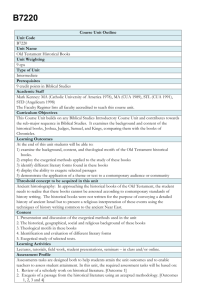
3600-2800 bc
advertisement

CHRONOLOGICAL OVERVIEW OF ANCIENT NEAR EASTERN PREHISTORY (3600-2800 BC) outlined by Daniel C. Browning, Jr. 3600 BC Mesopotamia 3500 BC 3400 BC 3300 BC Uruk Period (ca. 4000-3200 BC) 3200 BC 3100 BC 3000 BC Jemdat Nasr Period (ca. 3200-3000 BC) 2900 BC 2800 BC Early Dynastic Period (ca. 3000-2350 BC) → Sumerian City States Ancient Near East (Eridu, Shurrupak, Uruk, Kish, Nippur, Ur)of Ur Nammu) Palestine Chalcolithic Age (ca. 4500-3150 BC) Early Bronze Age (ca. 3150-2200 BC) → (highly urbanized culture) Egypt The Biblical Story ← Archaic Period (3100-2700 BC) → Predynastic Period (Dynasties 1-2) NO HISTORICAL BIBLICAL EVENTS CAN BE IDENTIFIED WITH ANY CERTAINTY 35th century BC 33rd century BC 31st century BC 29st century BC CHRONOLOGICAL OVERVIEW OF EARLY ANCIENT NEAR EASTERN HISTORY (2800-2000 BC) outlined by Daniel C. Browning, Jr. 2800 BC 2700 BC ← Mesopotamia 2600 BC 2500 BC 2400 BC 2300 BC Early Dynastic Period (ca. 3000-2350 BC) Sumerian City States Ancient Near East (Eridu, Shurrupak, Uruk, Kish, Nippur, Ur) ← Palestine Archaic Period (3100-2700 BC) (Dynasties 1-2) Major Historical Figures The Biblical Story Ur III Period Semitic domination st 1 empire in Mesopotamia Sumerian revival Early Bronze Age (ca. 3150-2200 BC) 2000 BC (Laws of Ur Nammu) Middle Bronze I 1 also called Early Bronze Age IV (nomadic life; no major cities) Old Kingdom (Dynasties 3-6) First Intermediate Period = “the Pyramid Age” (disunity; Asiatics in the Delta region) (the “Great Pyramid;” other major pyramids) Sargon Naram-Sin Ur-Nammu Djoser, Khufu, Khafre NO HISTORICAL BIBLICAL EVENTS CAN BE IDENTIFIED WITH CERTAINTY 28th century BC 1 2100 BC Akkadian Dynasty (highly urbanized culture) ← Egypt 2200 BC 25th century BC 23rd century BC Two systems of nomenclature are used for the Bronze Ages in Palestine; the older system of Albright is used here with the newer system of Dever in italics 21st century BC CHRONOLOGICAL OVERVIEW OF BIBLICAL HISTORY (2000-1200 BC) outlined by Daniel C. Browning, Jr. Ancient Near East 2000 BC Mesopotamia Palestine Egypt 1900 BC 1800 BC Isin and Larsa Period Biblical Books in Face Value Story Order 1600 BC 1500 BC Old Babylonian Period (Amorites in S; Laws of Eshnunna1) 3 1400 BC 1300 BC Middle Bronze IIb-c (MB II) 3 Late Bronze Age (reurbanization) (classic Canaanite culture) Middle Kingdom (ca. 2000-1750 BC) 2 Intermediate Period New Kingdom (ca. 1550-1000 BC) (prosperous, peaceful period) (= Hyksos Period; Asiatics rule Delta) (Hyksos expelled; Empire established) nd Hammurabi 1200 BC Kassite Period (Amorites; Law Code of Hammurabi2) Middle Bronze IIa (Middle Bronze I) Major Historical Figures The Biblical Story 1700 BC (smaller cities; Egyptian domination) Thutmose III Tutankhamen Merneptah Ahmose I Hatshepsut Amenhotep III Seti I Akhenaten Rameses II THE PATRIARCHS SOJOURN IN EGYPT Genesis 12-50 EXODUS WILDERNESS CONQUEST Exodus Leviticus Numbers Deuteronomy Joshua Biblical Characters Major Theological Events Critical View of Composition Biblical Writings ABRAHAM, Isaac, Jacob (exact dates uncertain) Joseph EXODUS Decalogue5 Sinai Covenant6 Abrahamic Covenant4 no major biblical compositions this early according to majority critical view th 19 century BC 1 MOSES Joshua 17th century BC 15th century BC Third oldest known ancient law code; similar to later biblical law. Fourth oldest known ancient law code; many similarities to biblical law. 3 Two systems of nomenclature are used for the Bronze Ages in Palestine; the older system of Albright is used here with the newer system of Dever in italics 4 Abrahamic Covenant = God promises Abraham: 1) descendants will be a great nation; 2) the Land will be inheritance forever. 5 Decalogue = The Ten Commandments 6 Sinai Covenant = God promises to fight Israel’s enemies, if Israel will keep God’s commandments. 2 13th century BC CHRONOLOGICAL OVERVIEW OF BIBLICAL HISTORY (1200-400 BC) outlined by Daniel C. Browning, Jr. 1200 BC 1100 BC 1000 BC 900 BC Ancient Near East Mesopotamia (Arameans appear) Iron Age II (1000-586 BC) poor isolated settlements development of centralized government, cities; ended by major destructions Shoshenq = Late Period Nubian Kings; Assyrian conquest Shishak (925 BC) THE JUDGES UNITED DIVIDED MONARCHY MONARCHY ISRAEL AND JUDAH 500 BC Persian Period JUDAH ASSYRIAN/BABYLONIAN INVASIONS poor, sparsely populated Persian dominance EXILE POST-EXILIC IN BABYLON Zephaniah Obadiah 1 Samuel 2 Samuel 1 Kings 2 Kings→ Amos Hosea Jeremiah→ Ezekiel Ruth 1 Chronicles 2 Chronicles→ Judges Isaiah Habakkuk Micah Nahum Lamentations Deborah Samson Samuel DAVID Saul Solomon Ahab, Elijah Elisha TEMPLE REBUILT Monarchy Established Hezekiah Josiah Daniel? Sennacherib Isaiah Jeremiah Cyrus Split of the Kingdom Composition of “J” source of Pentateuch Critical View of Composition Biblical Writings th 12 century BC 1 Davidic Covenant2 th 11 century BC th 10 century BC th 9 century BC Ezra Nehemiah Haggai Joel? Zechariah Esther Malachi Nebuchadnezzar Major Theological Events Deuteronomic Reform3 Comp. of “D” Comp. of “E” source of source of Pentateuch Pentateuch Isaiah and Deut. Hist.4 th 8 century BC 400 BC Neo-Babylonian/ Persian Emp. Chaldean Emp. (Nebuchadnezzar (Cyrus takes expands Babylon) Babylon, 539 BC) Iron Age I (1200-1000 BC) The Biblical Story Biblical Characters 600 BC (Shalmaneser III; Tiglath-pileser III; Sargon; Sennacherib make major campaigns and conquests in Levant) Egypt Biblical Books in Face Value 1 Story Order 700 BC Neo-Assyrian Empire (911-612 BC) Middle Assyrian Period Palestine 800 BC th 7 century BC Ezra Nehemiah Esther? Partial Destruction of Restoration Temple EXILE Comp. of “P” Chronicles, material in Ezra-Nehemiah Pentateuch 2nd Isaiah Ruth, Job, Jonah th 6 century BC th 5 century BC Chronological positions approximate; books which cannot be “placed,” in terms of events contained therein are not listed. For example, Psalms contains material from many periods and cannot be assigned a place on a event-based time line. 2 Davidic Covenant = God would “establish” David’s throne forever; i.e., his descendants would continue to rule God’s people 3 Primarily as recorded of Josiah, guided by the discovery of “a book of the Law” (Deuteronomy?) in the Temple. 4 Deut. Hist. = Deuteronomic History, primarily Deuteronomy plus the Former Prophets (Josh, Judg, 1-2 Sam, 1-2 Kings).