Angiogenesis
advertisement

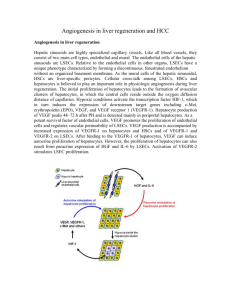
KBH3 The development of blood vessels in embryogenesis and tissue repair Mesodermal precursor Vessel repair VEGFR-1 and -2 PlGF, VEGF-A Mesoderm induction Mature vascular system Maturation, remodelling ‘Hemangioblast’ Hemangioblast’ VEGFRVEGFR-2+ Haematopoiesis Haematopoietic stem cell VEGFRVEGFR-2+ Scl/tal+ TGFβR PDGFβR Pruning, remodelling Vasculogenesis Angioblast VEGFRVEGFR-2+ Scl/tal- VEGFR-1 VEGFR-2 Tie-1 Tie-2 RasGAP Sprouting and non-sprouting angiogenesis VEGFR-1 VEGFR-2 Tie-1 Tie-2 TGFβR Vasculogenesis Primary capillary plexus Formation of a functional circulation from endothelial progenitors KBH1 1 Slide 1 KBH3 Risau, Nature 386, 671(1997) Kurt Ballmer-Hofer; 13.10.2004 Slide 2 KBH1 a, Vascular progenitors appear in response to basic fibroblast growth factor(bFGF) and bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4) in the posterior primitive streak (PPS) as vascular endothelial growth receptor-2 (VEGFR-2)/Flk1-positive mesodermal cells. b, Flk1-positive cells in the primitive streak give rise to both blood and endothelium haemangioblasts), but are restricted to haematopoietic or angiogenic fate after emigrating into extra-embryonic sites (extra-embryonic ectoderm (EXE), yolk sac and allantois) and intraembryonic sites (embryonic ectoderm (EEC)). c, In the yolk sac, these progenitors aggregate into endothelial-lined blood islands that then fuse to generate a primary capillary plexus (see main text). d, The primary capillary plexus undergoes remodelling along with intra-embryonic vessels to form a mature circulation (g). e, Intra-embryonic angioblasts migrate along distinct pathways before (f) aggregating directly into the dorsal aorta or cardinal vein, without a plexus intermediate. g, The primary vessels (capillary plexus, dorsal aorta and cardinal vein) then remodel, together with the xtraembryonicplexus, to form a mature vasculature, which along with VEGF and Notch involves the angiopoietins and Tie receptors4. h, Mural cells (pericytesand smooth-muscle cells) proliferate and differentiate in response to transforming growth factor- (TGF- ) signalling, and are recruited to vessels by platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) secreted by endothelial cells5,6. Ang, angiopoietin; Eph, Eph receptor family; Shh, sonic hedgehog; Np, neuropilin. Coultas et al. Nature 438 937 (2005) K. Ballmer-Hofer; 30.03.2006 The development of blood vessels: vasculogenesis versus angiogenesis Peptide Hormones Involved in Vasculogenesis and Angiogenesis In embryonic development Vasculogenesis Ligand Receptor Mature Vessels VEGF VEGFR-2 (Flk-1/KDR) Development of angioblasts Ang1 VEGFR-1 (Flt1) Tie2 Basal membrane In an adult organism Angiogenesis Ang2 Regression VEGF AntiVEGF Tie2 VEGFR-1/2 Therapie Ang2 Tie2 Pericytes Interaction with Destabilization of Lack of matrix and pericytes, maintenance matrix-cell and survival factors, cell of vessel integrity cell-cell interactions, death via apoptosis Interaction between angiogenesis endothelial cells Adapted from D. Hanahan, Science 277, 48 (1977) KBH2 Artery and vein formation are genetically determined ¾ In arteries VEGFR-2/NRP-1 signaling leads to ERK1/2 activation • • this is followed by notch signaling and EphrinB2 expression ¾ In veins signaling by COUP TFII, a transcription factor, blocks NRP-1 expression resulting in altered VEGFR-2 signaling • • PI 3-kinase activation which blocks ERK1/2 and Eph B4 expression 2 Slide 4 KBH2 A model for the genetic specification of arterial and venous fates in the major vessels of the trunk incorporating experimental data from mouse and zebrafish. Shh expressed in the notochord and floor plate induces VEGF expression in the somites, which in turn activates the receptor VEGFR2, expressed on endothelial cells. Activation of the PLC-–MAPK cascade downstream of VEGFR2 results in activation of ERK and of the Notch pathway. Foxc1 and Foxc2 promote expression of Notch1 and Dll4, leading to expression of ephrinB2 and an arterial fate. The interaction between activated ERK and Foxc1 and Foxc2 has not been elucidated, as indicated by a dashed line. Conversely, activation of the PI3K pathway results in activation of Akt and inhibition of ERK, which promotes venous fate, while repressing arterial fate. Small chemical inhibitors that block either the PLC-–MAPK or PI3K pathways, such as SL327, GS4898, and wortmannin, can influence the promotion of cell fate as indicated. Within a venous cell, the presence of COUP-TFII inhibits neuropilin1 expression, thus reducing VEGFR2 signaling and Notch activation. As a result, EphB4 is expressed and ephrinB2 is not. Because EphB4 is still present at reduced levels in venous cells of COUP-TFII null embryos, its expression must be partially controlled by an unknown pathway. R. E. Lamont et al., Sci. STKE 2006, pe39 (2006) K. Ballmer-Hofer; 19.06.2007 Formation of a capillary network Some cellular factors regulating angiogenesis Pro-angiogenmic factors General factors VEGF, Vascular endothelial growth factor bFGF, basic fibroblast growth factor PlGF, Placenta growth factor PDGF, Platelet-derived growth factor TGFα, Estrogens, EPO EGF, IGF 1, IL-3, IL-8 Angiopoietins 1,2 Angiogenin HIV-1 Tat protein, RGD-peptide Tumor Necrosis Factor α (TNFα) ... Anti-Angiogenic factors Tissue specific factors EG-VEGF, endocrine gland derived VEGF ... Tissue specific factors Pigment epithelium derived factor, PEDF ... General factors Thrombospondin (ECM-Protein) Endostatin (collagen XVIII fragment) Angiostatin (plasminogen kringle-domain) Antibodies against VEGF/VEGFR or Integrins Soluble VEGFR, ‚VEGF trap‘ (sFlt, Ig domain) Inhibitors of VEGFR kinase, e.g. SU5416 Interferonα TNFα PEX, a noncatalytic fragment of MMP-2 Kininostatin, a kinin fragment Bradykinin ... 3 Regulators of angiogenesis ¾ VEGFs and angiopoietins acting on endothelial cells; ¾ Cytokines, chemokines and angiogenic enzymes activating various cell types such as EC or SMCs; ¾ Indirectly acting factors released by other cell types such as macrophages, platelets, tumor cells, endothelial cells. Morphology of endothelial cells Resting endothelial cell layer Angiogenic endothelial cell layer 4 Overexpression of angiopoietin 1 promotes excessive vessel growth KB3 Hemostasis leads to the formation of fibrinclots and a thrombus by platelets Platelets Fibrin Fibrin attracts endothelial cells coagulation factors stimulate sprouting of blood vessels via HIF-1 und VEGF 5 Slide 9 KB3 Suri,C. et al., Science 282:468 Kurt Ballmer-Hofer; 01.11.2004 A juvenile hemangioma with many capillaries From: Tumour angiogenesis, R. Bicknell et al. eds., 1997 Infiltrating ductal breast carcinoma Prognosis good Prognosis poor From: Tumour angiogenesis, R. Bicknell et al. eds., 1997 6