Chap.6_Sec.3
advertisement
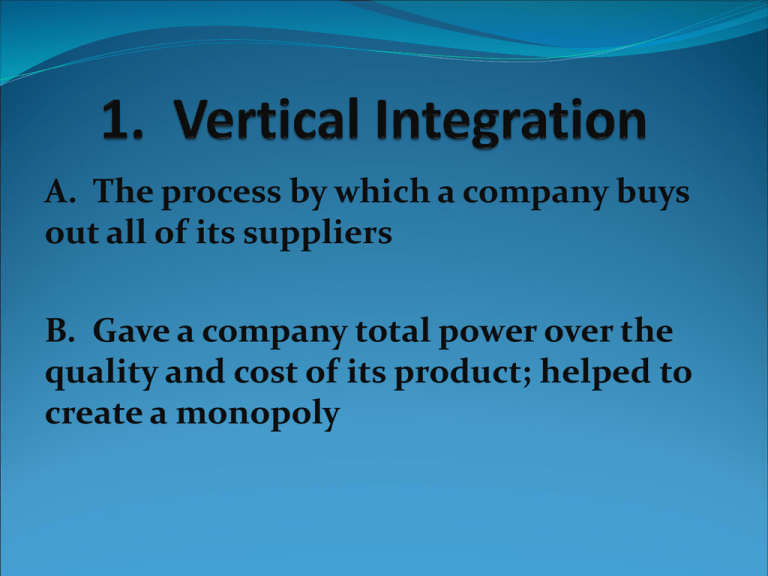
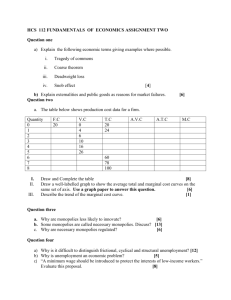
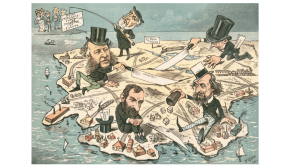
A. The process by which a company buys out all of its suppliers B. Gave a company total power over the quality and cost of its product; helped to create a monopoly A. The Process in which a company buys out, or merges with, its competitors B. Gave a company control over its competition; helped to create a monopoly A. An economic theory based on Darwin’s theory of biological evolution; it asserted that free competition would ensure success or failure B. Glorified big business and tycoons; also discouraged government interference with big business A. Complete control over an industry’s production, quality, wages, and prices B. Eliminated a company’s competition, allowing it to increase profits A. A corporation that does nothing but buy out the stock of other companies B. Helped to create monopolies A. A large corporation made up of many companies that receive certificates entitling them to dividends on profits earned by all the companies combined B. Helped to create monopolies Put tycoons on the defensive; turned public opinion against them and their businesses; finally, encouraged government regulation of big business Made trusts (and monopolies) illegal in interstate trade; made it possible (though not easy) to prosecute companies