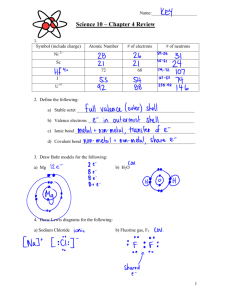
Writing Chemical formula with polyatomic groups
advertisement

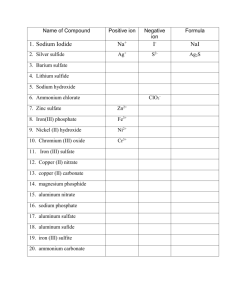
Writing Chemical formula with polyatomic groups 1. Use the Periodic table to determine the combining powers of single elements. Eg. Magnesium is in Group 2 and has a combining power of 2. 2. Use Table 1 to determine the valency of the major polyatomic groups. Table 1: The Combining Power of Polyatomic Ions Combining power of 1 Combining power of 2 Ammonium ion, NH4+ Carbonate ion, CO32- Hydrogen carbonate ion, HCO3- Sulfate ion, SO42- Combining power of 3 Phosphate ion, PO43- Hydroxide ion, OHNitrate ion, NO3Chemical Formula Help Rule 1: The charge tells you the combining power. Do not write the charge in the chemical formula! Eg. The chemical formula for magnesium nitrate is Mg(NO3)2 and not Mg2+(NO3-)2 or Mg(NO3-)2 Rule 2: Brackets() are needed when a polyatomic group > 1 in a compound. Poly = ‘many’ The hydroxide ion, formula OH-, is a polyatomic group since it is made up of two different elements. Eg. The chemical formula for strontium hydroxide is Sr(OH)2 and not SrOH2 Eg. The formula for lithium hydroxide is LiOH and not Li(OH) since there is only one OH group. Rule 3: Do not use brackets when single elements are > 1 in a formula. Eg. The chemical formula for lithium carbonate is Li2CO3 and not (Li)2CO3 Rule 4. Roman numerals are used for metal valencies that vary. Eg. Iron(II) oxide, FeO If in doubt use a combining power of 2. Eg. Copper sulfate, CuSO4 and lead chloride, PbCl2 Rule 5. The valency of silver is always 1. The valency of zinc is always 2. “Aluminum” is a commonly used spelling alternative spelling for “aluminium” that is used in the US May be freely copied for educational use. ©www.chemicalformula.org 1 H 1.008 KEY Hydrogen 3 Li 6.941 4 Be 9.012 Lithium Beryllium 11 Na 22.99 12 Mg 24.31 Atomic Number Symbol Standard Atomic Weight Name Helium 5 B 10.81 79 Au 197.0 Gold Boron 13 Al 26.98 The Combining Power or Valencies of the Transition Metals Vary Sodium Magnesium 19 K 39.10 20 Ca 40.08 Calcium Scandium Titanium Vanadium 37 Rb 85.47 Rubidium 38 Sr 87.61 Strontium 39 Y 88.91 Yttrium 40 Zr 91.22 Zirconium 41 Nb 92.91 Niobium Molybdenum Technetium Ruthenium 55 Cs 132.9 56 Ba 137.3 57–71 Cesium Barium Lanthanoids 72 Hf 178.5 Hafnium 73 Ta 180.9 Tantalum 74 W 183.9 Tungsten 75 Re 186.2 Rhenium 76 Os 190.2 87 Fr 88 Ra 89–103 104 Rf 105 Db 106 Sg 107 Bh Francium Radium Actinoids Rutherfordium Dubnium Seaborgium Bohrium Potassium 2 He 4.003 The Combining Power or Valencies of the Elements of the Periodic Table 21 Sc 44.96 22 Ti 47.87 23 V 50.94 Carbon 7 N 14.01 Nitrogen 8 O 16.00 9 F 19.00 10 Ne 20.18 14 Si 28.09 15 P 30.97 16 S 32.07 Sulfur 17 Cl 35.45 Chlorine 18 Ar 39.95 34 Se 78.96 35 Br 79.90 36 Kr 83.80 Oxygen Fluorine Neon Aluminum Silicon Phosphorus 32 Ge 72.64 33 As 74.92 Arsenic Selenium Bromine 51 Sb 121.8 52 Te 127.6 53 I 126.9 54 Xe 131.3 Argon Chromium 25 Mn 54.94 Manganese 26 Fe 55.85 27 Co 58.93 28 Ni 58.69 29 Cu 63.55 30 Zn 65.38 31 Ga 69.72 Gallium Germanium 42 Mo 95.96 43 Tc 44 Ru 101.1 45 Rh 102.9 Rhodium 46 Pd 106.4 Palladium 47 Ag 107.9 Silver 48 Cd 112.4 Cadmium 49 In 114.8 50 Sn 118.7 Tin Antimony Tellurium 77 Ir 192.2 80 Hg 200.6 81 Tl 204.4 82 Pb 207.2 83 Bi 209.0 85 At 86 Rn Platinum 79 Au 197.0 84 Po Iridium 78 Pt 195.1 Polonium Astatine Radon 108 Hs 109 Mt 110 Ds 111 Rg 112 Cn Hassium Meitnerium 24 Cr 52.00 Mg(OH)2 Al2(SO4)3 6 C 12.01 Iron Osmium Cobalt Nickel Copper Gold Darmstadtium Roentgenium Zinc Mercury Indium Thallium Lead Bismuth Iodine Krypton Xenon Copernicium NH4Cl Na2SO4 MgCO3 www.chemicalformula.org Chemical Formula of Compounds with Polyatomic Groups – Sheet 1 A polyatomic group contains more than 1 element. Eg. The hydroxide group, OH- contains oxygen and hydrogen. Polyatomic groups greater than 1 in a formula need brackets. eg. Mg(OH)2 and not MgOH2 No. Compound 1 silver nitrate 2 ammonium nitrate 3 zinc sulfate 4 aluminum hydroxide 5 sodium sulfate 6 potassium carbonate 7 magnesium hydroxide 8 calcium carbonate 9 potassium phosphate 10 sodium nitrate 11 potassium hydroxide 12 magnesium phosphate 13 barium hydroxide 14 ammonium sulfate 15 aluminum phosphate 16 sodium hydrogen carbonate 17 barium nitrate 18 iron(II) hydroxide 19 zinc phosphate 20 aluminum carbonate 21 silver phosphate 22 aluminum sulfate 23 potassium sulfate 24 silver sulfate 25 magnesium nitrate Chemical formula “Aluminum” is a commonly used spelling alternative spelling for “aluminium” that is used in the US May be freely copied for educational use. ©www.chemicalformula.org Chemical Formula of Compounds with Polyatomic Groups – Sheet 2 A polyatomic group contains more than 1 element. Eg. The hydroxide group, OH- contains oxygen and hydrogen. Polyatomic groups greater than 1 in a formula need brackets. eg. Mg(OH)2 and not MgOH2 No. Compound 26 sodium hydroxide 27 barium phosphate 28 calcium sulfate 29 potassium hydrogen carbonate 30 copper nitrate 31 calcium phosphate 32 sodium carbonate 33 lead(II) sulfate 34 silver hydroxide 35 calcium nitrate 36 calcium hydroxide 37 sodium phosphate 38 ammonium phosphate 39 aluminum nitrate 40 barium sulfate 41 magnesium sulfate 42 iron(II) sulfate 43 iron(III) hydroxide 44 lead(II) nitrate 45 copper sulfate 46 barium carbonate 47 copper hydroxide 48 copper carbonate 49 zinc nitrate 50 potassium nitrate Chemical formula “Aluminum” is a commonly used spelling alternative spelling for “aluminium” that is used in the US May be freely copied for educational use. ©www.chemicalformula.org Chemical Formula of Compounds with Polyatomic Groups – Sheet 1- ANSWERS No. Compound Chemical formula 1 silver nitrate AgNO3 2 ammonium nitrate NH4NO3 3 zinc sulfate ZnSO4 4 aluminum hydroxide Al(OH)3 5 sodium sulfate Na2SO4 6 potassium carbonate K2CO3 7 magnesium hydroxide Mg(OH)2 8 calcium carbonate CaCO3 9 potassium phosphate K3PO4 10 sodium nitrate NaNO3 11 potassium hydroxide KOH 12 magnesium phosphate Mg3(PO4)2 13 barium hydroxide Ba(OH)2 14 ammonium sulfate (NH4)2SO4 15 aluminum phosphate AlPO4 16 sodium hydrogen carbonate NaHCO3 17 barium nitrate Ba(NO3)2 18 iron(II) hydroxide Fe(OH)2 19 zinc phosphate Zn3(PO4)2 20 aluminum carbonate Al2(CO3)3 21 silver phosphate Ag3PO4 22 aluminum sulfate Al2(SO4)3 23 potassium sulfate K2SO4 24 silver sulfate Ag2SO4 25 magnesium nitrate Mg(NO3)2 “Aluminum” is a commonly used spelling alternative spelling for “aluminium” that is used in the US May be freely copied for educational use. ©www.chemicalformula.org Chemical Formula of Compounds with Polyatomic Groups – Sheet 2 - ANSWERS No. Compound Chemical formula 26 sodium hydroxide NaOH 27 barium phosphate Ba3(PO4)2 28 calcium sulfate CaSO4 29 potassium hydrogen carbonate KHCO3 30 copper nitrate Cu(NO3)2 31 calcium phosphate Ca3(PO4)2 32 sodium carbonate Na2CO3 33 lead(II) sulfate PbSO4 34 silver hydroxide AgOH 35 calcium nitrate Ca(NO3)2 36 calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2 37 sodium phosphate Na3PO4 38 ammonium phosphate (NH4)3PO4 39 aluminum nitrate Al(NO3)3 40 barium sulfate BaSO4 41 magnesium sulfate MgSO4 42 iron(II) sulfate FeSO4 43 iron(III) hydroxide Fe(OH)3 44 lead(II) nitrate Pb(NO3)2 45 copper sulfate CuSO4 46 barium carbonate BaCO3 47 copper hydroxide Cu(OH)2 48 copper carbonate CuCO3 49 zinc nitrate Zn(NO3)2 50 potassium nitrate KNO3 “Aluminum” is a commonly used spelling alternative spelling for “aluminium” that is used in the US May be freely copied for educational use. ©www.chemicalformula.org