Study Guide for the HBS Digestive System Lessons
advertisement

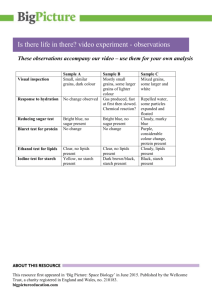
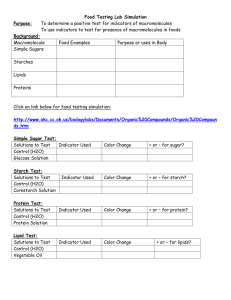
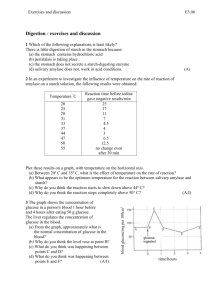
Study Guide for the HBS Digestive System Lessons 1-7 HBS Lesson 1: A Preassessment Part I. Directions: Fill in the space with the best vocabulary word. Cell Body system Tissue Organism Organ Galen ________________ A group of organs that work together to perform a task. ________________ Basic unit of structure or life. _________________ A group of cells working together to form a task. _________________ Group of tissues working together to perform a task. __________________ Dr. whom some people call the first sports medicine doctor. He was the official doctor for the gladiators and identified 300 muscles. HBS Lessons 2 & 3: Moving through the Digestive Tract & Exploring Carbohydrates Digestion * Mechanical Digestion * Peristalsis * Sphincter * Chemical Digestion * Mucus * Amino Acids * Nutrients * Carbohydrates * Glucose * Glycogen * Unsaturated Fats * Fiber * Proteins * Saturated Fats * Vitamins * Minerals * Water * Fats _________________ The process of breaking down food _________________ Regular muscular contractions that move food through the digestive tract _________________ A physical change that occurs while food is breaking down. (i.e. tongue mashing & teeth grinding) _________________ A ring of muscles found at organ connections that assist in the forward movement of food, in digestion _________________ A chemical change in food which changes the food into a different form (chemical bonds are broken down) _________________ Lubrication to help food travel through the digestive tract _________________ The simplest carbohydrate is a sugar called? This is the first type of fuel your body will use. _________________ Sugar and starch are the 2 major parts of this basic food group. _________________ Fuel your body needs to keep you going ________________ Is a carbohydrate that doesn’t digest but helps move food through and out of your intestines. ________________ Builds tissue and repairs damage to muscle tissue. ________________ Is needed in small amounts in your body, too much can cause you to gain weight. Helps to protect the internal organs. Gives 2 times the energy than carbohydrates or proteins ________________ Meat, cheese, butter, sweet baked goods are examples of what kind of fat? ________________ Plant products (vegetables) and nuts are all examples of what kind of fat? ________________ We need 13 kinds of these daily. They help to build blood cells and help the chemicals in our body that control the nervous system. ________________ This nutrient helps build bones, teeth, and blood cells. ________________ Even though this liquid doesn’t contain any nutrients, it helps transport nutrients and waste through out the body. It helps control our body temperature. Our cells, brain, and muscles are packed with this liquid which we need to replenish daily. ________________ If you have too much glucose in your body it will turn into this and be stored in your muscles and liver. ________________ if a food has all 9 of these, it is a complete protein, if a food has less than 9 of these it is called an incomplete protein. HBS Lessons 4 & 5: Digestion in the Mouth & Stomach Incisors * Epiglottis * Bolus * Salivary Amylase * Canines * Molars * Pre-molars * Chyme * Ulcer * HCl * Pepsin * Mucus * Gastric Juice The ________________ covers over the trachea to allow food to go down the esophagus. ________________ are the pointed teeth, at the sides of the mouth, used for tearing. When food is chewed and mixed, it turns into a moist ball or a ________________. ________________ and ______________ are the flat teeth found at the back of the mouth, on top and bottom, used to crush and grind food to make it soft. ________________ a digestive enzyme, found in saliva, begins the chemical process of breaking down starches into simple sugar. The front teeth or _________________, are used for cutting and slicing food. ________________ is the enzyme which begins the breakdown of proteins. HCL and Pepsin make up ________________. The soupy mixture of digested proteins and carbohydrates is called ___________________. An ________________ is a hole in your stomach lining. The glands in the stomach walls secrete __________________ which in turn triggers the release of pepsin. The thick coating in the stomach called _________________ protects the stomach from its own gastric juices digesting itself. True or False: Based on your findings from Lessons 4 and 5, answer the following questions. ____________ The starch solution tested positive for starch. ____________ The amylase tested positive for both sugar and starch. ____________ Amylase and Starch solution tested positive for both sugar and starch. ____________ The starch solution tested positive for sugar. _____________ The sugar molecules were able to pass through the membrane into the water in the test tube. _____________ The starch molecules were able to pass through the membrane into the water in the test tube. HBS Lessons 6 & 7: Diffusion & Absorption Some words may be used more than once. Duodenum * Lymph Vessels * Diffusion * Active Transport * Blood Vessels * Cellular Respiration * Passive transport * Absorption * Microvilli * Villi * Surface Area * Liver * Appendix * Gallbladder* The majority of digestion takes place in the ________________, the first part of the small intestine. Fats are allowed into the bloodstream by______________________. __________________________ allows nutrients to be absorbed into the body. _________________ and ______________ are the two ways that materials/substances can pass through blood vessels and lymph vessels. _________________ is an organ with no known function. _________________ is the organ which produces bile and _________________ is the organ which stores the bile. _________________ is the process by which a substance can pass through a cell membrane without needing any cellular energy. The process by which materials, using energy supplied by the cell, are moved across a membrane is called __________________________. Diffusion is also called ________________. Cellular Respiration is also known as _________________. The process by which nutrients are passed through the cell walls that line the digestive tract is known as _________________. __________________, finger-like projections and __________________, microscopic finger-like projections line the wall of the small intestine, increasing its surface area, allowing nutrients to be absorbed The area on the surface of the small intestine is called its _______________________. Unfolded it would cover about an entire football field. Find the Surface area of the following rectangular solid: 3 cm 2 cm 6 cm True or False: ____________the sugar molecules passed through the membrane. ____________ the starch molecules passed through the membrane.