BUSINESS ARCHITECTURE (BA) Organization Structure
advertisement

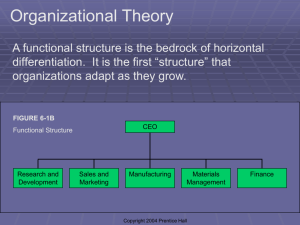
BUSINESS ARCHITECTURE (BA) Organization Structure The organization chart Organization manual BP and organization structure Exercises Review questions Organization Structure • A BP may cross multiple organizations, and, in turn, an organization may be involved in multiple BPs. • Organization may be described from a static or dynamic perspective • Organizational dynamics describes the behavior of organizations under certain conditions, as change; this field is typical of social sciences • Organization structure describes the static aspect. This field is typical of business sciences and management culture. • A structure description is Organization Chart. • Organization Chart is integrated by Organization Manual that describes details Organization Chart: first level (example) President & Chief Executive Officer (CEO) Vice President Research & Development Vice President Production External Relations Legal & Security Internal Audit Human Resources Vice President Sales (US) Vice President International Operations Vice President Finance Vice President Marketing Organization Chart: organization levels (example) Regional Accounting Branch (6-10 in a Region) Sales Support New Installations Sales VP Sales Region (8 regions in US) Service Installations Regional Operations Repair Maintenance Level 1 (VP) Level 2 (Director) Level 3 (Manager) Level 4 Supervisor / Employee Level 5 Foreman/ Employee Organization Chart: comments • President & Chief Executive Officer (CEO) Vice President Research & Development Vice President Production External Relations Legal & Security Internal Audit Human Resources Vice President Sales (US) Vice President International Operations The chart defines the responsibility of each organization unit. – – Vice President Finance Vice President Marketing – – Regional Accounting Branch (6-10 in a Region) Sales Support – New Installations Sales VP Sales Region (8 regions in US) Service Installations Regional Operations – Repair President has the authority to decide the objectives of all Vice Presidents (VP). At a lower level, each VP plans and controls the objectives of organizational units that report to him or her. E.g. The VP of Sales plans and controls operations of the Regions that report to him, and each Region in turn plans and controls the actions of the operations and branches that report to the Region. Each first tier unit is further divided in smaller units, and the breakdown may include up to 5 levels, depending on the size and complexity of the units. Sales division is broken down in Regions, each in charge of an area (e.g. New York City, East Coast, etc.). Each Region includes staff (Regional Accounting, Sales Support), technicians and engineers in charge of installing, maintaining and repairing elevators, and local branches, with a small team of salesmen, in charge, respectively, of selling installations or service to installed elevators. Assuming that each region has an 8 branches, branches would be around 50. Maintenance 5 Organization Manual • Organization charts are often integrated by text comments, that state objectives, tasks, responsibility, authority of each organizational unit. – Objectives define what the organizational unit (and its manager) should obtain. – Tasks are the activities the unit should perform and ideally coincide with the activities of the business processes the unit is involved in. – Responsibility is given by the results the unit is accountable for; e.g. a factory is responsible for the quality of products. – Authority are the areas where the unit can decide. E.g. a factory manager is responsible for the quality but has no authority to decide on quality standards. • The set of these descriptions make an “organizational manual”, that are also partially incorporated in ISO 9000 quality requirements. Organization Manual Organization Chart Description of each organization unit / position Objectives Responsibility Authority Tasks 6 Forms of Organization Structure • The structure of any large organization has to deal with diverse coordination dimensions: – Geography, where departments are grouped by region, typical of banks, railways, post office etc. – Function, where departments are grouped by competence, that are typical of small companies – Product or Customer, where departments are grouped by the customers they serve or the product they deliver – Program or Projects, where departments are grouped by projects they are working on • Traditionally structures are classified in three main categories – Step 1 Functional – Step 2 Divisional – Step 3 Matrix 7 Functional structure: Railways (early times) CEO Regional Operations Staff Personnel • • • Accounting Traffic Equipment Transport Functional structures have been historically the earliest organization form Railways in late Eighteen Hundred engineered a functional structure with central departments and a series of identical geographic structures The pure functional structure is rather rigid and hardly supports cross organizational BPs Region 1 Region … Region n Personnel Personnel Personnel Accounting Accounting Accounting Traffic Traffic Traffic Equipment Equipment Equipment Transport Transport Transport 8 Divisional structure: Automotive Enterprise • Divisional structures were born with large manufacturers • In the example Divisions reflect the product life cycle from the design down to the service; each Division cover a phase of product life cycle • The divisional structure is rather resilient structure and supports cross functional BPs CEO R&D Division Personnel Finance Legal, Audit etc. IT Product Division A Product Division B Production Division Sales & Service Div. Design Marketing Marketing Production Staff USA & Canada Test Lab Product dev Product dev Plant A EU Plant B FE (PRC, Japan etc.) Plant C Other Countries 9 Complex Structures: Aerospace CEO • • • • Complex structures were born with high technology programs Typically the vendor is a systems integrator that assembles subsystems made by a variety of suppliers In the example Divisions reflect the breakdown of the program in work packages The program structure is resilient and supports cross enterprise BPs R&D Division Program XXX Personnel Finance Legal, Audit etc. IT Program YYY Production Division Sales Service Design QA QA Production Staff Air Carriers Spare part Test Lab Wings Wings Plant A Government and Military Central serviice Fuselage Fuselage Plant B Systems Systems Plant C Cockpit Cockpit Engine Engine Assembly & Test Assembly & Test 10 Milan Municipality (2007) 11 The assembly line of Boeing 787 Source: The Boeing company: The Mooshine Shop , HBS, 9-607-130 12 Work packages in 787 programs Source: Boeing 787: The Dreamliner (B) 13 Organization Structure versus Business Processes • A many-to-many relation occurs between BP and Organization Structure. • Accordingly a BP may be – Functional: segregated within the boundaries of an individual organization unit (it seldom happens) – Cross-functional: across multiple units of the same organization – Cross-organizational: across multiple organizations 14 Functional BP: example Corporate Dpts Finance Dpt Info request Gather data Publish report Report Analyze data 15 Cross-functional BP : example Corporate Dpts Production Planning Production request Gather data Materials Mngt Plant Production deliver y Expedite Execute 16 Cross-organizational BP: example Information Deliver Books Track Order Book request Order Books Front-end Control Credit Credit Organization Book delivery Pick Books Bookshop Courier 17 Review questions • • • • What is an organization structure? What is an organization chart? What is the content of an organization manual? What is the relation between organization structure and business processes? • Describe: – A functional BP – A cross functional BP – A cross organizations BP Exercises Sketch and comment organization charts Exercise 1: organization structure of UNIPV 20 Exercise 2: organization structure of MIT 21 Exercise 3: organization structure of IBM 22