View PDF
advertisement

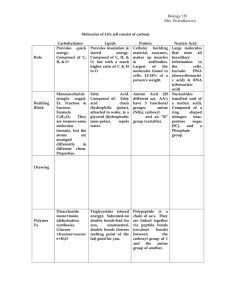
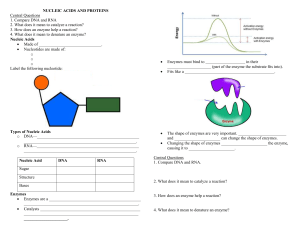
Name___________________________________Date________Period_____ Biology Review Sheet Biomolecules Match the following terms to the correct definition: Organic Compound Lipids Macromolecule Globular Glucose Digestion Enzyme Amino Acids Fibrous Saccharide 1. FIBROUS - type of protein found in skeletal and connective tissue 2. GLUCOSE - a simple sugar that cells use for energy 3. ORGANIC COMPOUND- a compound that contains carbon 4. GLOBULAR -any protein whose polypeptide chain(s) are folded so as to give the whole molecule a rounded shape 5. DIGESTION -the process in which food is broken down to release nutrients 6. MACROMOLECULE -large molecule 7. ENZYME - a protein that helps start or speeds up a chemical reaction 8. LIPIDS - olive oil, beeswax, vitamins, -made up of carbon & hydrogen 9. AMINO ACIDS - building blocks of proteins 10. SACCHARIDE - means “sugar List the 4 major organic compounds and describe their role helping living organisms. CARBOHYDRATES – ENERGY FOR CELLS, INCLUDES STARCHES AND SUGARS LIPIDS – ENERGY STORAGE, STRUCTURE OF CELL MEMBRANES PROTEINS – BUILDS CELLS, TISSUES, SKIN, BONES, INCLUDES ENZYMES, HORMONES, ANTIBODIES NUCLEIC ACIDS – DNA AND RNA, CARRY GENETIC INFORMATION, CODE FOR PROTEINS Whatis the chemical formula for a carbohydrate? Cn(H2O)m n=#of carbon atoms, m=water molecules Glucose is broken down and turned into ATP that gives cells the energy they need. Carbohydrates aren’t always sugary. What is the carbohydrate plants use to store extra sugar called?CELLULOSE ex. FOUND IN CELL WALLS OF PLANTS What condition do some people suffer from that by eating breads, potatoes and other starches could be dangerous?diabetes What happens? All carbohydrates that the person eats are turned into sugar. This causes a rise in their blood sugar level. When amino acids are joined together they form what type of macromolecule? protein List the two types of Nucleic Acids and what they are used for. DNA – CARRIES THE GENETIC INFORMATION FOR LIVING ORGANISMS, CODES FOR RNA, FOUND IN ALL LIVING ORGANISMS AND VIRUSES WHICH ARE NOT LIVING RNA – CODES FOR PROTEIN Enzymes, Hormones and antibodies are part of which biomolecule? PROTEIN What are the lipid membranes called and what is the function? Lipids form a lipid bilayer (also called the phospholipid bilayer) in the cell membrane. The cell membrane is important in helping the cell maintain homeostasis. It allows water to move in and out of the cell as needed. Give three examples of Lipids. fats, waxes, vitamins Lipids are a compound made up of __________ and __________. (look at the drawing) NOT ON TEST/not covered in notes: Explain the terms saturated-__________________________________________________ Monounsaturated-__________________________________________________________ Polyunsaturated-___________________________________________________________ Triglycerides are stored in adipose tissue Label the following structures: Triglyceride, Glucose/Monosaccharide, Disaccharide, Nucleotide, Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA TRIGLYCERIDE GLUCOSE NUCLEOTIDE DISACCHARIDE Describe in detail how enzymes work: Enzymes fit specifically to a substrate like a key fits a lock. The enzyme attached to the substrate and changes it into a new product that can be used by the cell or organism. The place where a substrate bonds to an enzyme is called the active site Enzyme denaturing happens when an enzyme’s shape is changed. Denaturing can be caused by changes in temperature or pH. One enzyme can catalyze how many chemical reactions? unlimited The reaction rate of an enzyme can be changed by changes in temperature or pH. Give examples of each: Proteins – meats, animal products, legumes, grains, nuts Lipids – oils, waxes, vitamins Carbohydrates – sweets, non-green veggies, baked goods Nucleic Acid – DNA, RNA Enzymes – amylase, lipase, polymerase, catalase, pepsin What is the base unit of a nucleic acid? nucleotide (the links in the chain) Name the three parts of a nucleotide pentose sugar, nitrogenous base, phosphate How can a student tell for sure if a nucleic acid is Deoxyribonucleic acid or Ribonucleic acid? Use the term pentose ring in your answer. The deoxyribonucleic acid will be missing an oxygen on the pentose sugar ring What is the range of numbers on the pH scale? 0-14 What do they mean? 0-7 acid; 7-neutral; 7-14 - base What is the difference between a polymer and a monomer? Monomer is a single unit, a polymer will have multiple units linked together, monomers make up polymers Nucleic Acid Nucleotide Substrate Product Polymerase Collagen DNA RNA Active Site Amylase Benedict’s Reagent Iodine Catalyze Catalase Biuret Reagent Activation Energy Fill in the blank using the words listed above. Collagen - fibrous protein that holds jell-0 together Active site - where an enzyme attaches to a substrate Biuret - indicator for the presence of protein ( light blue to violet) Catalyze - increase the rate of Catalase - enzyme that breaks substrate (Hydrogen Peroxide) to product (O2 DNA - Deoxyribonucleic Acid – 2 strands, holds genetic info Substrate - a substance on which an enzyme acts during a chemical reaction and H2O) Activation energy - energy needed to start a chemical reaction Product - newly formed substance Nucleotide - Pentose sugar, phosphate, base RNA - Ribonucleic acid, single strand, key role in manufacturing protein Amylase - an enzyme that breaks starch into sugar Polymerase - an enzyme that can “code” DNA strands and also “proofread” the strand Nucleic acid - made up of a chain of nucleotides Iodine - indicator for presence of starch Benedict’s reagent - indicator for presence of sugar