Economic Order Quantity
advertisement

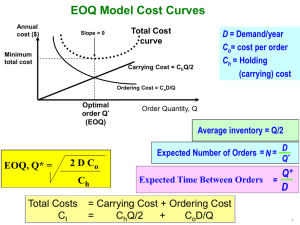
The Decisions to be Made Economic Order Quantity The Definition of EOQ EOQ, or Economic Order Quantity, is defined as the optimal quantity of orders that minimizes total variable costs required to order and hold inventory. One of the most frequent decisions faced by operations managers is “how much” or “how many” of something to make or buy in order to satisfy external or internal requirements for some item. Many times, this decision is made with little or no thought about its cost consequences. The basic model makes the following assumptions: Demand is uniform, constant and continuous over time; The leadtime is constant; There is no limit on order size due either to stores capacity; The cost of placing an order is independent of size of order; The cost of holding a unit of stock does not depend on the quantity in stock; Exactly the same quantity is ordered each time that a purchase is made. 1 How to use EOQ in your organization Costs How much inventory should we order each month? EOQ accounts for 3 types of costs: The EOQ tool can be used to model the amount of inventory that we should order. Inventory Holding Costs Reasonably Typical Profile Category % of Inventory Value Housing (building) cost 6% Material handling costs 3% Labor cost 3% Inventory investment costs 11% Pilferage, scrap, & obsolescence 3% Total holding cost 26% Unit Cost: the cost of the units themselves, assumed to be fixed, regardless of the number of units ordered Inventory-Holding Cost: the cost of holding units in inventory Fixed order cost: represents all the costs associated with placing an order excluding the cost of the units themselves (any administrative costs of placing and/or receiving an order) EOQ Model Annual Cost Holding Cost Order Quantity 2 Why Order Cost Decreases EOQ Model Cost is spread over more units Example: You need 1000 microwave ovens 1 Order (Postage $ 0.35) Annual Cost 1000 Orders (Postage $350) Purchase Order Description Qty. Microwave 1000 Holding Cost Purchase Order Purchase Order Purchase Order Description Qty. Purchase Order Description Qty. Description Qty. Microwave Description Qty.11 Microwave Microwave Microwave 11 Order Cost Order quantity Order Quantity How EOQ Works EOQ Model The Total Cost Formula Annual Cost Total Cost Curve Total Cost = Purchase Cost Holding Cost Order Cost Optimal Order Quantity (Q*) + Order Cost + Holding Cost Order Quantity 3 How EOQ Works The Total Cost Formula How EOQ Works The Total Cost Formula This represents the unchanging fixed costs This represents the variable order costs P = Purchase cost per unit R = Annual usage in units C = Cost per order event (not per unit) Q = The number of units ordered P = Purchase cost per unit R = Annual usage in units How EOQ Works How EOQ Works The EOQ Formula The Total Cost Formula Total Cost Formula This represents the variable holding costs Taking the derivative of both sides of the equation and setting equal to zero to find the minimum value of the function, one obtains: P = Purchase cost per unit R = Annual usage in units C = Cost per order event (not per unit) Q = The number of units ordered F = Holding cost factor 4 How EOQ Works How EOQ Works The result of differentiation The Economic Order Quantity How EOQ Works P = Purchase cost per unit R = Annual usage in units C = Cost per order event (not per unit) F = Holding cost factor How EOQ Works The graphic representation of the EOQ equation Expected Number Orders = N = R/Q* Expected time between orders: T= Working days / Year N 5 Real Life Example: Real Life Example: Real Life Example: Real Life Example: Next let’s identify the correct variables… First, Recall the EOQ Equation: P = Purchase cost per unit R = Annual usage in units C = Cost per order event F = Holding cost factor 6 Real Life Example: Forecasted Amount Real Life Example: Cost per Unit Real Life Example: Ordering Costs Real Life Example: Holding Cost Factor 7 Real Life Example: Real Life Example: R = Annual demand R = 5200 C = Fixed ordering cost C = $10 per order P = Cost per case P = $2 F = Holding Cost Factor F = 20% of value of inventory per year Real Life Example: Wrapping It Up EOQ, or Economic Order Quantity, is defined as the optimal quantity of orders that minimizes total variable costs required to order and hold inventory. EOQ = 2 (10) (5200) (2 )(.20) 8 Conclusion EOQ Example You’re a buyer for SaveMart. EOQ is useful for minor stock items of low values with known steady prices, demands and supply lead times; Where there is demand variability, such as seasonality, EOQ can still be calculated but using shorter time period. SaveMart EOQ R= C= P= F= H= H= 1000 $100 $ 78 40% PxF $31.20 EOQ SaveMart needs 1000 coffee makers per year. The cost of each coffee maker is $78. Ordering cost is $100 per order. Carrying cost is 40% of per unit cost. Lead time is 5 days. SaveMart is open 365 days/yr. What is the optimal order quantity? Homework 2 1000 $100 $31.20 Calculate the EOQ of „A” materials if: The quartal demand for material "A" is 1.500 pieces The purchase price per unit is $80 The rate of storage cost is of 20% of the purchase price per unit Fixed costs are $50 per order How many times should we order to meet the annual demand for material "A"? EOQ = 80 coffeemakers 9