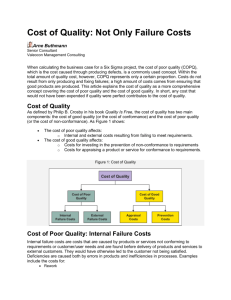
Cost of Quality
advertisement

Using the Cost of Quality Concept in Design and Improvement of Laboratory Processes Richard Carlson Fazi Amirahmadi 1 Presentation Objectives • Explain relationship between cost & quality • Describe the elements of cost of quality 2 Impact of Lab & Pathology on Healthcare • 6.8 billion clinical laboratory tests were performed in the U.S. (2007) • Generating about $52 billion in revenues • Only 2.3% of healthcare spending Laboratory Medicine: A National Status Report. May 2008 3 Impact of Lab & Pathology on Healthcare • 70% medical decisions influenced by test results American Clinical Laboratory Association: http://www.clinical-labs.org/issues/value/index.shtml • Lab & path quality has high impact on quality and affordability of patient care. 4 Errors Rates in Lab and Pathology Services • One estimate – 1 in 330 to 1 in 164 events or laboratory results The value of laboratory medicine. ADVANCE for Medical Laboratory Professionals. http://laboratorian.advanceweb.com/Article/The-Value-of-Laboratory-Medicine-4.aspx. • Converts to 3,030 to 6,098 Defects per Million Opportunities (DPMO) > Assuming 1 defect opportunity / unit of test 5 Six Sigma Sigma 6 sigma 5 sigma 4 sigma 3 sigma 2 sigma 1 sigma DPMO 3.4 233 6,210 66,807 308,537 690,000 Cost as % of Sales <10 10 - 15 15 – 20 20 – 30 30 - 40 World class Industry average Noncompetitive 6 Three Phases of End-to-End Testing Process Pre-analytic steps Clinical question Test selected Test ordered Specimen collected Analytic steps Sample prepared Analysis performed Results verified Post-analytic steps Result reported Clinical answer Action taken Effect on patient care 70 61.9 Carraro P., Plebani M. Errors in a stat laboratory: types and frequencies 10 years later. Clin Chem 2007; 53:7 1338–1342 60 50 40 Distribution of errors (%) 30 20 23.1 15 10 0 7 Value Stream Map of Testing Process 8 Outcome-oriented Process Management • “Make sure we send a good result out the door.” • Detect defects before they reach the customer > Add inspections or quality checks > Instruct staff to “be more careful” 9 Hidden Laboratories Hidden Laboratories (cost centers) Hidden Laboratories (cost centers) 10 Cost per Unit of Product or Service = Cost of Error/Waste-free Product/Service + Cost of Quality 11 What is Quality? • Conformance to requirements > defined by the customer > first time at each step in the value stream > deliverable that is free of deficiencies • Error-free, Waste-free 12 Cost of Quality • Two main components: > The cost of attaining quality (or the cost of conformance) > The cost of poor quality (or the cost of non-conformance) 13 Cost of Product or Service NonConformance Cost Error Free Cost Conformance Cost 14 Cost of Attaining Quality (or the cost of conformance) • Prevention Costs • Appraisal Costs 15 Cost of Attaining Quality (or the cost of conformance) • Examples • Prevention Costs Costs of all activities that > Planning for quality are designed to prevent > Design and review of a new service or test poor quality from arising in > Mistake/error proofing products or services > Quality improvement team meetings > Quality education and training > Supplier evaluation 16 Cost of Attaining Quality (or the cost of conformance) • Appraisal Costs • Examples Costs that occur because > Checking & testing purchased supplies & of the need to control services products and services to > In-process and final ensure: > a high quality level in all stages > conformance to quality standards > performance requirements are met inspections/checking > Product, process or service audits > Calibration of measuring and test equipment > Validation of instruments 17 Cost of Poor Quality (or the cost of non-conformance) • Internal Failure Costs • External Failure Costs 18 Cost of Poor Quality (or the cost of non-conformance) • Examples • Internal Failure Costs > Incoming defects Caused by products or > Repeat testing services not conforming to > Lost specimens customer requirements > Poor staff scheduling and found before delivery > Instrument downtime to external customers > > > > > High inventory cost Sample mix-up Data entry error Specimen Recollection Long turnaround time 19 Cost of Poor Quality (or the cost of non-conformance) • Examples • External Failure Costs Caused by deficiencies > Revised reports found after delivery to > Redoing services/tests external customers > Complaints > Loss of revenue due to unhappy clients/patients > Financial loss because of lawsuits > Environmental costs 20 Eight types of waste • Poor quality costs result from all waste. > Failure to meet customer requirements • Waiting, transportation, over-processing, inventory, motions (movement), defects, overproduction, and mis-utilization of skills, knowledge, creativity, and experience. 21 Cost of Product or Service External Failure Cost NonConformance Costs Error Free Cost Internal Failure Cost Conformance Costs Appraisal Cost Prevention Cost 22 Quality Iceberg 23 Relationship Between Cost and Quality 24 Common Assumption • Improved quality requires additional resources > Reduced re-work should save resources > Adherence to standards should decrease variation and save costs > New technology may require additional resources > Increased resources do not guarantee improved quality 25 Traditional Thinking • Prevention & Appraisal > Used to catch and reduce % of defective units > Internal & External costs will be reduced. • Focus is on Appraisal 26 Traditional Thinking Cost of good unit al rn te Ex t s & Cos al rn re te ilu In Fa Prevention & Appraisal Costs • To catch all defects, cost of good unit approaches infinity (very high cost) 27 Lean Thinking • Emphasis on prevention • Therefore the cost of good unit reaches its limit at Error Proofed stage. Cost of good unit = Cost of Error free & Waste free unit + Prevention & Appraisal Costs + Internal & External Failure Costs In al rn te E x ts & Cos al rn re te ailu F tion Cos Preven Prevention Costs = Cost of Mistakeproofing the value stream ts Cost of error & waste free unit 100% of units defective Quality Level of Outcome 0% of units defective Lean Thinking 28 Cost of Quality Four components: • Prevention Costs • Appraisal Costs • Internal Failure Costs • External Failure Costs } • High Quality High Cost of Appraisal & Internal Failure • We need emphasis on prevention “An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.” — Benjamin Franklin 29 Mistake-Proofing Principles BEST! Prevention of Errors Immediate Signaling & Correction of Errors Containment of Defects 30 Designing Quality at the Source • Mistake (error) proofing at source of root cause • Source Inspection > Assure quality of deliverable passed to next workstation is acceptable. — Provide means to perform inspection — Visual examples of standards — Document requirements for quality 31 Cost of a Good Unit External Failure Costs Internal Failure Costs Appraisal Costs Prevention Costs Waste Costs Error / Waste-free Unit Cost Outcome-Oriented (Traditional) Thinking Transition Phase Lean Thinking (State of Perfection) 32 “Quality means doing it right when no one is looking.” Henry Ford 33 Key Success Factors • Ensure linkage to business performance • Use for decision making > Justify business performance improvement • The point is to drive change > A behavior modification tool • Balances outcome measures with internal process and financial measures 34 Conclusion • Reducing the cost of poor quality is one of the best ways to reduce expenses • Aligns quality with financial goals • Enables prioritization and measurement of improvement • Promotes the effective use of resources • Makes quality more visible and creates incentives for doing the job right every time 35 Questions? 36