Chemistry Assignment #1
advertisement

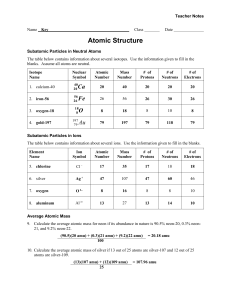
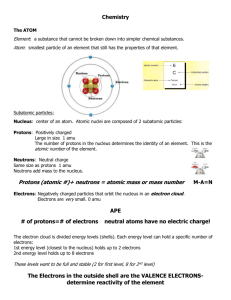
Chemistry Assignment #1 Chapter 4 3. Matter is composed of small particles called atoms that are indivisible. Atoms of an element are identical in size, mass, and chemical properties. Atoms of a specific element are different from atoms of another element. Different atoms combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compound. In a chemical reaction, atoms are separated, combined, or rearranged. 4. Dalton explained that atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions, but only rearranged. 7. A typical atom consists of a central, small, dense nucleus containing protons and neutrons. The nucleus is surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. 9. The deflection toward positively charged plates demonstrated the negatively charged nature of electrons; the fact that changing the type of electrode or the type of gas used in the cathode ray tube did not affect the ray produced led to the conclusion that electrons are present in all matter. 10. Particle Electron Proton Neutron Relative Charge -1 +1 0 Relative Mass 1/1,840 1 1 12. a. radon, 86 protons and 86 electrons b. magnesium, 12 protons and 12 electrons 13. dysprosium 14. silicon 15. Yes. 9 16. Protons and Electrons 20 8 26 30 80 Neutrons 26 9 31 34 124 Isotope calcium-46 oxygen-17 iron-57 zinc-64 mercury-204 Symbol 46 20Ca 17 57 26Fe 64 204 8O 30Zn 80Hg 17. 25 protons, 25 electrons, 30 neutrons. Manganese 18. B –10 10.013 amu x .198 = 1.98 amu B -11 11.009 amu x .802 = 8.83 amu Atomic Mass 1.98 amu + 8.83 amu = 10.81 amu 20. by the atomic number 21. the proton 23. Cu –63 62.930 amu x 0.692 = 43.5 amu Cu -64 64.928 amu x 0.308 = 20.0 amu Atomic Mass 43.5 amu + 20.0 amu = 63.5 amu 24. Mg –24 23.985 amu x 0.7999 = 19.19 amu Mg –25 24.986 amu x 0.1000 = 2.497 amu Mg –26 25.982 amu x 0.1101 = 2.861 amu Atomic Mass 19.19 amu + 2.497 amu + 2.861 amu = 24.55amu 27. a. nuclear b. chemical 30. Democritus 31.John Dalton c. neither d. chemical 32. Democritus’s ideas Atoms move through empty space composed of matter. Different kinds of atoms have different sizes and shapes. The movement, size and shape of different atoms result in unique properties of matter. Atoms are indivisible, solid, homogenous and indestructible. Observed changes in matter, result from changes in the groupings of atoms and not from changes in the atoms themselves. Dalton’s atomic theory Matter is composed of small particles called atoms Atoms of a given element are identical having the same size, mass and chemical properties. Different atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. Atoms cannot be created, destroyed or divided into smaller particles. In a chemical reaction, atoms are separated, rearranged or combined. 38. Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass. For example: desk, chair 39. protons and neutrons; positive charge equal to the number of protons 43. electron < proton = neutron 44. The number of positively charged protons equals the number of negatively charged electrons. 46. protons and neutrons 48. the electron 58. differ: number of neutrons, masses; similar: chemical properties, number of protons and electrons 59. They are all equal. 60. mass number = number of protons + number of neutrons 61. number of neutrons = mass number – atomic number 73. Symbol 132 55Cs 59 27Co 163 69Tm 70 30Zn Electrons 55 27 69 30 Protons 55 27 69 30 Neutrons 77 32 94 40 74. . Symbol Ga-69 F-23 Ti-48 Ta-181 Electrons 31 9 22 73 Protons 31 9 22 73 Neutrons 38 14 26 108