Transistors - Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy
advertisement

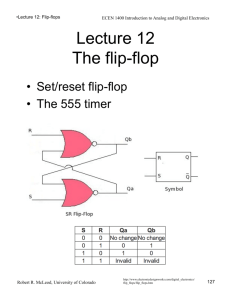
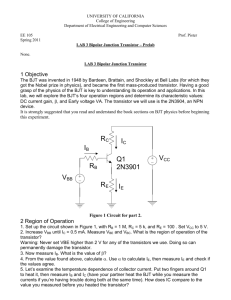
• Lecture 9: Transistors ECEN 1400 Introduction to Analog and Digital Electronics Lecture 9 Transistors • Physics • Transistor/transistor logic • CMOS logic CA 1947 http://www.extremetech.com/extreme/164301-graphenetransistors-based-on-negative-resistance-could-spell-theend-of-silicon-and-semiconductors http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moore's_law Robert R. McLeod, University of Colorado 100 • Lecture 9: Transistors ECEN 1400 Introduction to Analog and Digital Electronics The Transistor Discrete Integrated Packages http://www.uobkupartnership.talktalk.net/ page13.htm http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Diopsis.jpg Physics http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bipolar_junction_transistor Symbols Robert R. McLeod, University of Colorado PNP P channel NPN N channel BJT MOSFET 101 • Lecture 9: Transistors ECEN 1400 Introduction to Analog and Digital Electronics NPN Bipolar Junction (BJT) transistor Symbol C = Collector E = Emitter B = Base Package Top-down view Construction and use This shows the “common emitter” mode which is how we will use the BJT. Concentrate on the BE junction which looks like a diode. When this is forward biased, a large current can flow from C to E. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bipolar_junction_transistor Hydraulic analogy The BJT is a current-controlled current amplifier. That is, a small current into the base results in a large current from collector to emitter. Cool hydraulic analogies. One error – the CE current is really larger than the base. Note that there are “normally on” and “normally off” versions. Robert R. McLeod, University of Colorado http://www.mine-control.com/zack/transistor/transistor.html 102 http • Lecture 9: Transistors ECEN 1400 Introduction to Analog and Digital Electronics BJT Inverter “Pull up resistor” causes VO to be high if IC is ~0 but allows VO to be low if the bottom of the resistor is grounded. Plot of VO vs. VI high Current limiting resistor Input Output 1 2 low high low Switch, either “open” or “short” Simplified operation http://jpkc.njau.edu.cn/szdzjs/ywjc2.htm If we give names to the input and output levels, we can construct a reduced description of the plot called a truth table: Input Output Low = 0 High = 1 High = 1 Low = 0 Robert R. McLeod, University of Colorado So the output is high if it is NOT the case that the input is high. We thus call this a NOT gate or Inverter. http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-andcomputer-science/6-071j-introduction-to-electronics-signalsand-measurement-spring-2006/lecture-notes/19_bjt_1.pdf 103 • Lecture 9: Transistors ECEN 1400 Introduction to Analog and Digital Electronics Transistor/transistor logic (TTL) NAND gate Consider a circuit like the previous one but now with two BJT transistors in series: +Vsource 0 or +Vsource 0 or +Vsource 0V A current can flow from top to bottom only if both A and B are high. The output will drop to a low voltage in this case, otherwise it will remain high. A B Out 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 So the output is high if it is NOT the case that A AND B are high. We thus call this a NOT AND gate or NAND for short. Robert R. McLeod, University of Colorado http://cpuville.com/logic_gates.htm 104 • Lecture 9: Transistors ECEN 1400 Introduction to Analog and Digital Electronics TTL NOR gate OK, what if we arranged the two BJT transistors in parallel: Output Input A Input B A current can flow from top to bottom only if either A or B are high. The output will drop to a low voltage in this case, otherwise it will remain high. A B Out 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 So the output is high if it is NOT the case that A OR B are high. We thus call this a NOT OR gate or NOR for short. Robert R. McLeod, University of Colorado http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-andcomputer-science/6-071j-introduction-to-electronics-signalsand-measurement-spring-2006/lecture-notes/19_bjt_1.pdf 105 • Lecture 9: Transistors ECEN 1400 Introduction to Analog and Digital Electronics Complementary metal–oxide– semiconductor (CMOS) logic TTL worked well, but it has a problem. Note that when the transistor is “on” and IC is high, there is power dissipated in RC. This is OK occasionally, but not in a million logic gates. The “pull up resistor” is thus a bad idea in general. Here is a complementary inverter that happens to be made with metal-oxide fieldeffect transistors (MOSFETs). For our purposes, they act like switches but with two polarities. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CMOS By replacing the pull-up resistor with a complementary transistor, the power dissipation is greatly reduced. CMOS is the dominant electronics platform and this is a major LOW reason. Robert R. McLeod, University of Colorado HIGH HIGH LOW 106 • Lecture 9: Transistors ECEN 1400 Introduction to Analog and Digital Electronics Quiz 9.1 A closer look at the BJT Active region above cutoff and below saturation Q: When we use the BJT as a switch, we take advantage of the fact that it switches between cutoff (off, reverse biased) to saturation (on, forward biased) very quickly. The intermediate region is called the “active” mode. Consider using a BJT transistor in this “active” mode. Given the plot above and assuming the x and y axes have the same scale, how would you describe the output if the input is confined to operate in the active region A. The output is an attenuated version of the input. B. The output is an amplified version of the input. C. The output is an inverted version of the input. D. A and C E. B and C The slope is large, thus the output is larger than the input = “amplified”. The slope is negative so the output will go down when the input goes up = “inverted”. Robert R. McLeod, University of Colorado 107 • Lecture 9: Transistors ECEN 1400 Introduction to Analog and Digital Electronics Quiz 9.2 A modification of the inverter http://www.interfacebus.com/Glossary-of-Terms-bjtamplifier-circuits.html Q: Assuming the BJT is ideal in that it switches between a perfect open circuit and a perfect short circuit with an infinitesimal active region, what is the function of this device? A. Logical buffer – the output is a binary copy of the input (1 gives 1) B. Logical inverter - the output is a binary inversion (1 gives 0) When input is high and BJT is “on” and thus nearly a short, the output is shorted to Vcc and thus high. When the input is low and BJT is “off” and thus nearly an open, the output is pulled low by the pull-down resistor RE. The assumption is that little current flows to the output thus there is little voltage drop across RE by Ohm’s law, thus the output is nearly grounded. Robert R. McLeod, University of Colorado 108