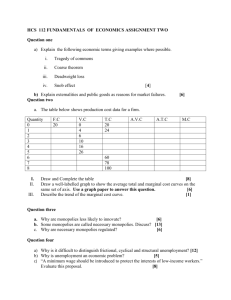
The Economic System at Work
advertisement

The Economic System at Work Why It Matters Tell students that American economic freedoms include the freedom to buy and sell, to earn a living, to earn a profit, to compete, and to own property. Ask students which of these freedoms they have experienced in their daily lives. (Possible answers: the freedom to compete for jobs, the freedom to buy and sell merchandise or services) Tell students to consider how these freedoms are important to the health and well being of U.S. citizens. TAKING BEFORE YOU READ The Main Idea Reading Focus Key Terms Countries form many types of economic systems to meet their citizens’ needs and wants. The United States has a market economy. 1. How do different economic market economy, p. 452 free market, p. 452 profit, p. 453 scarcity, p. 453 law of supply, p. 453 law of demand, p. 453 free enterprise, p. 455 capitalism, p. 455 monopoly, p. 456 systems help satisfy people’s needs? 2. What factors shape life in a market economy? 3. What is the U.S. economic system like? As you read, take NOTES notes on economic systems, life in a market economy, and the U.S. economic system. Use a chart like this one to record your notes. Key Terms Preteach the following terms: market economy economy in which people are free to obtain goods and services in almost any way they want (p. 452) free market right to buy and sell goods as you want (p. 452) profit money that a business has left after expenses (p. 453) scarcity lack of a particular resource (p. 453) law of supply economic principle that businesses will produce more products when they can sell them at higher prices and fewer products when prices are low (p. 453) law of demand economic principle that buyers will demand and buy more products when prices are low and fewer products when prices are higher (p. 453) free enterprise principle that business owners in a free market are allowed to run their businesses in any way they see fit, with little government interference (p. 455) capitalism economic system in which the means of production are owned by private citizens (p. 455) monopoly what a company has when it is the only one selling a product or providing a service (p. 456) Taking Notes Economic Systems • How people obtain goods and services • Traditional, command, and market economies 450 Life in a Market Economy • Competition for resources • Supply and demand • Free enterprise, capitalism CHAPTER 17 Our society is based on principles of individual freedom. Those same principles of freedom apply to the U.S. economic system. We have what is called a free market economy. This means that if you want to start a business, you can. Your success will be determined by your business ability and the market, not by a government agency. Economic Systems Suppose you wanted to make a sandwich but you discovered that you had no bread. How could you get more? Would you have to grind wheat into flour so that you could bake a new loaf? Might you have to stand in a long line for hours before someone gave you a few slices? Of course you wouldn’t. With a quick trip to the store, you could buy as many loaves of bread as you wanted. In other parts of the world, however, getting items like bread is not as simple. How people get the things they want is determined by a country’s economic system. The nature of economic systems varies widely from place to place. However, they all help people create and obtain the goods and services they need. 450 The Need for Economic Systems All around the world, people need certain things to survive. People cannot live without food and water, shelter, and clothing. These basic materials that people cannot live without are called needs. In addition to their needs, there are many items that people want in order to make their lives more comfortable. These items are not necessary for survival, but they can have great value to people. For example, you may want a television, a cell phone, or a car. You do not really need any of these things in order to live, but they can make your life easier, more comfortable, or more enjoyable. These types of items are called wants. Different people have different wants. In addition, a person’s wants can change over time. People satisfy their wants by obtaining goods and services. For example, if you want fun, you can buy a new game. The process of obtaining goods and services to satisfy your wants is called the want-satisfaction chain. How people obtain goods and services is what distinguishes different economic systems from each other. CHAPTER 17 Teach the Main Idea At Level The Economic System at Work U.S. Economic System • U.S. mixed economy • Mostly market economy • Some government regulation 1. Teach Ask students the Reading Focus 3. Review Create a master list of the section’s questions to teach this section. 2. Apply Have students preview the section and create a list of all of the illustrations in the section. Ask them to leave room next to each illustration description for comments. As students read the section, ask them to analyze how each illustration shows a concept discussed in the text. illustrations on the board. Ask students to share their observations about each illustration. 4. Practice/Homework Have students write a one-paragraph story to illustrate each of the four American economic freedoms. The WantSatisfaction Chain To satisfy your need for food, you may want a sandwich on a bun. This want-satisfaction chain shows the steps involved in helping you satisfy that want. Reading Focus How do different economic systems help satisfy people’s needs? Economic Systems Contrast In what ways is a market 1 Grain 2 Flour 3 Bread becomes Flour becomes Bread is Delivered Farmers harvest grain and send it to mills where it is ground into flour. Bakers use flour to make all kinds of bread products, including sandwich buns. Kitchens, restaurants, and cafeterias receive bread from bakeries. economy different from a command economy and a traditional economy? A market economy is based on producers’ and consumers’ freedom to make decisions about what they buy and sell, and it involves trade and money. In a traditional economy, people grow their own food and make their own products. In a command economy, the government makes all economic decisions. Elaborate What are some of your wants, and what influences them? Students’ answers will vary but should show understanding of wants and what influences them. From the Source: Readings in Economics and Government: Reading 64: Price Making in a Democracy; Reading 67: The Affluent Society 4 Lunch is Served The final step in the want-satisfaction chain is a tasty sandwich on a bun. Linking to Today ANALYSIS SKILL ANALYZING VISUALS What different industries are involved in the want-satisfaction chain? THE ECONOMIC SYSTEM Collaborative Learning 451 At Level Create a Graphic Organizer 1. Organize students into small groups. Have each group select an economic freedom and imagine that this economic freedom does not exist. 2. Have each group create a chart or diagram describing the problems or limitations that the U.S. economy would experience if that specific economic freedom were missing. For example, students might indicate that Satisfying Customers’ Wants Sometimes manufacturers change their products in order to better satisfy customers’ wants. For example, the Nabisco company has been producing cookies and crackers since 1898. In 2005 the company introduced new versions of several kinds of cookies and crackers made with whole grains. The company hoped that the new snacks would satisfy the wants of health-conscious consumers, inspire them to buy the new snacks, and help the company make money. consumers would be unable to shop for the best price if they did not have the freedom to buy what they want from different merchants. 3. Invite groups to present their charts or diagrams to the class. Visual/Spatial, Verbal/Linguistic Alternative Assessment Handbook: Rubric 13: Graphic Organizers Answers Analyzing Visuals farming, milling, baking, delivery, food service 451 Types of Economic Systems There are three basic economic systems in the world: traditional, command, and market economies. Most countries today use a mix of these systems to satisfy their citizens’ wants and needs. In a traditional economy, economic decisions are based on how economic activity has been carried out in the past. People may grow their own food and make their own goods. They might grow and make everything they need to survive, or they might trade to obtain things that they cannot make themselves. If they do trade, they may or may not use money. They may use a barter system in which they trade goods for other goods. A second type of economic system is called a command economy. In this kind of system, the government makes all economic decisions. In addition, the government owns or controls all capital, tools, and production equipment. It tells managers and workers on farms and in factories what they can produce, how much of it to produce, and how much they can charge for it. Historically, many Communist countries have tried to set up command economies. Most of these economies have collapsed, but North Korea and Cuba still have command economies. MISCONCEPTION ALERT Make sure students understand that the text refers to the American economic system in four ways: a market economy, a free market, capitalism, and a free enterprise system. Clarify that these terms all describe the same American economic system. The third type of economy is the one found in most countries, including the United States. It is called a market economy. A market economy is one in which economic decisions are made by individuals looking out for their own and their families’ best interests. People can start businesses to make and sell any legal products they choose. Based on the market, they can also set their own prices for these products. In other words, the government does not tell people what to produce or buy. In this way, a market economy is the opposite of a command economy. A market economy is based on freedom. People are free to own property, to create companies, and to buy products as they choose. The right to buy and sell goods as you want is called a free market. Companies also need to be free to compete with each other. In a free market, competition among sellers—not any government policy—is the main factor in setting prices. Sellers try to price their goods lower than their competitors so that people will buy them. At the same time, they have to be careful not to set their prices so low that they lose money. READING CHECK Explaining Why do countries need economic systems? American Economic Freedoms Among the basic rights we have as Americans are certain economic freedoms. These economic freedoms are the foundation of our free market economy. How do these freedoms affect our everyday lives? Freedom to Own Property Freedom to Compete 452 CHAPTER 17 Differentiating Instruction Advanced Learners/GATE Research Command Economies 1. Have students research the Cuban economic Answers (photo) Possible answer: They allow us to make our own decisions about how to earn and spend money. Reading Check to satisfy people’s needs and wants 452 system and another example of a command economy using reference books and the Internet. Allow students to use historical examples, such as the Soviet Union. 2. Ask students to write an informational essay about the government’s role in the Cuban economy and the other economy they chose Above Level Research Required that incorporates their research. Remind them to use specific examples in their essays. Students may also wish to compare the two economies in their essays. 3. Allow students to share their essays with the class. Verbal/Linguistic Alternative Assessment Handbook: Rubric 42: Writing to Inform Supply and Demand Life in a Market Economy In a market economy, people are free to start a business and pursue profit. Profit is the money a business has left after it has paid its expenses. The profit motive, or the desire to make a profit, is essential to a successful market economy. If people do not want profit, they will not start businesses and people will have no way to obtain goods and services. Competition for Resources In order to make a profit, people need to provide a good or service. In order to provide a good or service, they need resources. As you know, however, resources are not unlimited. As a result, businesses and individuals must compete for the resources they need. This competition eventually affects everyone, not just business owners. In time, it affects the prices we pay for the goods we want. One result of the competition for these resources is scarcity. Scarcity is the lack of a particular resource. When a resource becomes scarce, it is harder for producers to obtain. Products made with that resource also become more difficult to obtain. As a result, the prices for these items usually rise. Changes in prices are usually the result of the laws of supply and demand. These laws are among the most basic of all economic principles. The law of supply states that businesses will produce more products when they can sell them at higher prices. They will produce fewer products when prices are low. The law of demand, on the other hand, states that buyers will demand, or want, a greater quantity of a good when its price is low. Likewise, as prices rise, the quantity demanded falls. That is, when the price of a good goes up, people buy less of that good. Although you may not realize it, you are probably already familiar with the principles of supply and demand. Imagine, for example, that you are paid $100 by each of your neighbors to mow their lawns. You will probably want to mow quite a few lawns, because that is a good price for your service. Imagine, however, that your neighbors only wanted to pay you $1 per lawn. Would you still want to mow as many? Most people would not, because that price is too low. That is what the law of supply states—people are more eager to provide a good or service for a high price than for a low one. Reading Focus What factors shape life in a market economy? Life in a Market Economy Explain What happens when a resource becomes scarce? It is harder for producers to obtain, and prices for products made with that resource might rise. Make Generalizations How do businesses use the laws of supply and demand to try to make a profit? To increase their profit, businesses have to find the highest price that customers are willing to pay for the goods or services they offer. Elaborate What factors might affect the demand for a good or service? Possible answers: its price, quality, usefulness, ease of use, advertising Political Cartoons for Civics, Government, and Economics: Cartoon 12: Concentration of the Country’s Wealth Connect to Math Freedom to Buy and Sell Freedom of Workers to Compete for Jobs Freedom to Earn Profits THE ECONOMIC SYSTEM Differentiating Instruction 453 Below Level Learners Having Difficulty Illustrate Supply and Demand 1. Have students look through newspapers and brief description of how the laws of supply and demand explain each headline. magazines to find headlines about events that illustrate the effects of supply and demand. 2. Ask each student to cut out these headlines, paste them onto a sheet of paper, and write a 3. Have volunteers explain their collages to the class. Visual/Spatial, Verbal/Linguistic Alternative Assessment Handbook: Rubric 8: Collages Supply and Demand To clarify the laws of supply and demand, present the following problem to students: Jan’s Records is selling CDs for $18. Today, Jan sold five CDs. Nita’s Music is selling CDs for $12. Today Nita sold ten CDs. Which merchant made more money? Why? (Jan made $90, while Nita made $120.) Help students to understand that although Jan wants to supply CDs at $18 a CD, there is limited demand for CDs at that price. In contrast, Nita is supplying CDs at a price which customers prefer, or demand. THE ECONOMIC SYSTEM 453 Info to Know Copyright Law Article 1, Section 8, Clause 8 of the United States Constitution reads, “To promote the Progress of Science and useful Arts, by securing for limited times to authors and inventors the exclusive right to their respective writings and discoveries.” The law protects the works of artists, scientists, authors, and inventors. File-Sharing and Copyright Law In June 2005 the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that a popular Web site was responsible for violating copyright laws. The company itself did not download illegal material. However, its file-sharing technology helped individuals share copyrighted materials, such as movies and music, without paying for them. Article I, Section 8 of the Constitution gives Congress the power to make copyright laws. Copyright laws give artists such as writers, painters, and performers lifetime ownership of their work. People who wish to use a copyrighted work must receive the owner’s permission and often pay a fee. For example, whenever you buy a CD, the copyright holder gets paid. But how would the copyright holder get paid if you did not pay for the CD? People are often tempted to download music files without paying. This is illegal—it violates the artist’s copyright. For some artists, the lost income from illegally downloaded works may threaten their ability to continue working. Other artists, however, offer free, legal downloads of their music on the Internet to attract more listeners. Downloading music from the Internet without paying for it may violate copyright laws. ANALYSIS SKILL EVALUATING THE LAW 1. Why do you think the framers of the Constitution wanted to protect artists’ rights to their works? 2. What do you think can be done to discourage people from illegally obtaining copyrighted music and movies? The law of demand works in the same way. If you went to a CD store and found that CDs were priced at $2 each, how many would you buy? At that price, you might buy quite a few of them. How many would you buy, though, if they cost $25 each? You would probably buy fewer, because the price is so much higher. That is the basic idea behind the law of demand. What business owners hope is that the supply of and demand for a product will balance each other. Because they want to find a price at which consumers will continue to buy a product, the price cannot be too high. At the same time, however, business owners need to make a profit. Therefore, the price cannot be too low either. 454 go.hrw.com KEYWORD: SZ7 CH17 To understand this balance, imagine that you are selling lemonade. You need to figure out a good price to charge for your product. First you think that you would like to charge $10 per glass. That way you will make a large profit on each glass that you sell. Unfortunately, however, people do not want to pay that much for it, and you are left with lots of unsold lemonade. To try to sell more, you decide to drop your price. Now you will sell lemonade for a nickel a glass. Lots of people are willing to buy it now. However, you quickly learn that it costs you more to make the lemonade than you earn by selling it. Obviously, you will need to raise your prices if you want to stay in business for long. CHAPTER 17 Collaborative Learning Above Level Discuss the Use of Copyright Law 1. Tell students that they will create arguments Answers Evaluating the Law 1. Possible answers: to ensure that they could make a living from their work; to prevent plagiarism 2. Possible answers: Jail those who disobey the law; create a technology that ensures that the material cannot be copied. 454 for and against the use of the U.S. copyright law as it pertains to file sharing of copyrighted material. 2. Have students work in small groups to portray the following: software companies, representatives of musical artists, customers supporting file sharing of copyrighted music, customers against file sharing of copyrighted musical material. Have students create arguments to present in a discussion on file-sharing. 3. Ask students to present their cases in a classroom panel. Interpersonal, Verbal/ Linguistic Alternative Assessment Handbook: Rubric 11: Discussions In response, you raise your prices to $2 per glass. You now have fewer customers than you did before, but your business is still steady. You are also making less profit per glass than you did when you charged $10, but you are not losing money. In other words, you have managed to achieve a balance between supply and demand. Free Enterprise In a market economy, no one orders business owners how to run their businesses. Of course, if owners do not follow the laws of supply and demand, their businesses fail. Still, business owners may operate however they see fit, with little direction or interference by government. This principle is called free enterprise. The free-enterprise system offers enterprising businesspeople the opportunity to make huge profits. For example, Bill Gates and Steve Jobs are two Americans who used their economic freedom to start successful companies. With no intervention from the government, they turned their companies— Microsoft and Apple Computer—into hugely successful operations. Most companies are not as successful as Microsoft and Apple, though. By accepting the opportunity to make profits, business owners also open themselves to the possibility of huge losses if their companies do not perform well. They might create a product only to learn that there is no demand for it, or they might find that they have to charge more than people are willing to pay for their goods. Mistakes like these can cost business owners. Some even end up losing their companies. This is the main risk that people face in a free-enterprise system. Competition is vital to the free-enterprise system. As you have already learned, competition between companies is the main factor in setting prices. In addition, competition drives companies to improve their products. Each company wants the products it creates to be the best so that people will buy them. The constant desire to improve products means that innovation is also important in free enterprise. Clever thinkers are always looking for new products they can create or for ways to improve existing products. They hope that their innovations will help them make huge profits from their products. Innovative people do not want others to steal their ideas. They want ways to protect what they have created so that no one else can take credit for it or make money from it. In the United States, there are two ways to protect ideas. A patent gives you the exclusive right to make and sell your invention for a certain number of years. A copyright is the exclusive right to publish or sell a piece of writing, music, or art. Checking for Understanding True or False Answer each statement T if it is true and F if it is false. If false, explain why. 1. The U.S. economic system is called capitalism. T 2. The U.S. economic system is also called a free enterprise system. T 3. There is a lot of government interference in the U.S. economic system. F; In the U.S. economic system, there is freedom to compete without unreasonable government interference. Capitalism The main driving force behind the American economy today is capitalism. Capitalism is an economic system in which the productive resources—farms, factories, machines, and so on—are owned by private citizens. Capitalism is closely linked to a market economy. People are free to buy and sell as they please. Capitalism also encourages people to invest their money so that they will be successful financially. If they are successful, they will be able to improve their quality of life. Anyone with a little extra money has the opportunity to invest it, either in a company of their own or in someone else’s company. If a company is successful, it can make huge profits, and not only for its owners. All the people who invested in the company can also make profits. By encouraging investment, innovation, and the production of quality goods, the capitalist system benefits the American people as a whole. Monopolies Since competition is an essential part of the free-enterprise system, business practices that limit competition are frowned upon. Such practices disrupt the free market and weaken a market economy. THE ECONOMIC SYSTEM Collaborative Learning 455 At Level Research African American Inventors’ Patents Research Required 1. Tell students that, before the Civil War, 3. Have each group identify and share with African American slaves could not receive patents on their inventions. This changed, however, in the years following the war, when African Americans were freed from slavery. 2. Divide students into small groups. Have each group research an African American inventor—such as Jan Matzelinger, William Purvis, Andrew Beard, or Granville Woods— who received at least one patent during the years 1870–1900. the class at least one item patented by the inventor they researched. Students should explain how each invention works and, if possible, show a picture of it. 4. Lead a class discussion on how receiving patents is an important economic freedom for all Americans. Verbal/Linguistic THE ECONOMIC SYSTEM 455 The U.S. Economic System POLITICAL CARTOON Reading Focus What is the U.S. economic system like? Monopolies Because monopolies limit competition, they harm our freeenterprise system. As a result, they are outlawed in the United States. The U.S. Economic System A Mixed Economy www.CartoonStock.com Identify What are some ways the government helps protect workers? by establishing minimum wage laws, laws guaranteeing workers’ safety, and laws to protect people from discrimination Make Judgments Do you think that the U.S. government should control parts of our economy? Why or why not? Possible answers: Yes— without government control some companies would take advantage of the public interest by polluting, creating monopolies, and other problems. No—the government should stay out of business because it interferes with people’s ability to make a living. As you have already learned, the United States has a market economy. For the most part, people are free to produce and buy any goods they wish in any way that they wish. In a few instances, however, the U.S. government does impose some regulations on businesses, much like you would find in a command economy. In this way, our market economy also includes a mix of elements of other economic systems. ANALYSIS SKILL ANALYZING PRIMARY SOURCES What is the artist’s point of view regarding monopolies? How can you tell? As a result, most countries that have market economies have banned companies from creating monopolies. A company is said to have a monopoly if it is the only one selling a product or providing a service. A company that holds a monopoly can set any price it wants. This can cause many problems, especially if the item in question is a necessity. In the United States, monopolies— except for certain public utilities—are illegal. The U.S. government watches businesses to see that no new monopolies are formed and that consumers are protected. U.S. Supreme Court Case Studies: Case 10: New Deal Cases READING CHECK Finding the Main Idea How are supply, demand, and free enterprise key to a market economy? 456 An economy that mixes elements of different economic systems is called a mixed economy. In most mixed economies, businesses are largely free to operate as they please. Their operations, however, must fall within certain regulations set up and monitored by the government. The U.S. economic system is a mixed economy. Many of our government’s regulations on business are intended to protect people. For example, federal and state governments have established laws, such as minimum wage laws, to help protect workers. Some laws guarantee workers’ safety and protect people from discrimination. Other government regulations are intended to protect the natural environment. For example, the government sets limits on how many chemicals companies can release into the air or water. These regulations sometimes cost companies money, which results in higher prices for consumers. At the same time, however, the regulations result in cleaner air and water and less pollution. The federal government may sometimes intervene in business to help control prices. One way the government does this is by subsidizing, or giving money to, certain industries. For example, to make sure that people can buy flour, cereal, and other wheat products cheaply, the government might give subsidies to wheat farmers. Because they are receiving money from the government, CHAPTER 17 Critical Thinking: Evaluating At Level Chart the Pros and Cons of Monopolies Answers Analyzing Primary Sources The artist does not approve of monopolies and refers to their unfair practices: rigging markets, restraining trade, and suppressing competition. Reading Check In a market economy, supply and demand help determine what goods are produced and how much manufacturers can charge for them; free enterprise allows business owners to make their own decisions. 456 example, a water and sewage monopoly might be beneficial because one company can do the legal, such as a public utility company. Have job more efficiently. However, consumers might students divide a sheet of paper into two not be able to get the company to improve columns and write the name of the monopoly service or lower its prices. at the top of the chart. Have them label the first column Pros and the second Cons. 3. Have students share their charts with the 2. Ask students to list reasons that the monopoly class. Visual/Spatial, Verbal/Linguistic is beneficial in the first column. Have them list Alternative Assessment Handbook: Rubric 13: Graphic Organizers its negative effects in the second column. For 1. Ask students to think of a monopoly that is the farmers do not have to charge high prices for their crops. As a result, prices for wheat products stay low. Comparing American Business Command, market, and traditional economies differ in the way goods are produced and sold. Most countries use a mix of two more of these systems. Think about the companies that made some of the products you own. What do you know about these companies? Most of the products you own were probably made by large companies. Many of the businesses we deal with in the United States today are huge. They employ millions of people and do business all around the world. This has not always been the case, however. In the early days of the United States, most businesses were small. They served only local needs. Few people ever needed to do business with people who lived far away. For example, a farmer who needed a new piece of equipment probably only had to travel a few miles to purchase it. In the late 1800s, however, larger businesses began to develop in the United States. Improvements in transportation allowed big companies to sell to customers who lived far away. As businesses became more successful, they gained more money. By reinvesting this money in their businesses, they were able to grow even larger. Today, big businesses are essential to the American economy. Many of the goods and services we use every day could not be produced by small companies. For example, to produce steel, electricity, automobiles, and ships requires large and expensive machines. Only large companies have the resources and the tools to produce these goods efficiently. Economists refer to this ability of large companies to produce many goods efficiently as the economy of scale. In the last few decades of the 1900s, companies began to grow even larger. Businesses began to join together to form huge organizations called conglomerates. A conglomerate is formed by the merger of businesses that produce, supply, or sell a number Economic Systems Info to Know This sign explains to customers that they are limited to only 113 grams of bread per person. Command Market The Microsoft Monopoly In May 1990 the Federal Trade Commission began an epic antitrust investigation of the Microsoft Corporation, charging that the software company illegally impeded competition with unfair pricing and hid codes in its operating system to prevent the use of competitors’ software applications. On June 7, 2000, after many legal battles, a federal judge ruled that Microsoft should be divided into two smaller companies. A year later a federal appeals court reversed the decision, but ruled that Microsoft had broken antitrust laws. In 2001 the Justice Department proposed a settlement requiring Microsoft to, among other things, allow computer manufacturers to decide which Microsoft products to load into their computers. The settlement was approved in 2002, but Microsoft still faced anti-trust complaints from other private companies. go.hrw.com Online Resources KEYWORD: SZ7 CH17 ACTIVITY: The U.S. Economic System Traditional ANALYSIS SKILL ANALYZING VISUALS How is the United States a mix of different economic systems? THE ECONOMIC SYSTEM Differentiating Instruction Learners Having Difficulty 1. Tell students that American conglomerates today produce a variety of well-known brandname products. 2. To help them understand the role of conglomerates in their life, have students list five products that they buy or use on a regular basis. 3. Have students conduct research to determine whether any of the products on their list 457 Below Level Research Required are sold by a conglomerate. Based on their findings, ask each student to create a chart identifying the company that produces each of the five products and if any of the companies are part of a conglomerate. Have students add other companies or products owned by the same conglomerate to their charts. 4. Ask students to share their charts with the class. Verbal/Linguistic Answers Analyzing Visuals The U.S. government imposes some regulations on businesses, but Americans are generally free to produce, buy, and sell whatever goods and services they choose. 457 PRESS CONFERENCES Close Discuss with students the structure of the U.S. economic system and the government’s role in regulating it. Review Online Quiz, Section 1 Quiz Game Assess SE Section 1 Assessment Daily Quizzes: Section 1 Understanding Publicity In 1997 the federal government charged the Microsoft corporation with violating antitrust laws. To announce the trial and its results, both the government and Microsoft used a powerful tool—the press conference. During a press conference reporters gather to hear statements from an individual or an organization. They generally report the information to the public in newspapers, on radio and television, or on the Internet. Often people hold press conferences to express their point of view. Press conferences are good publicity tools because they give people control over the way in which information is presented. They are an opportunity for photographs to be taken with a background and presentation. Reteach Main Idea Activities for Differentiated Instruction: Section 1 An attorney for the U.S. Justice Department holds a press conference during the Microsoft antitrust trial. ANALYSIS SKILL go.hrw.com MEDIA INVESTIGATION KEYWORD: SZ7 CH17 What steps would one have to take to hold a press conference? of unrelated goods. For example, a single conglomerate might control communication systems, insurance companies, hotel chains, and many other businesses. The government monitors conglomerates closely to be sure that economic competition is not harmed. Of course, small businesses have never disappeared in the United States. Even as big companies get bigger, many small companies continue to thrive. It is largely because of the mix of large and small businesses that the U.S. economy remains powerful today. READING CHECK Summarizing What is the U.S. economy like today? go.hrw.com Online Quiz KEYWORD: SZ7 HP17 SECTION 1 ASSESSMENT Reviewing Ideas and Terms Critical Thinking 1. a. Define Write a definition for the terms market economy, free market, profit, scarcity, law of supply, and law of demand. b. Analyze Information How are scarcity and the laws of supply and demand connected? 2. a. Define Write a definition for the terms free enterprise, capitalism, and monopoly. b. Draw Conclusions How do monopolies harm free enterprise? 3. a. Summarize Why is the United States described as a mixed economy? b. Analyze How is capitalism linked to a market economy? 4. Summarizing Use your notes and a graphic organizer like this one to identify the five economic freedoms that Americans enjoy. 458 Economic Freedoms Focus on Writing 5. Contrasting Explain how the U.S. economic system differs from the economic system in Cuba. CHAPTER 17 Section 1 Assessment Answers 1. a. market economy, p. 452; free market, p. 452; profit, p. 453; scarcity, p. 453; law of supply, p. 453; law of demand, p. 453 b. When a good is scarce, the demand for it is greater than the supply, and its price might go up. Answers Media Investigations prepare a statement; inform the press Reading Check It is a mixed economy with many large and small businesses. 458 2. a. free enterprise, p. 455; capitalism, p. 455; monopoly, p. 456 b. They limit competition and consumer choice and may make a necessity too expensive. 3. a. because it mixes elements of different economic systems b. Capitalism requires the freedom of a market economy to allow pri- vate citizens to invest their money and make other economic choices. 4. Students should identify the freedoms to buy, sell, earn a living, earn a profit, and own property. 5. Students should explain how Cuba’s command economy differs from the American mixed economy. For example, the Cuban government makes all economic decisions. In the United States, people are free to buy and sell products as they choose.