Additional Mathematics
advertisement
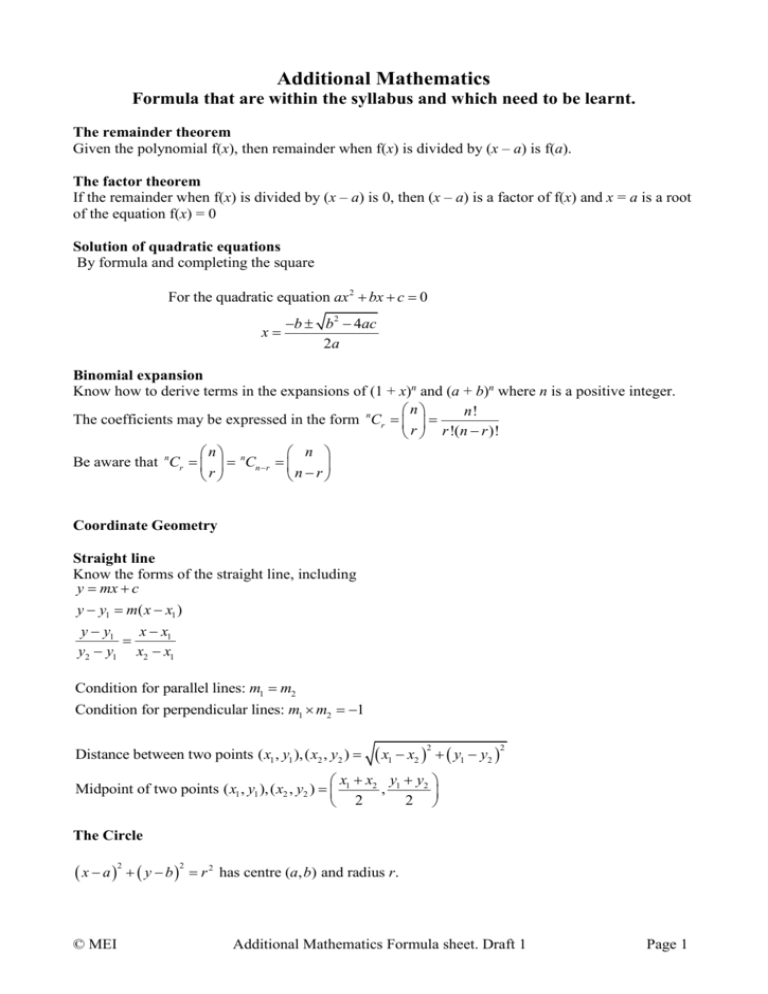
Additional Mathematics Formula that are within the syllabus and which need to be learnt. The remainder theorem Given the polynomial f(x), then remainder when f(x) is divided by (x – a) is f(a). The factor theorem If the remainder when f(x) is divided by (x – a) is 0, then (x – a) is a factor of f(x) and x = a is a root of the equation f(x) = 0 Solution of quadratic equations By formula and completing the square For the quadratic equation ax 2 bx c 0 x b b 2 4ac 2a Binomial expansion Know how to derive terms in the expansions of (1 + x)n and (a + b)n where n is a positive integer. n n! The coefficients may be expressed in the form nCr r r !(n r )! n n Be aware that nCr nCn r r nr Coordinate Geometry Straight line Know the forms of the straight line, including y mx c y y1 m( x x1 ) y y1 x x1 y2 y1 x2 x1 Condition for parallel lines: m1 m2 Condition for perpendicular lines: m1 m2 1 Distance between two points ( x1 , y1 ), ( x2 , y2 ) x1 x2 y1 y2 2 2 x x y y Midpoint of two points ( x1 , y1 ), ( x2 , y2 ) 1 2 , 1 2 2 2 The Circle x a y b 2 © MEI 2 r 2 has centre (a, b) and radius r. Additional Mathematics Formula sheet. Draft 1 Page 1 Trigonometry In a right-angled triangle: opposite adjacent opposite , cos , tan hypotenuse hypotenuse adjacent Identities: sin sin cos 2 sin cos 2 1 tan = Sin rule: a b c SinA SinB SinC Cos rule: a 2 b 2 c 2 2bc cos A cos A b2 c2 a 2 2bc Calculus y ax n dy nax n 1 dx Stationary points occur when dy 0 dx b Area under curve between x a and x b is y dx a Kinematics Constant acceleration formulae 1 s ut at 2 2 u v t s 2 v u at v 2 u 2 2as © MEI Additional Mathematics Formula sheet. Draft 1 Page 2