Calculating Critical Path & Float for a Network
advertisement
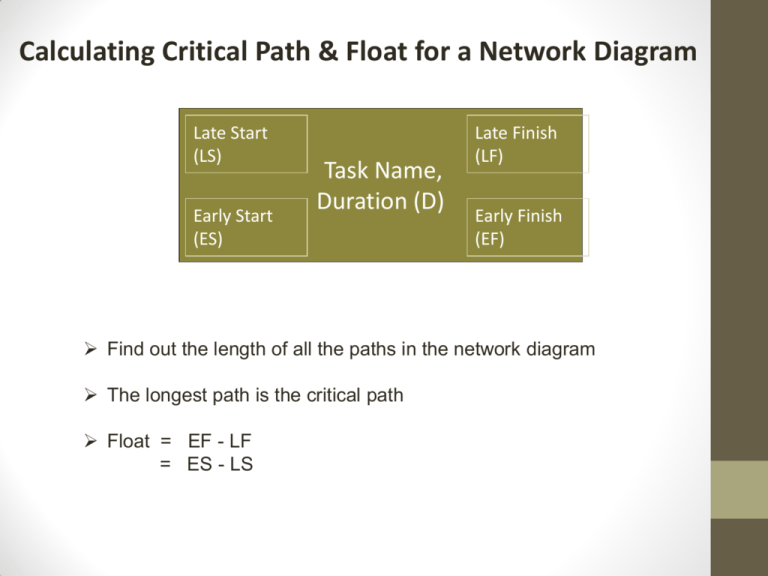
Calculating Critical Path & Float for a Network Diagram Late Start (LS) Early Start (ES) Task Name, Duration (D) Late Finish (LF) Early Finish (EF) Find out the length of all the paths in the network diagram The longest path is the critical path Float = EF - LF = ES - LS Calculating Critical Path for a Network Diagram Identify tasks, durations & dependencies. 5 days Task 2 4 days 4 days Task 1 Task 5 3 days Task 3 7 days Task 4 Step 1: Draw a Network Diagram For forward pass, calculate the Early Start (ES) and Early Finish (EF). Task 2, 5 days 4 Task 1, 4 days 0 9 Task 5, 4 days 14 18 4 Task 3, 3 days 4 7 Task 4, 7 days 7 14 Task 5 is dependent on Task 2 and Task 4 being complete. So, ES for Task 5 is 14 days (dependent on Task 4, which is the longer task. Step 2: Determine Critical Path To determine critical path, calculate length (durations) of all the paths: Length of all tasks: • Task1 → Task2 → Task5 = 4 + 5 + 4 = 13 days • Task1 → Task3 → Task4 → Task5 = 4 + 3 + 7 + 4 = 18 days The longest path is the critical path Critical path = longest path = 18 days Critical Path = Task1 → Task3 → Task4 → Task5 Step 3: Calculate Float in all tasks – Backward Pass ES = Early Start EF = Early Finish LS = Late Start LF = Late Finish 0 9 14 Task 2, 5 days 4 14 18 Task 5, 4 days 14 18 9 4 Task 1, 4 days 0 4 4 Task 3, 3 days 4 7 7 14 Task 4, 7 days 7 7 14 For all tasks on Critical Path (Task1, Task 3, Task 4, Task 5), EF = LF & ES = LS Thus, float (slack) for tasks on Critical Path = LF – EF = 0 Float for Task 2 = LF – EF = 14 – 9 = 5 days Step 4: Calculate Project Float Customer requests an end date of 25 days. Project Float is the total amount of time that the project can be delayed without delaying the project completion date required by the customer. 25 days – 18 days = 7 days. Project float can be negative when the date imposed by the customer is before the duration required in the project schedule. For negative project float, the project must be crashed or fast-tracked. Crashing is a technique used to decrease the duration of the project by assigning additional resources to tasks and decreasing the duration required for those tasks. Fast Tracking is a technique used to shorten project time by scheduling some activities concurrently that were originally scheduled sequentially.