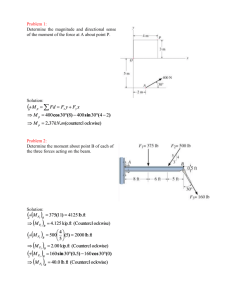
Solutions
advertisement

Solutions to Practice Test for Midterm 2 You must show all your work. The number of points earned on each problem will be determined by how well you have justified your work. 1. Determine whether the equation is exact. If it is, then solve it. ¡y 2 sin x sin y¢dx ¡2xy " cos x cos y¢dy 0 M y N x y 2 sinxsiny y 2x"cos xcos y x 2y sin x cos y 2y sin x cos y The equation is exact by Theorem 2, page 59. Fx, y sin x sin y dx y 2 x " cos x sin y gy F 2yx " cos x cos y g y ® y y g y 0 ® gy C ;y 2 y 2 x"cos x sinygy U U Therefore, the solution to the equation is given implicitly by y 2 x " cos x sin y C 0. 2. Find an integrating factor of the form x n y m . Solve the equation. 2x 2 y x "7 y 2 dx 4x 3 x "6 y dy 0 x n y m 2x 2 y x "7 y 2 dx x n y m 4x 3 x "6 y dy 2x n2 y m1 x n"7 y m2 dx 4x n3 y m x n"6 y m1 dy 0 2x n2 y m1 x n"7 y m2 2m 2 x n2 y m m 2 x n"7 y m1 y 4x n3 y m x n"6 y m1 x 4n 12 x n2 y m n " 6 x n"7 y m1 2m 2 4n 12 ® 2m " 4n 10 m 2 n " 6 ® m " n "8 ® m "21, n "13 Fx, y F y " ;2x "11 y "20 1 5x 10 y 20 " 1 19x 19 y 19 x "20 y "19 dx " gy y 4 x 10 y 21 1 5x 10 y 20 1 x 19 y 20 " ® ® gy 1 19x 19 y 19 g U y ® g y 0 U ® Therefore, the solution to the equation is given implicitly by " 5x 101y 20 " gy C 1 19x 19 y 19 C 0. 3. Determine whether Theorem 2, page 157, applies. If it does, then discuss what conclusions can be drawn. cos xy xy " x 3 y tan x, y =4 5, y =4 "= UU U U x We write the equation in standard form : y cosx x y " cos x y sin x 3 x x = The functions cos x and " cos x are not continuous at 2 k=, k an integer, but we can say that they are continuous in the interval " =2 , =2 which contains =4 . By Theorem 2, there exists a unique solution yx on the interval " =2 , =2 . UU U 3 4. Use Definition 3, page 163, to determine whether the functions y 1 and y 2 are linearly dependent on the interval 0, 1 . Also compute the Wronksian W¡ y 1 , y 2 ¢x . y 1 x x 2 " 2x, y 2 x 4x 2 " 6x Consider c 1 x 2 " 2c 1 x 4c 2 x 2 " 6c 2 x 0 ® (c 1 4c 2 x 2 "2c 1 " 6c 2 x 0x 2 0x ® c 1 4c 2 0 ® c 1 "4c 2 "2c 1 " 6c 2 0 ® "2"4c 2 " 6c 2 2c 2 0 ® c 2 0 ® c 1 0 We also note that neither y 1 x nor y 2 x achieve the value 0 in the interval 0, 1 . Therefore, the functions are linearly independent. W¡ y 1 , y 2 ¢x x 2 " 2x 4x 2 " 6x 2x " 2 determinant: "2x 2 p 0 on 0, 1 . 8x " 6 5. Find a general solution to y 4 26y 25y 0 Try using your calculator to find the roots. UU The auxiliary equation is r 4 26r 2 25 0, Solution is : £r 5i ¤, £r "5i ¤, £r i ¤, £r "i ¤ The general solution is y c 1 cos5x c 2 sin5x c 3 cos x c 4 sin x 6. Solve the initial value problem y " 26y 169y 0, y0 3, y 0 "1 UU U U The auxiliary equation is r 2 " 26r 169 " 0 ®, Solution is : £r 13 ¤, £r 13 ¤ Therefore, the general solution is y c 1 e 13x c 2 xe 13x