5 XUV L
advertisement

4,
Jÿ
Name:
4th SIX WEEKS TEST REVIEW
REPRODUCTION
5 XUV L
is the type of reproduction that requires two ÿs.
a.
Thistype of reproduction requires Z (#) sex ceÿis: an Eÿ_.ÿ
b.
in this type of reproduction, offspring are genetically ÿ ÿiE..P-.,SF___
and a ÿ-ÿ
which means
D \PT: ÿ---.Aÿ!,4 T
c. Name 3 organisms that reproduce in this manner:
DOGS
,
ASÿ-ÿ tAÿL
,
"
,,
t4bbÿtÿ ÿ
©ZÿT5
is the type of reproduction that requires on_ee parÿent.
"
ÿ-"ÿs
(#) s cÿx-c-ÿ.
b. In this type of reproduction, offspring are genetically l ÿ)_t::=ÿ ÿxJTÿ O!ÿ, L
means ÿ-iÿ_. ÿAÿtF___
(which
) to the parent. ÿ/ÿL$o; LÿkÿF_OÿIÿXÿ
c. Name g organisms that reproduce in this manner: ÿ piS H
Lÿ/VZTÿmt A
.
Which type of reproduction causes more variation/diversity among offspring? WHY?
Bÿc4ÿ,usm TNE.Y GPT A COMBtkÿATÿo!ÿ OF- Gÿ-nc AÿA-ÿ,zÿ-;
4. Determine if the diagrams illustrate sexual Or asexual reproduction and label below.
I. ÿSÿ.:'XUÿ_NL
III. ÿ_ÿW.bL,ÿL
Ii. ÿE.ÿbLÿ L
IV. A-SEx: L.LA.L
HEREDITY
5. Define'Heredity:. -Tÿ--
FP-.ofÿ
SOME- FIÿ,O
Dichotomous Key
17. Define Dichotomous
ÿ
.
.
ÿ
ÿ,
ÿ
/
18. When using a dichotomous key, what type of characteristics is most helpful for making anÿ°ÿ:ÿ
identification?
ÿ
19. Give 3 examples of characteristics you might find on a dichotomous key.
Complete the attached Dichotomous Key for added practice.
True/False - Mark your answer. Correct any false statements to make them true.
1,
A recessive trait is ÿveÿsÿeÿ
Genes control traits.
.
,o
3.
ÿuÿeproduction only involves one parent.
,
Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of a cell.
°
Asexual offspring are genetically identical to their parent.`'
o
The presence of a brightly colored, detachable tail is an advantage for some lizards because
predators are more likely to grab them by the tail.
.
A dichotomous key is used to identify different types of organisms.
,
Budding is a type ofÿrÿFreproduction.
,
Camouflage is an adaptation that increases survival.
All humans haveÿ4ÿ5ÿchromosomes•
6. Put the fol
Dli,lA
7. How man
in order from smallest to largest: DNA, chromosome, cell, nucleus, gene
eÿcg_ÿ . + ÿoÿo5oMÿs + tVUÿOLÿU-S
÷ Ce_LL
es are in every human cell's nucleus, with the exception of 2 types? /4
8. How many chromosomes are ÿn sperm and egg ce,s? 2_53 Why? 25 rÿ0ÿ mprÿt ÿ Z3
=ÿzoM EJs6 coÿmÿ To ÿE %ÿG ÿFTÿ pmÿT!ÿmÿTÿO4_
9. What is a dominant trait? /ÿ -{iÿ.ÿT ÿ ÿT COVP_.ÿ Lÿ /MÿOl-i'HEtZ r--oÿ7ÿt, ÿTSÿ0-ÿJ
:20. What is a recessive trait? OÿvfF_ ÿAÿT ÿ H ÿDE)P_-Iÿ B'ÿ" ÿK)0TÿF_ÿ-, IT- ÿF---ÿNÿ-
SH0
1:2. All sexually reproducing organisms, including humans, acquire one set of their genes from their
mother and one from their father. These are passed down in the form or chromosomes, which
reside in the ÿJ ULC,LÿU%ÿ
of the cell.
:22. Explain how two parents showing a dominant trait have offspring showing the recessive trait?
_S40ku, -ÿ-HF_ OFÿSi>ÿG iÿ4{4ÿPÿCTs g;ÿP4 ÿSlXJÿ GF_JÿF__ÿ
ADAPTATIONS
!3. Define adaptations. TÿF-- ÿIÿ.OCÿF_.ÿS ÿ'1" WH[C-Jrÿ L ÿ'ÿ©pLLLÿ-ÿ"[O]J
14. Definenaturalselection._OÿGÿ&ÿ\ÿMÿ% ÿt'T'ÿ "Tÿ.]-ÿ -I-ÿ-ÿ-T ÿÿ ÿTÿ
a. Explain how natural selection affected the finches on the Galapagos Islands:
THEÿE D\FT-P-PÿFÿT T-O0b sOumcrrÿ oM "THE_ ÿ£LAÿDS SO THE
.-l"ÿosÿ_ ÿ.-ÿJÿ£Tÿ Oÿ -To ÿn-lÿ_A ÿ- OT--Eÿ2M tdG
15. Define selective breeÿing. ÿ:bpÿ_: C,,ÿ4OoSÿ_ I"F-A-[-f'ÿ q'ÿ4ÿ_,y ÿNÿT -TO 1ÿ<ÿ oÿ
4Tt4ÿ'f C4zÿSS-ÿlb oÿ C£-ZÿS-pOLLÿMÿqÿ To Gÿ--T'TÿtOSÿ ÿCÿ.zÿqTÿ,
a. Explain why a farmer would use selective breeding: ÿ ÿ,,OÿLLCÿ
ÿPS
J
3.6. Predator- iÿIÿLÿ I-Tÿ_-i- ÿUÿtJT O-iÿHÿ=-9ÿ ÿ,K)ÿVÿiÿL.S ÿ ÿ-ÿT
:27. Prey ÿ" ÿÿ_ÿ ÿ-ÿA-T ÿtÿ_ ÿ4L£tÿTÿ_£:) ÿ'ÿ ]pÿ-ÿ_ÿ:)ÿ'-ÿDÿ--S
:$8. Explain how a mutation becomes an adaptation. A- I2.ZÿOobÿ C_ÿE.t-flC N%ULÿ-ÿIOÿO
s zvwe; -to
rÿpÿZObbLCÿ ,ÿ ÿAggt kl Ca ou T'ÿAT
Name:
Taxonomy, Classification, and Dichotomous Keys
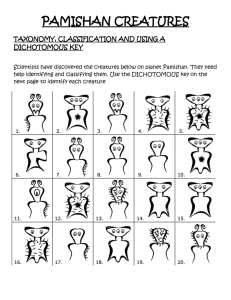
.Help! Scientists have discovered quite-a few new crewatures on planet Pamishan, They need
your help to identify and classify them. Use the dichotomous key on the next page to identify
these creatures.
-
"=1ÿ'
n
=
• - ..
6.
15,
!4,
13,
12,
11,
10.
=
=
=
')}
16,
....
POR-.-T'DL 5
2..:,tÿ,
ixi<Cÿ4bts
PL/AIb4 O.S
A\EiIS
Aÿ.sob4
7. ÿx[,
8.}4
9.
4oÿTAÿ4\A}4
12. ÿ)
13. H
14. ÿ)
20= •
LAÿ b4 LÿS
GEO£.rq \Aÿ4 A
SLAÿ<UÿS
10.
!1. ÿ%ÿ
4.b
19,
18,
1"7,
YCLoÿ S
16.
V-. \ P EIÿ.Lÿ S
17.
SWAÿ.ÿO,ÿP-b bÿ S
18. ÿ)
}4A ÿ &h/ s-Vÿ P-- uLS 19.
5Eÿg-b bt S
NÿLTF--P-ÿ
20. ÿXÿ
F tÿZZ ÿ-S
A Key to New Pamishan Creatures
i.
a
The creature has a large wide head
b
2.
a
b
3.
4.
5,
............................
The creature has a small narrow head
It has 3 eyes
It has 2 eyes
................................................
a
There is a star in the middle of its chest
b
There is no star in the middle of its chest
a
The creature has hair spikes
b
The creature has no hair spikes
7.
a. The creature has hairy spikes
b. The creature has an M-shaped bottom
I0 a
b
!I a
b
12 a
b
13 a
b
14 a
b
15 a
b
16 a
b
17 a
b
18 a
b
19 a
b
The creature has an M shaped bottum
The body is symmetrical
The creature has antennae
There are spikes on the face
.......................
Broadus kiferus
Broadus walter
Broadus anderson
go to 12
.................................
Narrowus wolfus
..............................
...........................
............................
........................................
Narrowus starboardus
go to 15
Narrowus cyclops
go to 16
.....................................
go to 17
.............................
...................................
Narrowus portus
Narrowus p!ainus
......................................
The creature has no spikes
go to 13
Narrowus blankus
......................................
There are spikes on the left leg
The creature has spikes
Broadus hairyemmus
..........................
.......................................
There are no spikes at all
go to 9
go to 14
There are spikes on the right leg
The creature has no mouth
go to !0
.................................
The creature has no spike anywhere
The creature has a mouth
Broadus tritops
go to 8
....................................
There are no spikes on the face
The creature has 2 eyes
Broadus p!ainus
Broadus hairystarus
.....................
...................................
The creatrue has no antennae
The creature has 1 eye
....................
......................................
The body is not symmetrical
Broadus emmus
.......................
....................................
a. The creature has an arch shaped bottom
go to 5
Broadus archus
...........................
b° The is no star in the middle of its body
b
....................
................................
a. There is a star in the middle of its body
go to 6
Broadus hairus
.......................
a. The creature has an arch-shaped bottom
go to 4
....
...............................
b. The bottom of the creature is M-shaped
9.
,
.................................
a. The bottom of the creature is arch-shaped
b0 The creature has no spikes
go to
....................
..............
go to II
go to 3
................................................
60
8.
go to 2
..........................
...................................
There are spikes on the head
There are spikes on the right leg
Narrowus georginia
.................................
.............................
There are spikes covering the face
...........................
go to 18
go to 19
Narrowus montanian
Narrowus beardus
There are spikes only on the outside edge of head ............ Narrowus fuzzus