17Monerans Eubacteria Archaebacteria Protists Fungi Plants

Virtual Science University
1
Texas TEK B (8) C—Student will identify characteristics of kingdoms including Monerans, Eubacteria,
(Archaebacteria) Protists, Fungi,
Plants, and Animals.
2
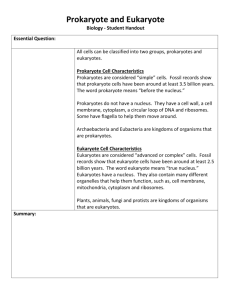
Biologists have always organized all living organisms into large groups called
Kingdoms.
For many years,
Scientists recognized two forms of life,
Prokaryotes
Eukaryotes.
3
Eukaryote is an organism that have cells with nuclei, or nucleus
Prokaryote is an organism without a nucleus.
4
Today, Biologists group organisms into six kingdoms, based on their similarities
Eubacteria and
Arachaebacteria were once grouped in the kingdom
Monera, which contained all the
Prokaryotes.
5
Today after the advances in Bio-
Technology, Scientists have gathered data from RNA and DNA
Sequencing
Monerans have now been divided into two distinct Kingdoms
Eubacteria
Archaebacteria
6
For many years
Scientists recognized two basic forms of life,
Prokaryotes
Eukaryotes.
In 1977, Carl Woese and his colleagues proposed that some prokaryotes are so di ff erent from others that they needed to be divided into their own broad division.
7
Woese and his colleagues based their proposal on comparisons of ribosomal RNA sequences.
They concluded that the prokaryotes that make up the kingdom
Archaebacteria are more closely related to
Eukaryotes than they are to the other
Kingdom of
Prokaryotes,
Eubacteria.
8
In 1996, Scientists made the first comparison between the DNA sequences of Archaebacterium and a Bacterium.
In light of the past di ff erences between the two groups of prokaryotes, biologists have adopted a classification system that divides all organism into three super kingdoms or domains:
Bacteria
Archae
Eukarya
9
The oldest of course is Bacteria.
This is followed by the
Archaebactera and then Domain
Eukarya which includes the other
Four Kingdoms:
Protista
Fungi
Plantae
Animalia
10
The Creative Process
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
www.VirtualScienceUniversity.com
1-877-920-5550
20