Print › Chapter 19: Drifting Toward Disunion (1854
advertisement

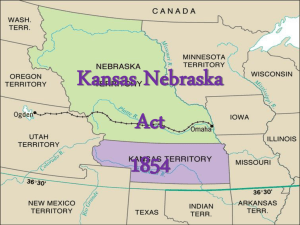
Chapter 19: Drifting Toward Disunion (1854-1861) Study online at quizlet.com/_ce4m3 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. "Beechers" Bibles rifles sent by the preacher husband of Harriet Beecher Stowe; they were hidden in a box of bibles and sent to abolitionists in Kansas "Bleeding Kansas" a sequence of violent events involving abolitionists and pro-Slavery elements that took place in the Kansas-Nebraska Territory; dispute further strained the relations of the North and South, making civil war imminent "Freeport Doctrine" Idea authored by Stephen Douglas that claimed slavery could only exist when popular sovereignty said so "KnowNothings" political party made up of nativists who answered questions about the society by answering "I know nothing."; supported only white, native born, protestatnt candidates 14. 15. 16. 17. "Lame Duck" a person still in office after he or she has lost a bid for reelection; Buchanan antiforeignism fear that immigrants would steal jobs and votes from "real Americans" 19. Charles Sumner gave a speech in May 1856 called " the Crime Against Kansas"; beat with a cane by Preston Brooks after the speech; he collapsed unconscious and couldn't return to Senate for 4 years; symbol throughout the north 20. on election day in 1855, hordes of Southerners "border ruffians" from Missouri flooded the polls and elected Kansas to be a slave state; free-soilers were unable to stomach this and set up their own government in Topeka 21. constitutional amendment introduced by James Henry Crittenden, compromise attempting to reconcile the South with the union by allowing slavery under 36; Lincoln opposed; didn't stop states from seceding 22. Democratic Convention of 1860 Democratic Party split into northern and southern wings, each nominating a different presidential candidate 23. Dred Scott vs. Stanford an 1858 Supreme Court case in which a slave sued for his freedom but the court ruled that slaves weren't citizens; damdged their reputation by saying black people/slaves were not citizens/people Election of 1860 Candidates Republicans nominated Abraham Lincoln; Northern Democrats nominated Stephan A. Douglas; Southern Democrats John C. Breckenridge; Constitutional Union (aka "Know-Nothings") nominated John Bell Contest for Kansas Crittenden Amendment Election of 1860 Issues mainly about slavery in the territories 18. 24. 25. 26. Election of 1860 Outcome Lincoln won with only 40% of the popular vote & won the electoral votes; South decides to secede Harper's Ferry John Brown's scheme to invade the South with armed slaves that was backed by sponsoring, northern abolitionists; tried to seize the federal arsenal; Brown and remnants were caught by Robert E. Lee and the US Marines; Brown was hanged Harriet Beecher Stowe wrote Uncle Tom's Cabin, a book about a slave who is treated badly, in 1852; persuaded more people, particularly Northerners, to become anti-slaver. Henry Crittenden from Kentucky; proposed the Crittenden Amendment Henry Ward Beecher preacher-abolitionist who funded weapons for antislavery pioneers in Kansas; brother of Harriet Beecher Stowe Hinton Helper Southern who argued against slavery not on moral grounds, but because he believed it was a system that impoverished poor southern whites and kept the South poorer than the North Homestead Act passed in 1862; gave 160 acres of public land to any settler who would farm the land for five years; settler would only have to pay a registration fee of $25; provided an easy way for more free-soilers to fill the territories Immigrant Aid Society founded by New Englanders to encourage new immigrants to start antislavery settlements in Kansas; immigrants were given wagons full of supplies if they agreed to move to Kansas and vote slavery down Jefferson Davis an American statesman and politician who served as President of the Confederate States of America for its entire history from 1861 to 1865 John Brown violent abolitionist who murdered slaveholders in Kansas and Missouri (1856-1858) before his raid at Harpers Ferry (1859), hoping to incite a slave rebellion; he failed and was executed, but his martyrdom by northern abolitionists frightened the South John Greenleaf Wittier was a Quaker poet who advocated abolitionism; influenced social action through anti-slavery poems Lawrence, Kansas where the pro-slavery /anti-slavery war in Kansas began in 1855 ("Bleeding Kansas") LeCompton Constitution pro-slavery constitution suggested for Kansas' admission to the union; It was rejected 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. nativists U.S. citizens who opposed immigration because they were suspicious of immigrants and feared losing jobs to them Outcome of Dred Scott Case inflamed millions of abolitionists against slavery and even those who didn't care much about it; Northerners complained; Southerners were ecstatic about the decision but inflamed by northern defiance, and more tension built Outcome of Harper's Ferry Brown became a martyr for abolitionists; Northerners rallied around his memory; abolitionists were infuriated by his execution; South was happy and saw justice & felt his actions were typical of the radical North Panic of 1857 notable sudden collapse in the economy caused by over speculation in railroads and lands, false banking practices, and a break in the flow of European capital to American investments as a result of the Crimean War; since it did not effect the South as bad as the North, they gained a sense of superiority Pottawatomie Creek Massacre In reaction to the sacking of Lawrence by pro-slavery forces, John Brown and a band of abolitionist settlers killed five pro-slavery settlers in Franklin County, Kansas Preston Brooks South Carolina representative who used a cane to beat Charles Sumner on the Senate floor for his criticisms of pro-slavery leaders Reasons for Secession South feared that their rights as a slaveholding minority were being threatened, and were alarmed at the growing power of the Republicans, plus, they believed that they would be unopposed despite what the Northerners claimed; also hoped to develop its own banking and shipping Roger B. Taney Chief Justice of the Supreme Court, who wrote the lead opinion in the Dred Scott case & said slaves weren't citizens, they were property Second Great Awakening second religious fervor that swept the nation; had an effect on moral movements such as prison reform, the temperance movement, and moral reasoning against slavery Shawnee Mission place where the pro-slavery Kansas government is established Simon Legree the cruel slave dealer in an anti-slavery novel by Harriet Beecher Stowe The Impending Crisis of the South trouble-brewing book written in 1857 by Hinton R. Helper, attempting to prove that slavery hurt non-slaveholding whites the most 39. 40. Topeka Constitution version of the Kansas state constitution written by a convention of Free State supporters that prohibited slavery; Congress rejected this version; Kansas' admission to the United States was delayed until 1861 Uncle Tom's Cabin book written by Harriet Beecher Stowe in 1853 that highly influenced England's view on the American Deep South and slavery; promoted abolition * intensified sectional conflict