Studies on Performance Management System of Sona Group
advertisement

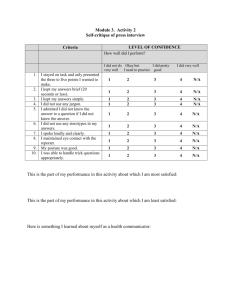
International Journal of Innovation, Management and Technology, Vol. 1, No. 5, December 2010 ISSN: 2010-0248 Studies on Performance Management System of Sona Group of Companies, Gurgaon, India Geeta Kumari and K.M.Pandey, Member, IACSIT Sona Koyo on 11th November 2003. As part of Sona Koyo’s globalization strategy the company has recently acquired stake in Fuji Autotech France S.A.S, which is the fourth largest steering column supplier in Europe. Sona koyo Steering System Limited was set up to manufacture Auto components for the Indian automotive market. Today the company is the largest manufacturer of steering gears in India. Sona koyo steering system ltd. is a technique and financial joint venture company of koyo Seiko Company, Japan—the global technology leader in steering systems. The company is the largest manufacturer of steering gears in India and is the leading supplier of— Hydraulic power steering system Manual rack and pinion steering system Collapsible, tilt and rigid steering columns for passengers vans and MUVs. The company’s product range also extends to Rear Axle Assemblies and Propeller Shafts. The world economic forum named the company as ―GLOBAL GROWTH COMPANY‖ in 1997. The company is now well positioned to lead the Indian automotive component industry to global standards. SONA CERTIFICATION: --1) TS 16949 2) ISO 14001 PRODUCTS:Its range of products includes Steering and Driveline components for the automotive OEM segments including passenger cars, utility vehicles, commercial vehicles and specialty vehicles. Sona offers its customers a diverse range of quality automotive components for passenger car, jeep and commercial vehicles with major automotive manufacturer of the world entering industry. PLANTS: -Sona koyo has two production plants located at GURGAON, DHARUHERA, SINGUR, RUDRAPUR and CHENNAI, and are operating at full capacity with increased levels of outsourcing, especially in steering parts operated. Sona believes in— Abstract—In this research report, performance management system of Sona group of companies are studied. The Overall finding is this that most of the employees are satisfied with the change in Performance Management System. And the changes what we have suggested for PMS in the company, has increased the satisfaction level of the employees. Index Terms—performance, satisfaction, system, challenges, innovation, management I. INTRODUCTION OF SONA GROUP In the automotive component industries, Sona is a name that stands for quality, dynamism and multifaceted growth. With its beginning as a small company in 1987, now Sona group comprises several companies each of which are in joint venture partnership and technical and financial collaboration with global leaders in their specialist areas. The Sona group comprises five operating and two services organizations. Sona is driving upon the strengths of its joint venture partners, which includes Koyo Seiko co. Japan; Mondo Korea; Mitsubishi Materials co. Japan; Somic Ishikawa, Japan; Fuji autotech, France& Fuji autotech AB, Sweden and ZF Lemforder, Germany to upgrade its systems, Skills, and Production values to offer its customers contemporary and high quality products. Sona is looking forward to the challenge ahead. The group is committed of rapid expansion of its products range and control by Govt. investing in contemporary and environment friendly technology. The Sona group hopes to touch the Rs. 8000 million mark as its stride ahead to the 21st century. Diverse and dynamic Sona is looking beyond the future. Under Dr. Surinder Kapur’s entrepreneurial leadership the industrial workforce of the group is turning Sona’ s vision of making product of International quality and meeting and exceeding customer’s requirements at all times into reality. A. Sona koyo—“partner of choice” Sona koyo the flagship company of the Sona group is currently the largest manufacturer of steering systems for the passenger car and utility vehicles market in India, with a Market share of 45%. Its collaborator and partner koyo Seiko Company limited, Japan, is the market leader in Japan and has recently announced a merger with Toyota Machine Works, making it number one steering systems manufacturer in the world. The company also has a technological collaboration with Ando Corporation, Korea. The Deming Award, the world’s most coveted Honour for excellence in Total Quality Management was awarded to 1) 2) 3) Respect for the individual Services to the customers Excellence in pursuit of our goal B. Key Milestones of The Company 1985--a) Technical collaboration agreement with Koyo Seiko co. ltd for manufacturer. b) Manual steering gear assemblies c) Steering column assemblies 527 International Journal of Innovation, Management and Technology, Vol. 1, No. 5, December 2010 ISSN: 2010-0248 1. Toyota India: supplier of the year 2002 (Silver for Sona koyo) 2. Hyundai 2002: Sona Koyo awarded 100 ppm recognition 3. Maruti Suzuki 2004: Vendor development awarded for Sona Koyo 4. ACMA 2004: Technology award for the Sona Koyo OTHER COMPETENCIES OF THE COMPANY: --TQM (Total quality management):- It includes –Exactness improvement 1) Visualization improvement 2) Policy management 3) Daily work management 4) JIT implementation 5) Flow manufacturing 6) Risk hazard analysis 7) Concept of doctors on the shop floor 8) Product, quality and cost management 9) Back to Back (B2B) program TPM (Total productivity management):- It was initiated in Sona koyo to achieve and maintain high level productivity in operations especially in manufacturing. With TPM it was possible to obtain and sustain the optimal condition of the machine and thus, achieve ZERO breakdowns and produce high quality output at low input cost. TPM was selected for the company, which is based on ZERO LOSS CONCEPT that includes zero breakdowns, zero rejection and zero accidents. TPM have helped in reducing the breakdown frequency to 1/3rd. TPM POLICIES: -Renovate the manufacturing system to achieve high efficiency Production through Zero failure and Zero defects. Improve the workplace environment through Zero accidents and Zero pollution. Develop skills of the employees through education and training. GKA (Group kaizen activity) R&D (Research and development):-- The group has partnered IIT-Delhi in research projects that deals with new concepts in steering system technology. In this field significant progress has been collaborated with IIT-Mumbai. MISSION OF THE COMPANY: ―Create a company that INDIA is proud of.‖ 1987--- Commencement of production 1992--- Equity participation (8%) by Koyo 1994--- ISO 9002 certification by TUV-CERT, Germany. 1995--- Technical collaboration agreement with Koyo for manufacturer of power steering gear. 1997--- KOYO increased equity to 20.5% 1998--- October-- Sona steering system ltd changed to Sona Koyo steering system Ltd December--- Established plant in Chennai 2000--- QS 9000/ ISO 9001 certification by TUV-CERT, Germany. 2002--- ISO 14001 certification by TUV-CERT, Germany. 2003--- November--- ―Deming Award’ by JUSE, Japan. December--- TS 16949 2004--- 21% equity participation in Fuji Auto tech, France C. Major Customers 1) MARUTI UDYOG LTD. 2) EICHER MOTOR LTD. 3) KOYO SEIKO LTD. 4) MAHINDRA & MAHINDRA 5) HINDUSTAN MOTORS LTD. 6) SWARAJ MAZDA 7) TELCO 8) HYUNDAI PRODUCT RANGE: Sona Koyo’s product portfolio includes two distinct product families— 1. Steering systems 2. Driveline products STEERING SYSTEM PRODUCTS ARE AS FOLLOWS— Rack and pinion manual steering 1. Rack and pinion hydraulic steering 2. Re-circulating ball screw type gear assembly 3. Column assembly – Rigid 4. Column assembly – collapsible 5. Column assembly—collapsible with tilt mechanism 6. Universal joints DRIVELINE PRODUCTS ARE AS FOLLOWS:1. Rear axle assembly 2. Case differentials 3. Propeller shaft SALES AND MANPOWER GROWTH: -- Net income from operations increased from Rs. 2340 mn in 2003-04 to Rs. 2975mn in 2004-05. Operating profit before depreciation, interest and tax (OPBDIT) excluding other income increased by 26% from Rs 283mn in 2003-04 to Rs 357mn in 2004-05 PAT increased by 37.7% from Rs 121mn in 2003-04 to Rs 167mn in 2004-05 Returns on net worth (RONW) increased from 19.8% in 2003-04 to 22% in 2004-05 EPS increased from Rs 2.75 in 2003-04 to Rs 3.7 in 2004-05 SONA INDUSTRY RECOGNITIONS: -- VISION OF THE COMPANY IN 2010 An organization of energised and involved employees. Growing and achieving high profitability. Supplying to major global OEMs directly or indirectly. At least 45% of sales are to overseas customers. Continues to be no. 1 steering system makers in India. II. STRATEGIES TO ACHIEVE THE CORPORATE MISSION AND VISION 1. 528 Identify the world leaders in technology and form strategies alliances with them: Sonia believes from these leaders in technology as well as management International Journal of Innovation, Management and Technology, Vol. 1, No. 5, December 2010 ISSN: 2010-0248 2. 3. 4. and production techniques. A technical centre is being developed in Gurgaon for development purposes. Energize Employees through education and training: Special programs are conducted for employees to keep them abreast wth the latest development. Upgrade suppliers: suppliers are instructed and aided in upgrading their quality and in adopting modern production techniques, by Sona’s Suppliers Quality Assurance (SQA) department. By helping its suppliers upgrade their quality and production and management techniques, Sona improves the quality of its own products creating a win situation for all. Implement the TOYOTA PRODUCTION SYSTEM (TPS) across the group: that lays stress on kaizen teams, Kanban and Jidoka, Self Study Groups and visits of experts from the partners is, now a part of the work ethos at Sona. TPS streamlines operations at the manufacturing end reducing cost and waste elimination. B. Data Collection Sources The project got support from the information available from a survey, which was conducted by the HR department. There was no extensive data available for any help. It was told by the AVP that no such survey was conducted yet though he has planned to conduct a study on performance management system. C. Data Collection Method Questionnaire method was used to collect the data. It is the most extensively used method in various economic and business surveys. The researcher and the respondent do come in contact with each other if this method of survey is adopted. D. Sampling Plan There were 400 JM & SM level employees. Selection of sample was done by random sampling method, where each and every member of the population has an equal chance of getting included in the sample, has the same probability of being selected. IV. INTERPRETATION AND ANALYSIS III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY A. Research Design The research design is the arrangement of conditions for the collection and analysis of data in a manner that aims to combine relevance to the research purpose with economy in procedure. More explicitly, the design decisions happen to be in respect of: 1. What is the study about— The study is all about Performance management system of the company. In today’s scenario there is a great importance of PMS. It plays an important role for employees as well as for the success of the company. 2. Why is the study being made— Performance management system being recognized as an important function of an organization, which contributes to the overall success of the organization. 3. Where will the study be carried out— the study was conducted at Sona koyo steering systems limited at its Gurgaon plant. 4. What periods of time will the study include— The time taken for the entire process took around eight weeks, which includes collecting PMS of different companies, noticing the key points, framing of the questionnaire, distribution of the questionnaires. Collection of it, then collection of the data and finally the interpretation of the data collected. 5. What will be the sample size— The sample size was selected by random sampling. There were around 400 employees at JM & SM out of which a sample size of 80 were selected, which were true representative of the population. 6. What technique of data collection will be used— Questionnaire technique was used to collect the data. 7. How will the data be analyzed— The statistical method used to analyse the data is Likert scale and Q. C. Tool (Bar Diagram) 529 For analysis part we have used the Likert Scale method and Q. C. Tool (Bar Diagram).Analysis done by grade wise. 100% 90% 80% 75% 75% 75% 75% 75% 70% 60% 50% 50% 50% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% 牋 Sat isf act ion 牋 燤ent or 牋 Review of 牋 Rat ing牋 Salary hike 牋 Weight age 牋 Division of牋 wit h PMS. Underst anding crit eria. Declarat ion. appraisal. crit eriat echnical and of PMS nont echnical compet ency. Figure-1 Analysis for Junior Manager-1 Grade: Here, by analysis it shows that 75% employees are satisfied with the new Performance management system of the company. 75% employees are happy with the understanding of the Performance management system.25% employees are happy with the rating criteria. 25% employees are happy with salary hike. 75% employees are satisfied with the weightage criteria.75% employees are happy with the division of technical and non-technical competencies.50% employees are satisfied with mentoring concept.75% employees are satisfied with the review of appraisal. Overall of this is that most of the employees are happy with the PMS but 25% employees are not happy with rating criteria and salary hike. For Junior Manager-2 Grade: International Journal of Innovation, Management and Technology, Vol. 1, No. 5, December 2010 ISSN: 2010-0248 happy with the division of technical and non-technical competencies.100% employees are satisfied with mentoring concept. 25% employees are satisfied with the review of appraisal. For Junior Manager -4 Grade: Figure-2 Here, by analysis it shows that 75% employees are satisfied with the new Performance management system of the company. 50% employees are happy with the understanding of the Performance management system. 50% employees are happy with the rating criteria. 25% employees are happy with salary hike. 75% employees are satisfied with the weightage criteria. 75% employees are happy with the division of technical and non-technical competencies.75% employees are satisfied with mentoring concept.75% employees are satisfied with the review of appraisal. For Junior Manager-3 Grade: Figure-4 Here, by the analysis it shows that the 75% employees are satisfied with the new Performance management system of the company. 75% employees are happy with the understanding of the Performance management system. 50% employees are happy with the rating criteria. 75% employees are happy with salary hike. 50% employees are satisfied with the weightage criteria. 75% employees are happy with the division of technical and non-technical competencies.75% employees are satisfied with mentoring concept. 50% employees are satisfied with the review of appraisal . For Junior Manager-5 Grade: Figure-3 Here, by analysis it shows that 50% employees are satisfied with the new Perfromance management system of the company. 50% employees are happy with the understanding of the Performance management system. 50% employees are happy with the rating criteria.25% employees are happy with salary hike. 75% employees are satisfied with the weightage criteria. 100% employees are Figure-5 Here, by analysis it shows that 75% employees are 530 International Journal of Innovation, Management and Technology, Vol. 1, No. 5, December 2010 ISSN: 2010-0248 satisfied with the new Performance management system of the company. 50% employees are happy with the understanding of the Performance management system. 75% employees are happy with the rating criteria. 75% employees are happy with salary hike. 75% employees are satisfied with the weightage criteria. 50% employees are happy with the division of technical and non-technical competencies.50% employees are satisfied with mentoring concept. 75% employees are satisfied with the review of appraisal. For Senior Manager Grade: Here, by analysis it shows that 75% employees are satisfied with the new Performance management system of the company. 75% employees are happy with the understanding of the Performance management system. 50% employees are happy with the rating criteria. 50% employees are happy with salary hike. 75% employees are satisfied with the weightage criteria. 75% employees are happy with the division of technical and non-technical competencies.100% employees are satisfied with mentoring concept. 75% employees are satisfied with the review of appraisal. V. CONCLUSIONS Here, by analysis it shows that 68% employees are satisfied with the new Performance management system of the company. 68% employees are happy with the understanding of the Performance management system. 61% employees are happy with the rating criteria. 57% employees are happy with salary hike. 82% employees are satisfied with the weightage criteria. 75% employees are happy with the division of technical and non-technical competencies.79% employees are satisfied with mentoring concept. 64% employees are satisfied with the review of appraisal. VI. SUGGESTIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS Figure-6 Here, by analysis it shows that 50% employees are satisfied with the new Performance management system of the company. 100% employees are happy with the understanding of the Performance management system. 75% employees are happy with the rating criteria. 50% employees are happy with salary hike. 75% employees are satisfied with the weightage criteria. 75% employees are happy with the division of technical and non-technical competencies.100% employees are satisfied with mentoring1. concept. 75% employees are satisfied with the review of appraisal. For GET Grade: 100% 100% 90% 80% 75% 75% 75% 75% 75% 70% 60% 50% 50% . a rie ti r c g in t a R e k i h y r la a S 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% . S M P th i w n o it c fa s it a S S M P f o g n i d n a t s r e d n U ia r e ti r c e g ta h ig e W d n a l a ic n h c e t f o n o is i iv D . y c n e t e p m o c l a ic n h c e t n o n . n o it a r a l c e D r o t n e M .l a s i a r p p a f o w e i v e R Key performance areas are the most important factor for evaluating the employee’s performance. So, there should be role clarity in the organization. Performance should be linked with reward and it should be given to employees timely. In PA Form company should also include preparing a Personal Action Plan (PAP) in which employees can chalks out a list of actions he will undertake for performance enhancement and self-improvement. HR department should give proper attention to section 3 i.e., performance factor. Because they are the basic competency which relates to long-term goal of the company. Rating scale should be changed into 4-point scale in which fourth scale would be no performance. For nontechnical competencies like, Leadership Skill quality it can be rated between 3 to 5 like this way- It will be either between 3 to 3.50 or 4. To 4.25 or 1.50 to 2.25. While defining competency proficiencies these rating ranges can be appropriately labeled such as Leadership Skill between 3 – 3.50 is considered to be good, but need improvement. Rating between 4. to 4.50 can be said excellent, and needs to be kept consistent, or rating between 2.00 to 2.50 needs immediate training program. It is also possible that ratings may fall and rise periodically because behaviors are not always constant; they change, improve or decline. REFERENCES [1] [2] [3] Figure-7 531 Gupta, C.B., ―Human Resource Management‖, Eleventh Edition, New Delhi, Sultan Chand and Sons Publication, 2009 Chhabra, T.N., ―Human Resource Management‖, Second Edition, New Delhi, Sun India Publication, 2008 . www.citehr.com International Journal of Innovation, Management and Technology, Vol. 1, No. 5, December 2010 ISSN: 2010-0248 [4] [5] [6] [7] www.sonagroup.com www.haripassion.com www.wikipedia.com www.answers.com Geeta Kumari- Geeta Kumari did MBA in 2007 and M.Phil in Business Administration in 2010. She is serving as Assistant Professor in Business Administration Department Since August 2008 at Gurgaon College of Engineering, Gurgaon, India. She has got 20 research publications to her credit in international and national conferences and journals. K.M.Pandey-K.M.Pandey is serving as Professor in Department of Mechanical Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Silchar, Asam, India. 533