderate, L.O. 4) 1-26 $10,200 15,000 10,700 35,900 32,400 27,500 59,900 $95,800 128. Dreame House Realtors, Inc., prepared the following random list of assets, liabilities, revenues, and expenses from its December 31, 2006, accounting records. The beginning retained earnings as of January 1, 2006, was $43,100 and the owner, John Dreame, received dividends of $12,600 during the year. Prepare the balance sheet for Dreame House Realtors, Inc., as of December 31, 2006. Accounts receivable Interest expense Supplies Accounts payable Utilities expense Furniture Salary payable Common stock $15,700 4,900 1,500 6,100 5,200 18,000 2,400 30,500 Service revenue Cash Note payable Salary expense Interest payable Rent expense Automobiles Land $50,500 28,000 17,000 18,000 1,600 9,400 14,900 23,000 Solution: Dreame House Realtors, Inc. Balance Sheet December 31, 2006 Assets Cash Accounts receivable Supplies Furniture Automobiles Land Total assets $ 28,000 15,700 1,500 18,000 14,900 23,000 $101,100 Liabilities Accounts payable Note payable Interest payable Salary payable Total liabilities $ 6,100 17,000 1,600 2,400 27,100 Stockholders’ equity Common stock 30,500 Retained earnings 43,500 * Total stockholders’ equity 74,000 Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity $101,100 * $43,500 = $43,100 + $13,000 (net income) - $12,600 Net income = $50,500 - $4,900 - $5,200 - $18,000 - $9,400 (difficult, L.O. 4) 1-27 129. Renee Parker started a new florist business, Parker’s Poseys, on July 2, 2007, by investing $100,000 cash and receiving common stock in return. On July 31, Parker’s bookkeeper examined the following facts: Parker had $18,000 in a personal checking account; the Parker’s Poseys account had a balance of $30,000. Parker’s Poseys had $45,000 of inventory. Parker still owes $15,000 on account for this inventory. Parker owed $5,000 on a personal credit card. Parker purchased a delivery van for the business for $38,000, paying $20,000 in cash and signing a note payable for the remainder. Parker purchased furniture for the business for $15,000 cash. Parker purchased with cash $5,000 of office supplies to be used in the business. Parker owes $165,000 for a mortgage on a personal residence purchased for $225,000. Prepare the balance sheet of Parker’s Poseys as of July 31, 2007. Solution: Parker’s Poseys, Inc. Balance Sheet July 31, 2007 Assets Cash Supplies Inventory Furniture Delivery van $ 30,000 5,000 45,000 15,000 38,000 Total assets (difficult, L.O. 4) $133,000 Liabilities Accounts payable Note payable Total liabilities $ 15,000 18,000 $ 33,000 Stockholders’ equity Common stock $100,000 Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity $133,000 1-28 130. Identify the financial statement where a decision maker can find the following items. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. Dividends Equipment Insurance expense Cash paid for supplies Accounts receivable Beginning retained earnings Sales revenue Common stock Accounts payable a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. statement of retained earnings balance sheet income statement statement of cash flows balance sheet statement of retained earnings income statement balance sheet balance sheet Solution: (moderate, L.O. 5) 131. Classify each statement below as an operating activity, investing activity, or a financing activity. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. Sold 10,000 shares of stock for cash. Paid salaries of employees. Paid amount due for income taxes. Paid interest expense. Purchased office equipment for cash. Sold old office equipment and received cash. Received interest income. Paid interest on a bank loan. Paid dividends to stockholders. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. financing activity operating activity operating activity operating activity investing activity investing activity operating activity operating activity financing activity Solution: (moderate, L.O. 4) 1-29 132. The following information was extracted from the accounting records of Home Makers, Inc., for the year ended December 31, 2006 (in thousands). Purchases of equipment $ 390 Net income 44 Revenues 553 Long-term borrowings 50 Adjustments to reconcile net income to cash 919 Issue common stock Payment of dividends Sales of equipment Accounts receivable Beginning cash $ 76 39 142 78 167 Prepare a statement of cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2006. Solution: Home Makers, Inc. Statement of Cash Flows For the Year Ended December 31, 2006 Cash flows from operating activities: Net income Adjustments to reconcile net income to cash Net cash provided by operating activities Cash flows from investing activities: Sale of equipment Purchase of equipment Net cash used for investing activities Cash flows from financing activities: Issue common stock Borrowings Payment of dividends Net cash used for financing activities Net increase in cash Cash balance, January 1, 2006 Cash balance, December 31, 2006 (difficult, L.O. 5) 1-30 $ 44 919 $963 $ 142 (390) (248) $ 76 50 (39) $ 87 $802 167 $969 133. Choose the appropriate definition for the terms below. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. a business owned by a single owner a statement summarizing the revenues and expenses for a given period resources which provide future economic benefits to a business claims by outsiders on the resources of a business revenues less expenses a business owned by stockholders shows the net change in the cash account for a given period a formal listing of the accounting equation on a specified date 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. corporation statement of cash flows income statement net income proprietorship balance sheet liabilities assets Solution: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. f g b e a h d c (moderate, L.O. all) 1-31 QUESTIONS ON DECISION GUIDELINES 134. Think about the impact accounting has on our economy and our nation. Name some external groups interested in reviewing a company’s financial statements. Solution: stockholders and other investors bankers other creditors Internal Revenue Service other governmental agencies the general public (easy, L.O. 5) 135. What do stockholders look for when reviewing and analyzing the income statement? Solution: When reviewing the income statement, stockholders look for steadily increasing levels of net income over time. Net income on an income statement means the company is profitable. A steady increase in net income indicates the company’s profits are solid. Net income affects both stock prices and future dividends. A stockholder’s personal wealth will be enhanced through an increase in the market price of the company’s stock and future dividends to be received. (moderate, L.O. 5) 136. What do stockholders look for when reviewing and analyzing the statement of cash flows? Solution: When reviewing the statement of cash flows, stockholders look for indications that management is using cash wisely. Stockholders also like to see that the main source of cash is from operating activities, rather than from investing or financing activities. Cash from operating activities indicates that business operations are providing the company with sufficient cash flow. (difficult, L.O. 5) 137. What do creditors such as bankers look for when reviewing assets and liabilities on the balance sheet? Solution: Assets show what the company can pledge as collateral that a creditor can collect if the company fails to pay its debts. Liabilities indicate how much the company owes other creditors. Assets should increase faster than liabilities over time. The amount of assets should exceed the amount of liabilities. (moderate, L.O. 5) 1-32 138. What is the purpose of a statement of cash flows? Solution: A statement of cash flows reports how the company generates and uses its cash. Wise use of cash usually generates revenues and additional cash. Operating activities should be the main source of cash. The statement of cash flows provides information that would be difficult to obtain from analyzing the other financial statements. (moderate, L.O. 5) 1-33