Covalent Bonding
advertisement

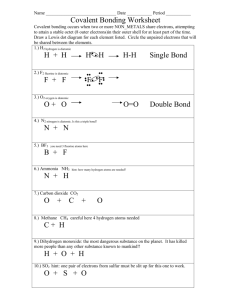
Chemical Bonding Part 1 Covalent Bonding Types of Chemical Bonds • Covalent Bonds – Single – Double – Triple -- Polar -- Non-Polar • Ionic Bonds • Metallic Bonds • Other “Bonds” – Inter-Molecular Forces first… A PREVIEW & SUMMMARY Ionic Bonds of the 3 main types of bond: while keeping in mind: Atoms are unhappy if their outer energy level is not full!! Atoms only bond with other atoms in order to fill their outer energy level. Covalent Bonds A covalent bond exists when two electrons are shared by non-metallic atoms. An ionic bond is the attraction between an anion and a cation, which form after an electron is transferred from a metal to a non-metal Metallic Bonding Takes place in a “SEA” OF MOBILE VALENCE ELECTRONS 1 Covalent Bonds: …are formed when two atoms share a pair of electrons. …always form between two non-metal atoms. …always form between atoms with similar electronegativity values. Covalent Bonding Example Time for an example: 6+ - - Vacancies Covalent Bonding Example Time for an example: How many electrons does carbon need to be happy? 4 electrons! 6+ - - - Carbon Covalent Bonding Example Remember, H has 1 e-(electron), and 1 p+(proton). - 1+ Carbon Covalent Bonding Example Covalent Bonding Example Remember, H has 1 e-(electron), and 1 p+(proton). Remember, H has 1 e-(electron), and 1 p+(proton). Is H happy? - 1+ How many vacancies does H have? - 1+ Nope! 1!!! 2 Covalent Bonding Example Covalent Bonding Example Let’s see how this looks… OK, time for the big moment: If C has 4 vacancies, and H has 1, how many H can bond with C? - - 4!!! Hydrogen Carbon Covalent Bonding Example Covalent Bonding Example Let’s see how this looks… Now we need to add our other H’s… - - Hydrogen - Carbon bonds with 4 hydrogens to form a methane molecule: - - - - - - Carbon Single, Double and Triple Bonds: a SINGLE covalent bond is formed by TWO electrons: Single, Double and Triple Bonds a DOUBLE covalent bond is formed by FOUR electrons: 3 Single, Double and Triple Bonds A water molecule contains two, single covalent bonds: a TRIPLE covalent bond is formed by SIX electrons: C Each bond consists of one pair of electrons being shared. C Other Examples of Covalent Bonding: Diatomic Molecules Other Examples of Covalent Bonding: Diatomic Molecules Hydrogen(H2) Whenever an element bonds with itself, a “diatomic molecule” is created. Many important molecules are covalently bonded diatomic molecules, for example H2, O2, N2, Cl2 (atmospheric & other gases) Other Examples of Covalent Bonding: Diatomic Molecules: Hydrogen(H2) two electrons form a covalent bond two H atoms held together by a single covalent bond Covalent Bonding Oxygen(O2) Double Bond 4 Naming Covalent Compounds Covalent bonding • Results from the sharing of a pair of valence electrons • Between non-metals only (and Hydrogen) • Single, Double or Triple Bonds • Unequal sharing is called a polar covalent bond (more on this later) some stuff you already know: _______________________ CO2 Carbon Dioxde _______________________ SO2 ____ Sulfur Dioxide NF3 ____ MonoDiTriTetraPenta- 6 7 8 9 10 HexaHeptaOctaNonaDeca- Examples: Carbon Tetrachloride CCl4 _______________________ Diphosphorous Pentoxide P2O5 _______________________ N2O4 ____ Dinitrogen Tetroxide P4S10 Tetraphosphorous Decasulfide ____ Nitrogen Trifluoride Rules for Naming Covalent Compounds Prefixes used for covalent compounds: 1 2 3 4 5 Carbon Monoxide CO 1. Name the first element (the least electronegative is first) (the furthest left on the periodic table.) 2. If there is more than one atom of that element, add a prefix. 3. Name the next element & add a prefix. (even if there is only one, add “mono-”) 4. Add the “-ide” suffix. LEWIS DOT STRUCTURES …are sketches of molecules or atoms that show valence electrons as dots C Carbon 4 valence e- Na Sodium 1 valence e- F Fluorine 7 valence e- 5 LEWIS DOT STRUCTURES The Octet Rule are helpful to show how valence electrons are involved in bonding: Remember: Atoms only bond in order to fill their valence shell. Two F atoms: F F In the case of Hydrogen, this means having 2 valence electrons. (duet rule) One F molecule: F F Single covalent bonds are drawn as single lines F Remember: Single Covalent Bond = 2 electrons Rules for Drawing Lewis Structures : F H : H In the case of most other non-metal elements this means getting 8 valence electrons (octet rule). • Use one pair of electrons to form a covalent bond between outside atoms and the central atom. 1. Calculate the total number of valence electrons for each atom, and add them up. • Arrange the remaining electrons to complete the octets of the outside atoms. 2. If there are more than two atoms, start with central atom (usually the least electronegative but never hydrogen). • If the central atom lacks an octet, then form double or triple bonds instead. Make sure all atoms have an octet, except Hydrogen, which always has 1 bond. Resonance structures Sometimes more than one correct Lewis structure can be drawn; especially if there are double and triple bonds. Example: In such a case we call the various structures resonance structures. 6