Are we unicellular, or multicellular? Cell Divisions
advertisement

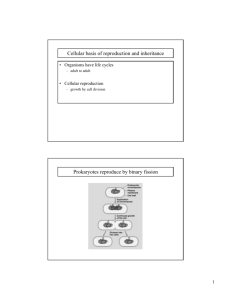
Are we unicellular, or multicellular? How can we get so big if we start off as 1 cell? Cells have to be able to divide What needs to be done for a cell to divide? DNA has to replicate and divide Cytoplasm needs to divide Vocabulary Cell Divisions Chromatin Chromosome Chromatid Cell cycle Interphase DNA ReplicationReplicationMitosis – Cytokinesis - 1 DNA DNA in the shape of a double helix DNA is made of Deoxyribose as the backbone and 4 types of nitrogen bases as the rungs of the ladder Chromatin to Chromosome DNA Replication— Replication—The DNA unzips and new bases are added making two identical strands of DNA The Life of a Cell The cell cycle begins when the cell is formed and ends when the cell divides and forms new cells. 2 Cell Cycle Phases of the cell cycle InterphaseInterphase- cell grows and DNA replicates Prophase— Prophase—DNA condenses into chromosomes and nucleus disappears Metaphase— Metaphase—Chromosomes line up on equator Anaphase— Anaphase—Chromosomes (sister chromatids) separate Telophase— Telophase—Nucleus reforms, Chromosomes unwind into chromatin, cell starts to split Cytokinesis– Cytokinesis– cytoplasm splits to form 2 cells Mitosis Click below to watch the Visual Concept. Visual Concept You may stop the video at any time by pressing the Esc key. 3 4 http://www.iknow.net/CDROMs/cell_cdrom/cellmovies.shtml Chapter 5 Section 3 Meiosis Asexual Reproduction Mitosis animation Mitosis animation Mitosis animation freeman Eukaryotic cell http://highered.mcgrawhttp://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/olc/dl/120073/bio14.swf • In asexual reproduction, only one parent cell is needed. The structures inside the cell are copied, and then the parent cell divides, making two exact copies. • This type of cell reproduction is called mitosis. Most of the cells in your body and most single-celled organisms reproduce this way. 5 Chapter 5 Section 3 Meiosis Chapter 5 Section 3 Meiosis Sexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction, continued • In sexual reproduction, two parent cells (sex cells) join together to form offspring that are different from both parents. • Meiosis Sex cells are made during meiosis. • Chromosomes that carry the same sets of genes are called homologous chromosomes. • Meiosis is a copying process that produces cells with half the usual number of chromosomes. • Each sex cell has only one of the chromosomes from the homologous pair. Chapter 5 Section 3 Meiosis Meiosis Meiosis Click below to watch the Visual Concept. Visual Concept You may stop the video at any time by pressing the Esc key. Humans have 46 chromosomes or 23 pairs ½ from mom and ½ from dad Meiosis = cell division that cuts the number of chromosomes in half and produces sex cells 4 sex cells are produced each with only half the number of chromosomes Diploid= having 2 sets of chromosomes Haploid= having 1 set of chromosomes 6 Moms Dads Each cell has 2 sets of doublestranded chromosomes 1 from mom and 1 from dad Could be either moms or dads Each of 2 cells now has only 1 set of double-stranded chromosomes The cells are now haploid-1/2 the number of chromosomes Each of 4 cells now have only one strand of each chromosome= sex cell Review How many cells does mitosis produce? 2 How many chromosomes are in each cell (full or half)? Full set – diploid How many cells does meiosis produce? 4 How many chromosomes are in each cell (full or half)? Half the chromosomes – haploid Where does mitosis occur? Body cells— cells—everywhere else besides reproductive organs Where does meiosis occur? Reproductive organs Activity 7