Generalized Root Locus Outline Variable Parameter Example
advertisement

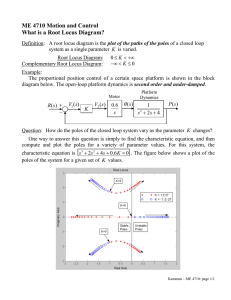
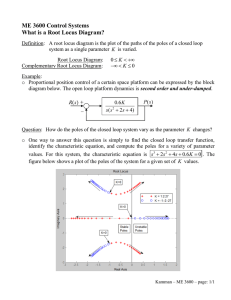
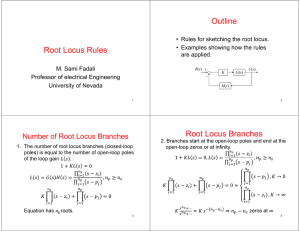
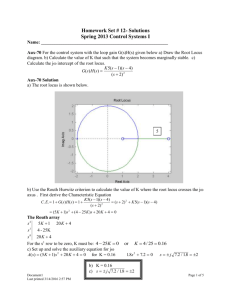
Outline • Generalize the root locus to examine the effect of varying other parameters. • Rewrite characteristic equation. • Example. Generalized Root Locus M. Sami Fadali Professor EE University of Nevada 1 Variable Parameter 2 Example: Variable Pole Location R(s) • Vary parameter other than the gain K. • Rewrite characteristic equation in the usual form with the parameter appearing in K’s place. • Closed-loop poles are still the roots of the new equation. 10 s 2s p C(s) K L(s ) Loop gain K L( s ) 1 K L( s ) 10 10 2 s 2s p 10 s 2s 10 p( s 2) T (s) 3 4 Root Locus: p Variable Rewrite Characteristic Eq. T (s) ଶ ଶ 10 s 2 2 s 10 p ( s 2) 3 2 Imaginary Axis Not the loop gain 0 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -10 -8 -6 5 Design: Tp about/2 s -4 -2 0 2 Real Axis 6 Solve for Poles Tp d 2 Root Locus 10 10 1 s2 1 p 2 0 s 2 s 10 4 Radius= Root Locus 4 10 s 2 2 s 10 1 p ( s 2) s 2 2 s 10 Characteristic Eq. ଶ • Radius= 3 d 2 rad/s 2 Imaginary Axis 1 n 2 10 4 2 6 4.45 rad/s 10 2 0 n ? 6 -1 n n 2 d2 4.88 rad/s 0 .9 -2 -3 -4 -10 -8 -6 -4 Real Axis -2 0 2 7 8 Using MATLAB Root Locus System: g Gain: 6.89 Pole: -4.44 + 2.01i Damping: 0.911 Overshoot (%): 0.0953 Frequency (rad/sec): 4.87 4 3 2 • Calculate p using the magnitude condition L p ( s) n 4.44 n 4.87 1 Imaginary Axis Determine p 1 s 2 2 s 10 6.89 p s2 L p ( s) ss s scl p 6.89 0 -1 cl -2 G (s) -3 -4 -10 s2 s 2 2s 10 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 9 Real Axis Conclusion • Can use root locus to determine the effect of varying any parameter. • Root contours: plot family of root loci with each plot obtained for one value of the first parameter (say K) as a second parameter (say p) is varied. 11 10 s 2s 6.89 10